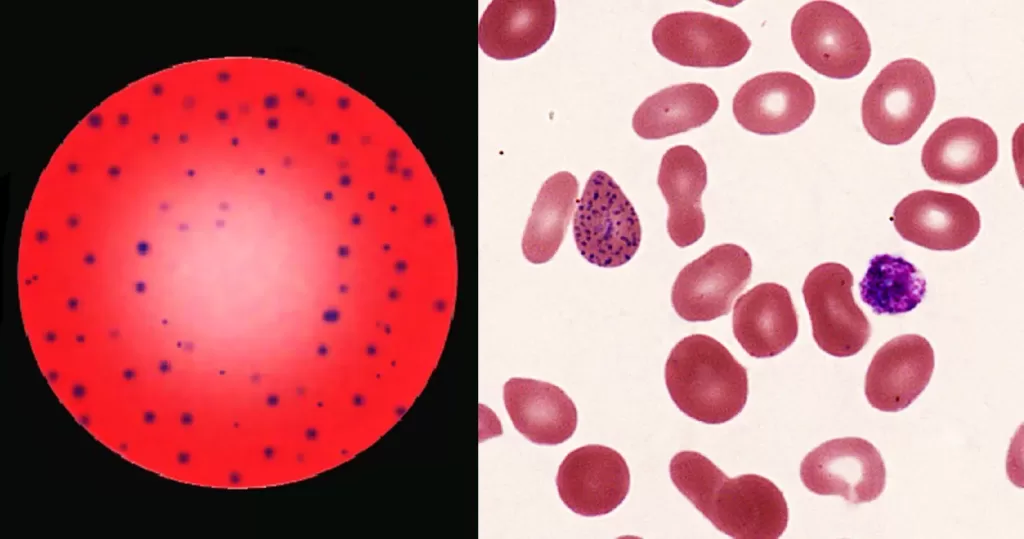
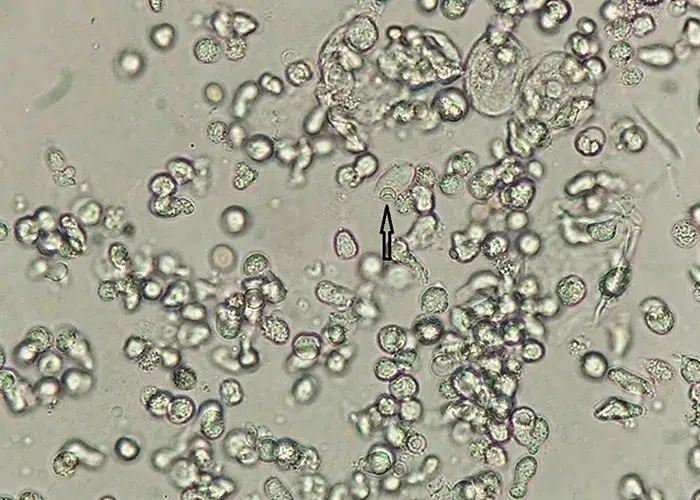
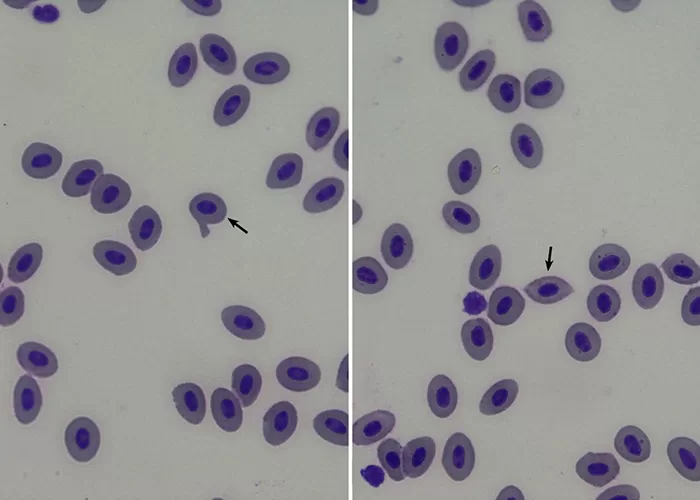
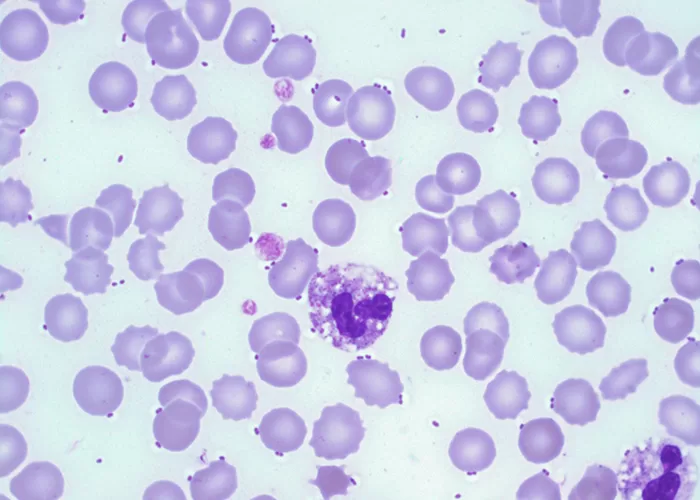
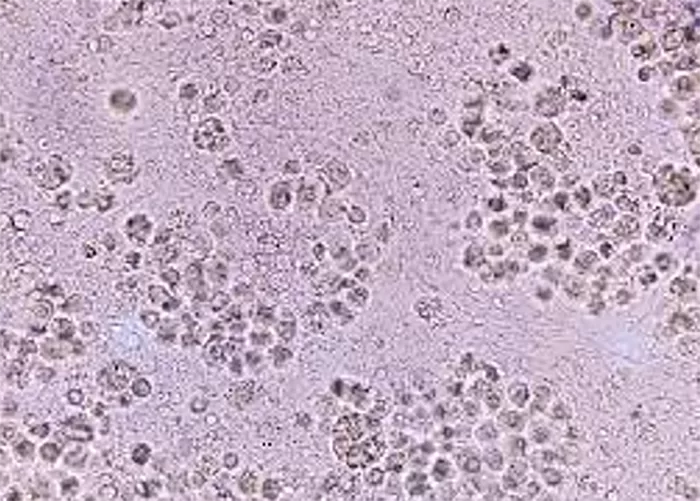
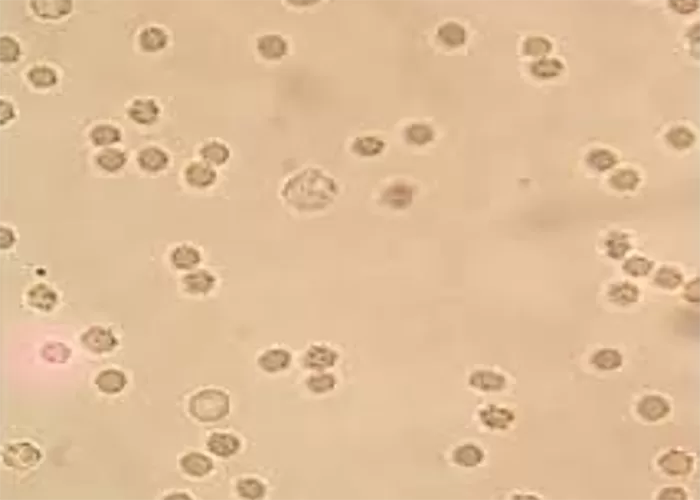
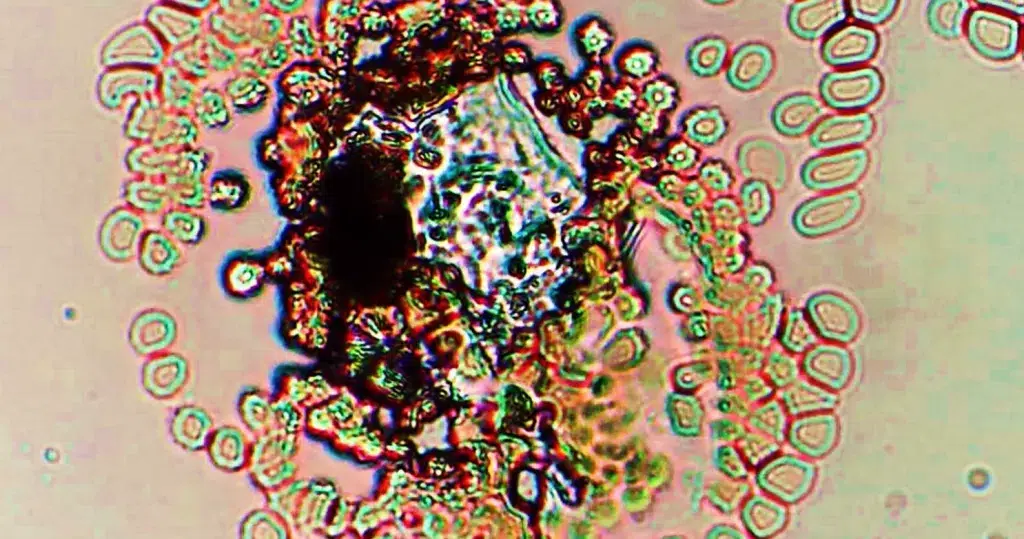
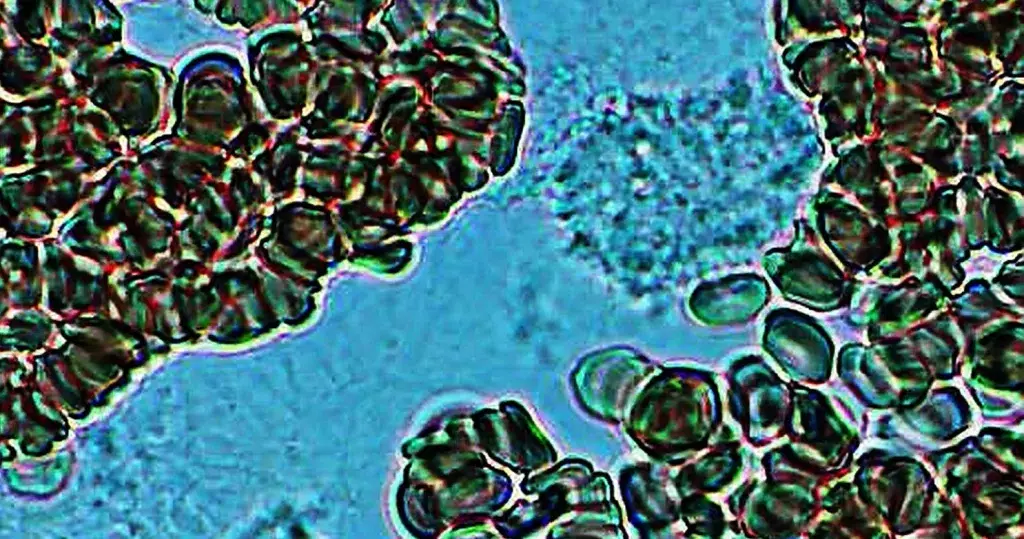
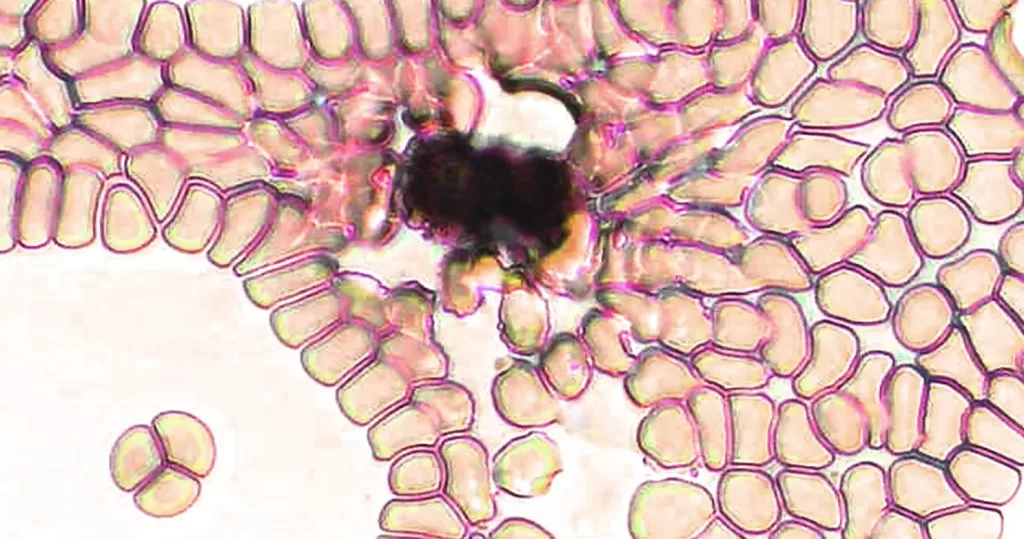
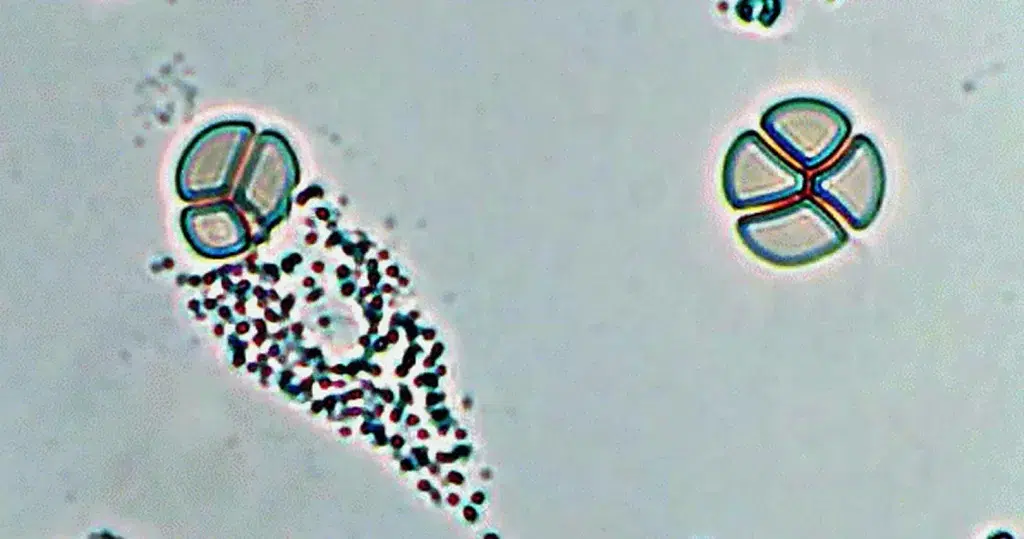
