Female Fertility & Hormones Balance Program
Explore the science behind female fertility & hormones balance—from FSH to progesterone—and evidence-based treatments for hormonal imbalance.
Rp. 12.000.000 (Non-Member testing only) – 25.000.000 (up to with therapies)
Rp. 7.700.000 (Member testing only) – 21.300.000 (up to with therapies)
BSI Membership required, inclusive of Level 2 Testing and Analysis
Depending on Diagnosis & Treatment needs.
Not just about fertility, but also about the 11 reproductive hormones, and 7 master gland hormones that BSI Labs tests and analyzes – that together play an important role in the regulation of several brain functions, bone health, skin health, sexual function/libido, cardiovascular function, and cholesterol regulation, among many others. Hormone balance and fertility are both realized in testing. Whether pre-pubesecent or menopausal, proper hormone balance is crucial for balanced life and well being.
Infertility means not being able to get pregnant after one year of trying (or six months if a woman is 35 or older). Women who can get pregnant but are unable to stay pregnant may also be infertile. Before the year 2020, approximately 10 percent of women ages 15-44 had difficulty getting pregnant or staying pregnant.
Pregnancy is the result of a process. To get pregnant:
A woman’s body must release an egg from one of her ovaries (ovulation).
The egg must go through a fallopian tube toward the uterus (womb).
A man’s sperm must join with (fertilize) the egg along the way.
The fertilized egg must attach to the inside of the uterus (implantation).
Infertility can happen if there are problems with any of these steps.
Classifications of Female Infertility
Ovulation Infrequency
The most common overall cause, which occurs in 40% of women with infertility issues.
Not ovulating can result from several causes, such as:
- Ovarian or gynecological conditions, such as primary ovarian insufficiency (POI) or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Aging, including “diminished ovarian reserve,” which refers to a low number of eggs
in a woman’s ovaries due to normal aging - Endocrine disorders, such as