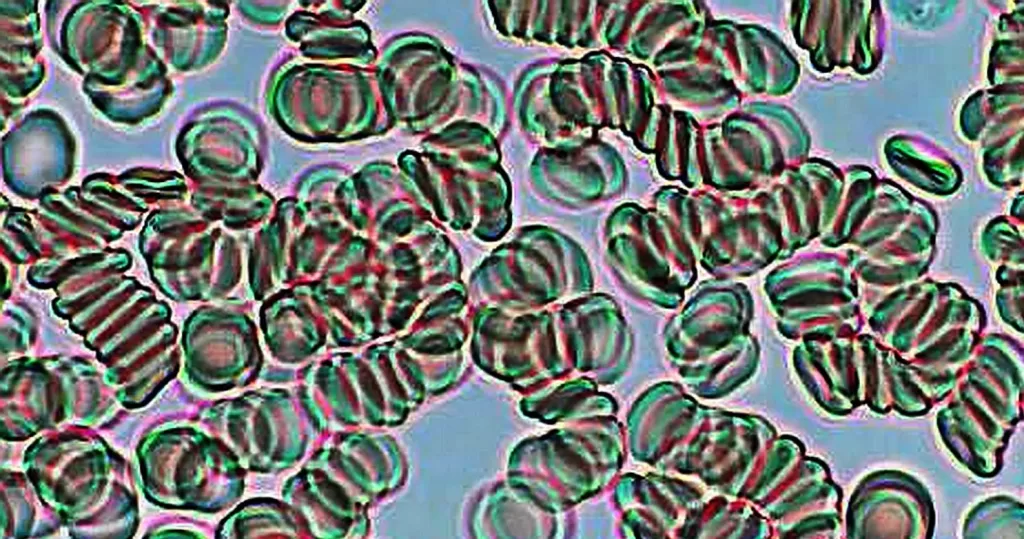
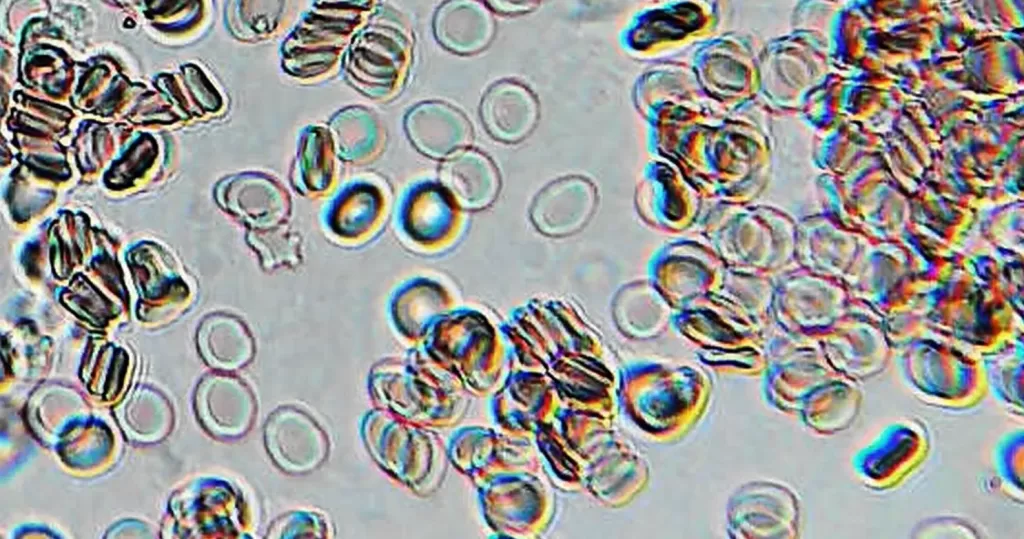
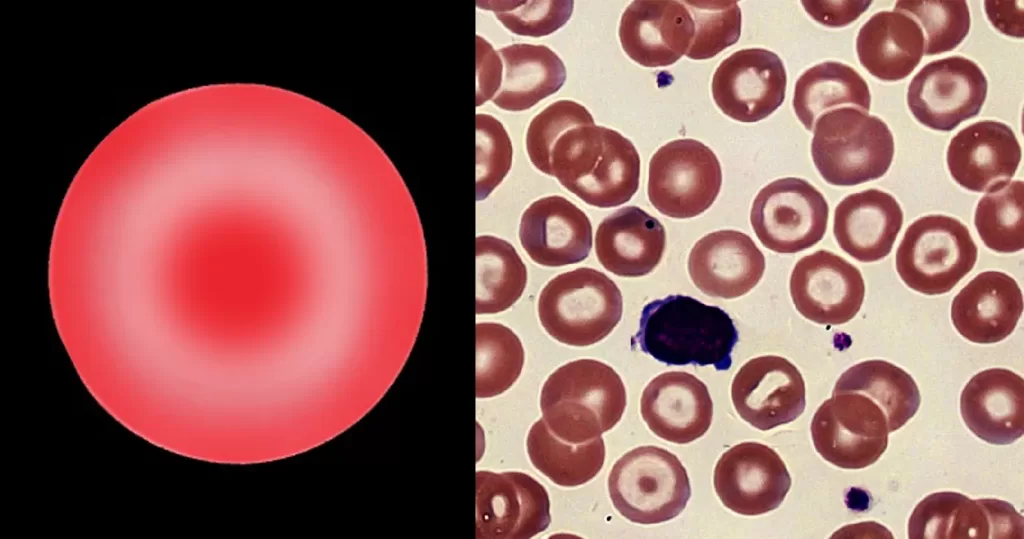
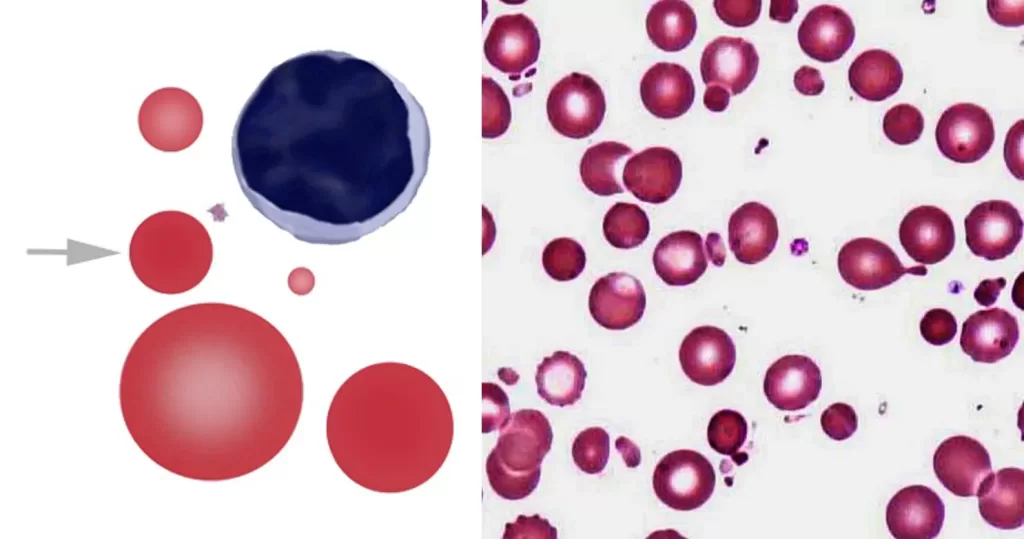
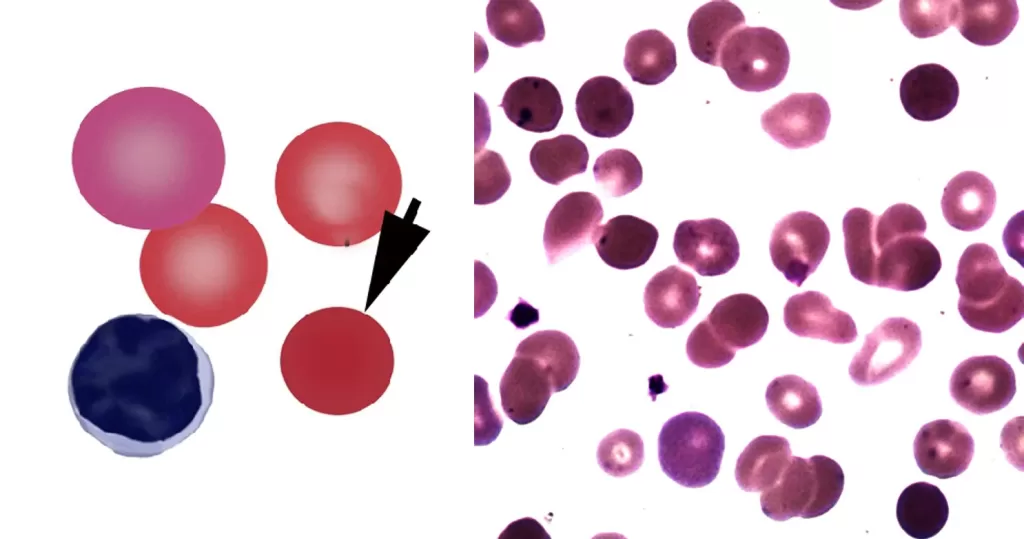
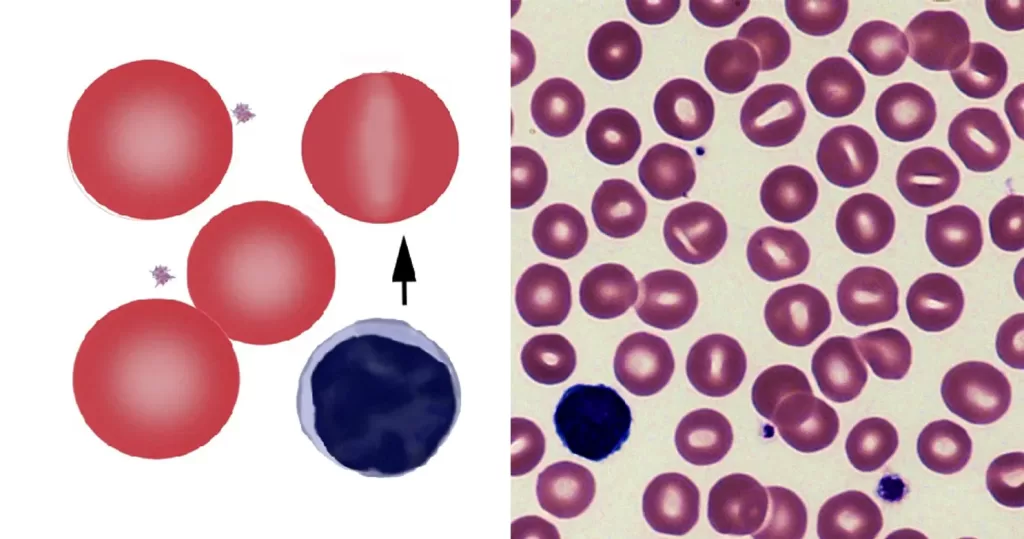
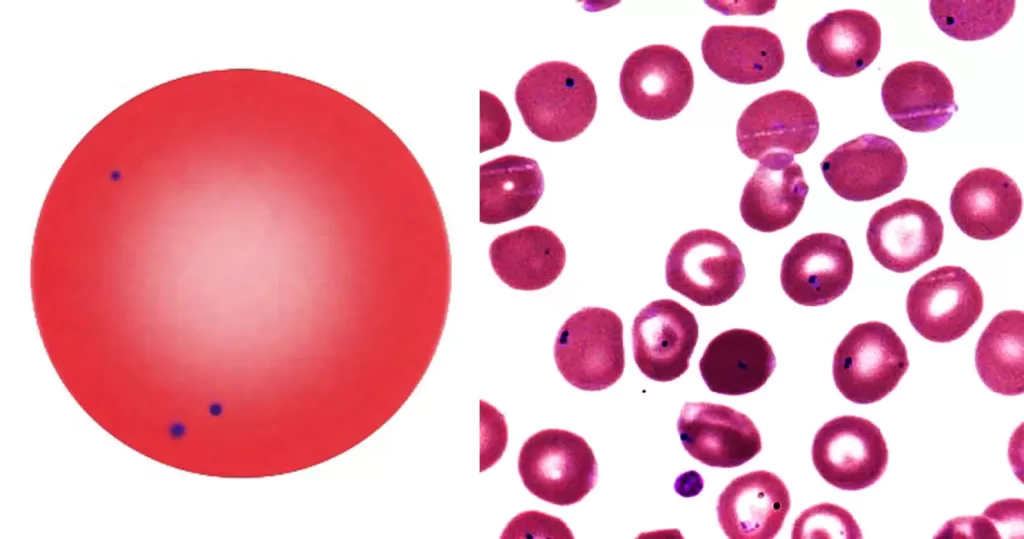
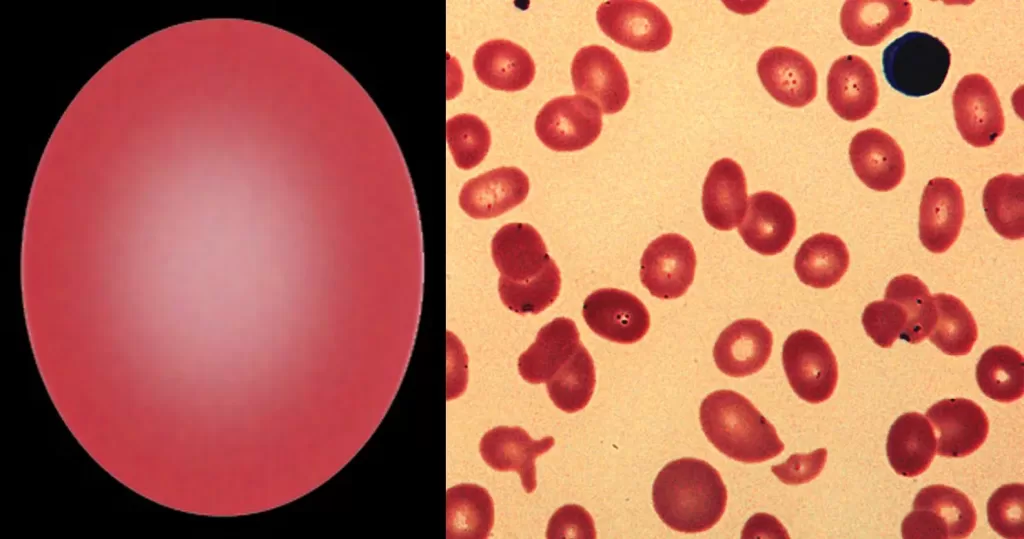
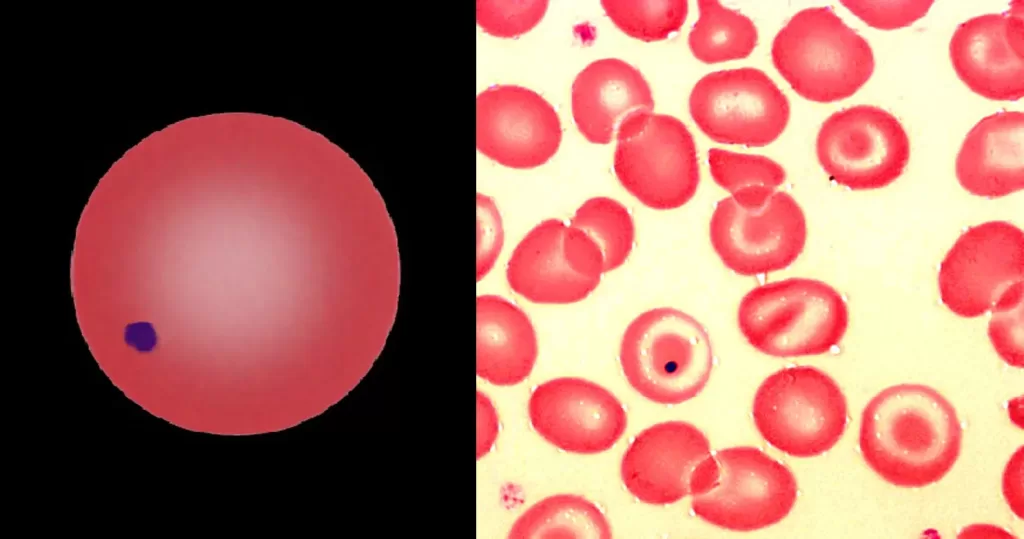
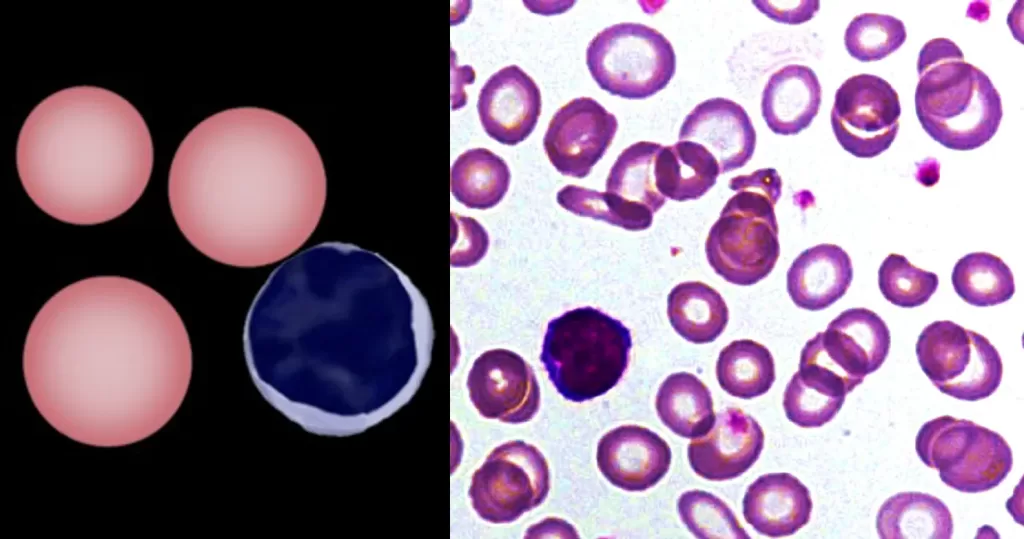
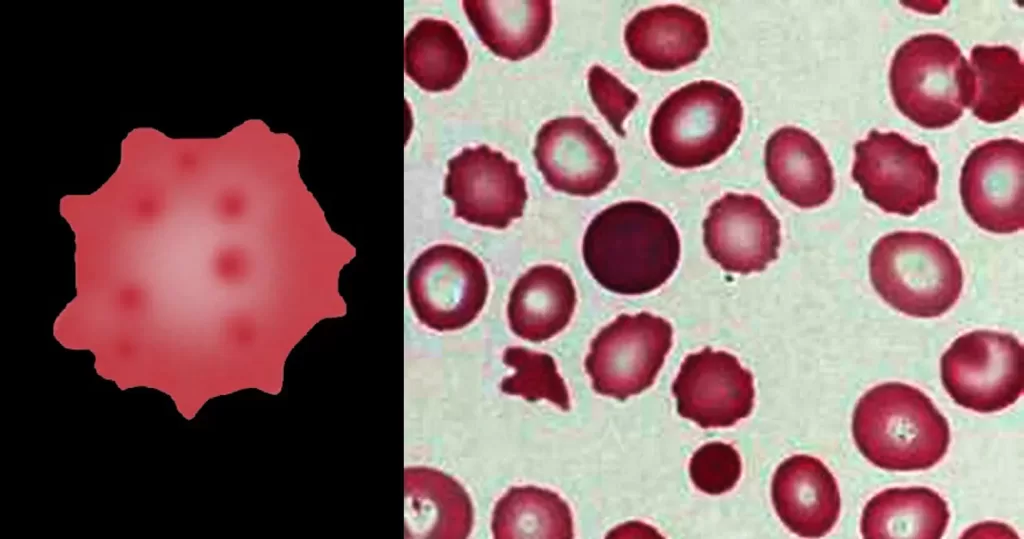
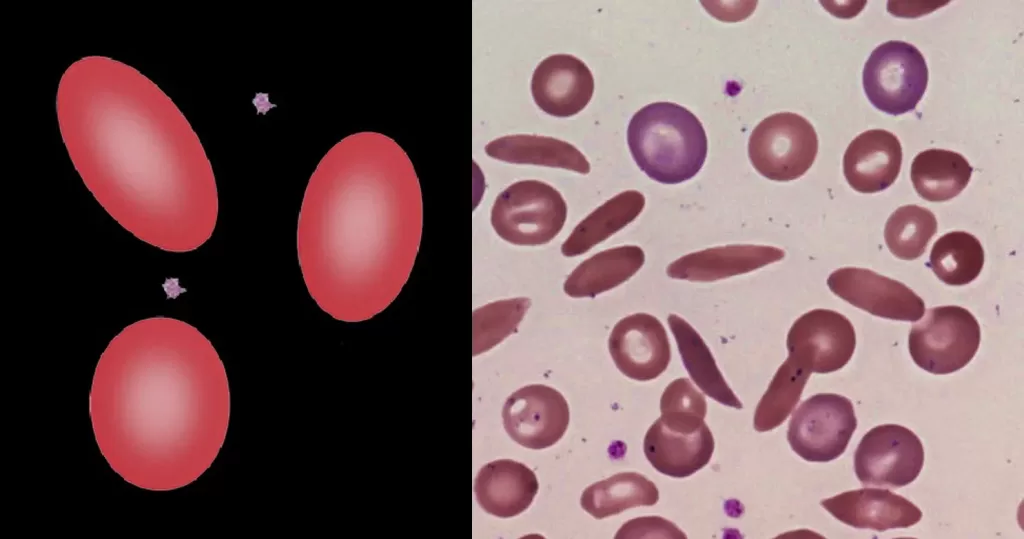
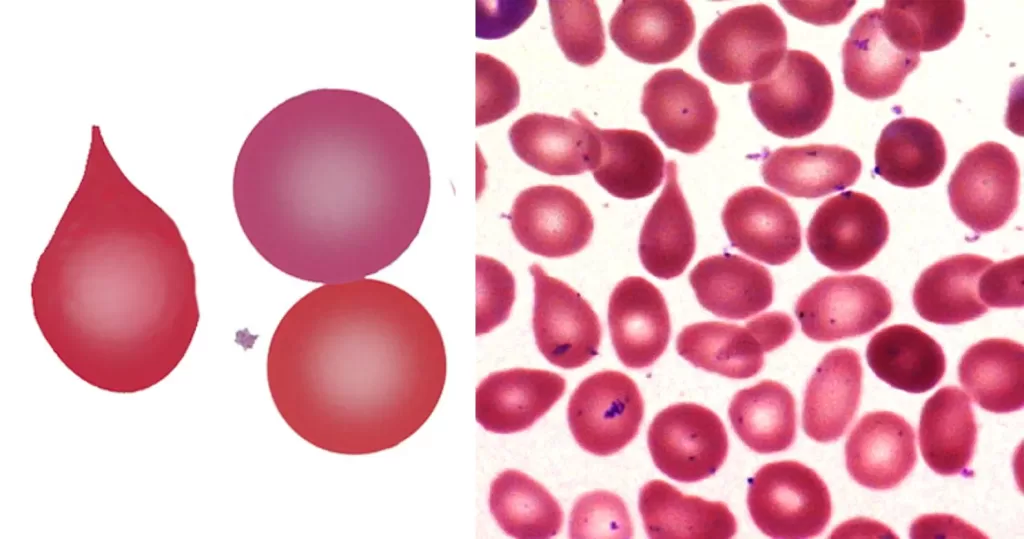
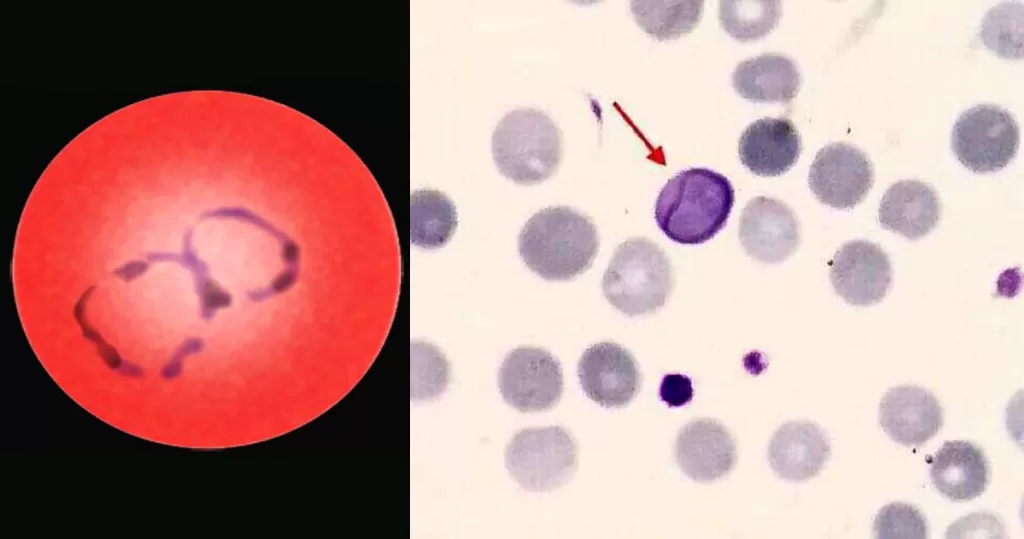
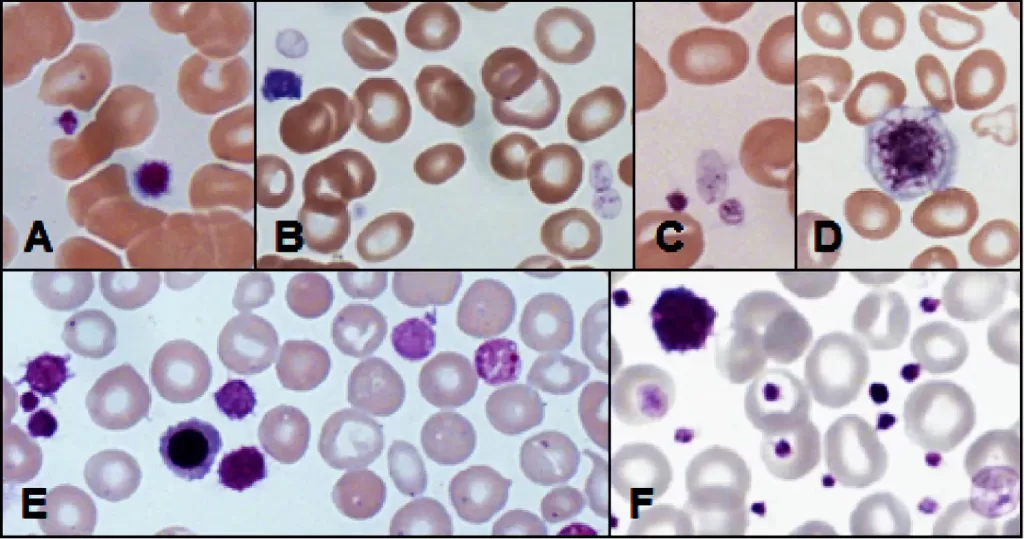
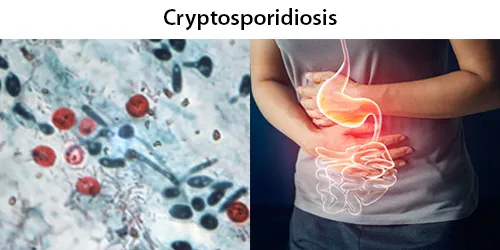
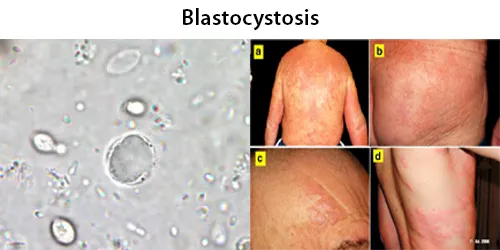
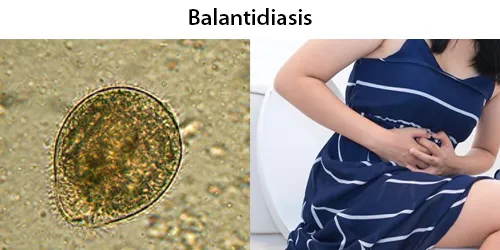
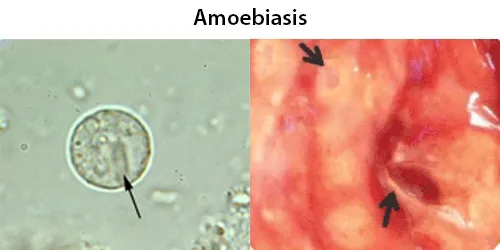
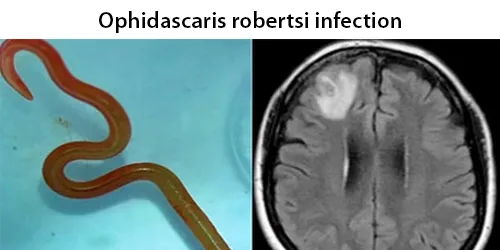
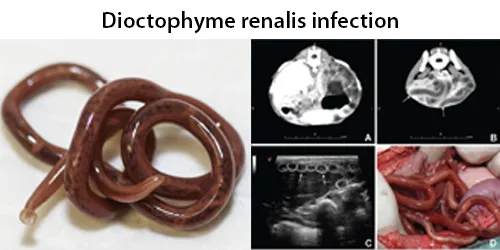
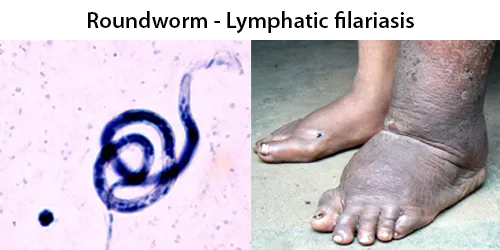
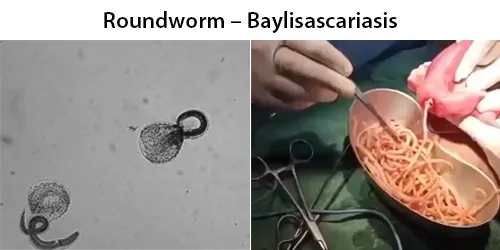
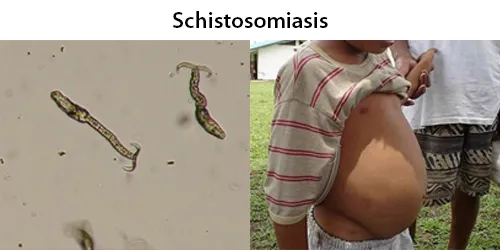
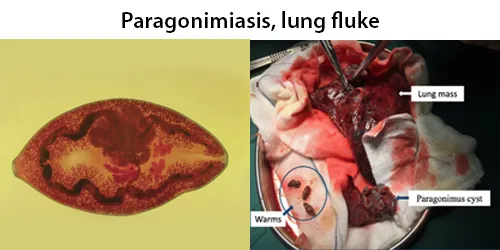
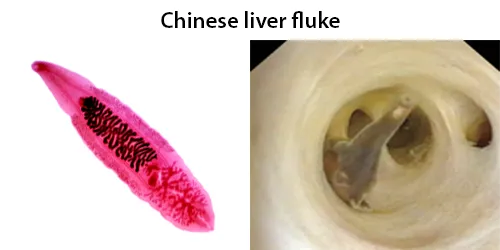
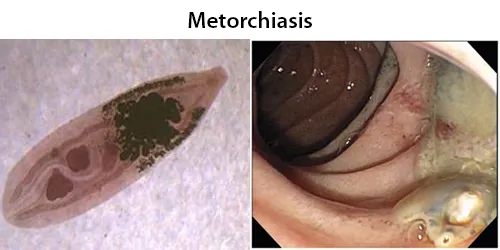
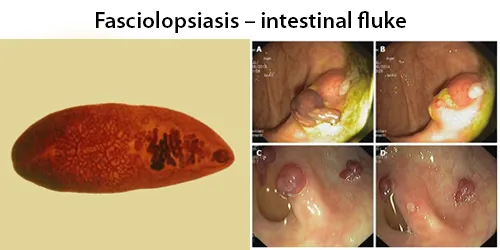
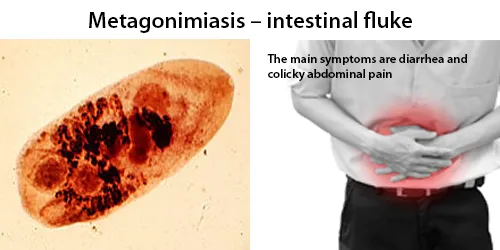
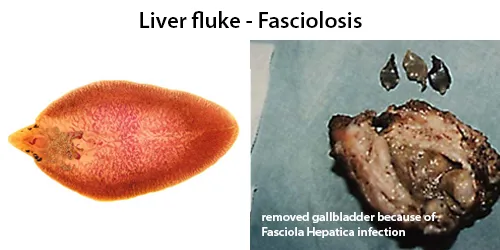
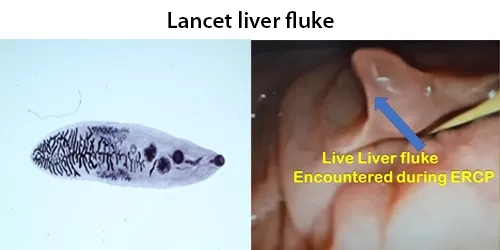
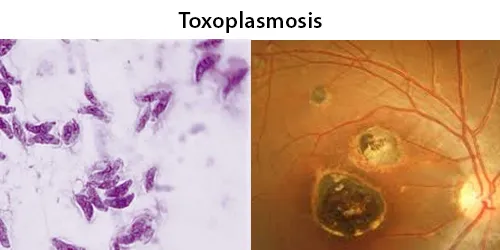
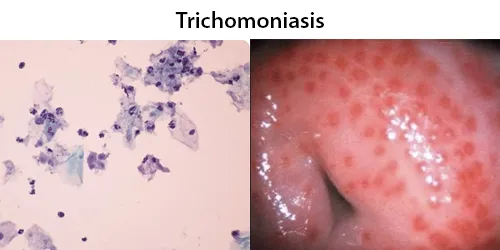
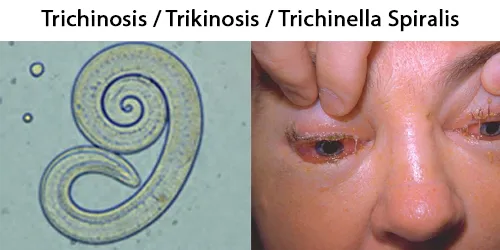
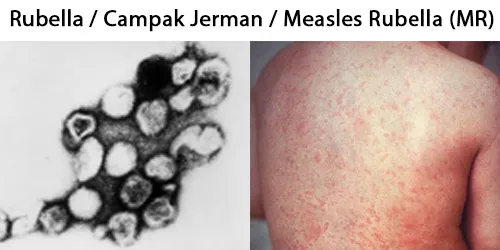
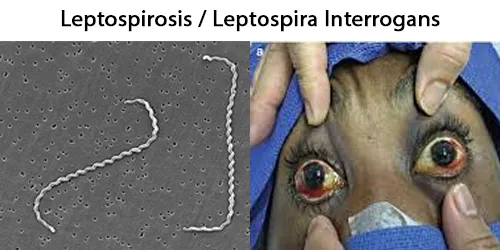
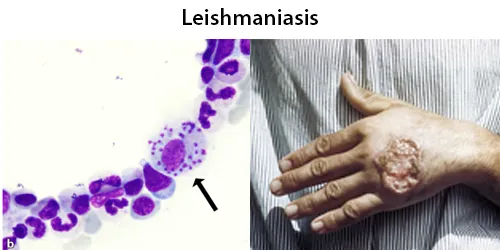
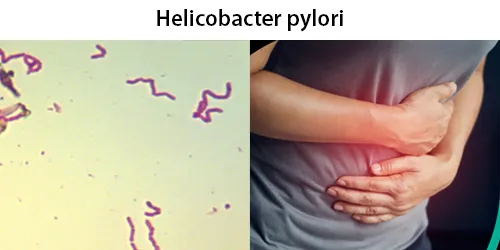
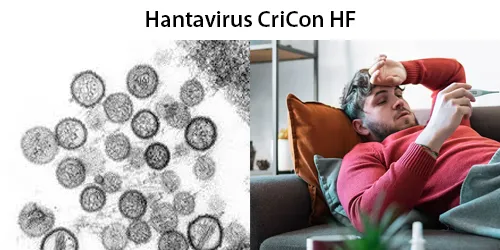
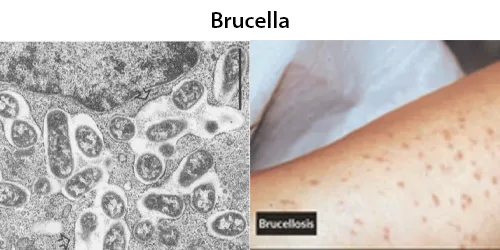
Basophilic Stippling
Most commonly arises when blood cell production is stressed or abnormal, may be associated with dysfunction of enzymes involved in RNA breakdown (either congenital deficiency or drug induced).
https://haematologyetc.co.uk/index.php?title=Basophilic_stippling
Normal individuals:
- Generally fine stippling – this may particularly be seen when there is an increased need for red cells e.g. during
haemolysis, but also a range of reactive states.
Pathological causes:
- Generally coarse stippling. Two basic pathological processes may contribute to significant basophilic stippling in mature erythrocytes.
Dyserythropoietic states:
- Infiltrated bone marrow: (look also for white cell precursor cells): consider leukemia, myelofibrosis or infiltrating solid tumor.
- Hemoglobinopathy (thalassaemia – most particularly hemaglobin H disease)
- Dyserythropoiesis – particularly sideroblastic anemia
- Megaloblastic anemia
Pathways of RNA breakdown are impaired:
- Poisoning (classically heavy metal, particularly lead, also consider arsenic)
- Pyrimidine 5’ nucleotidase deficiency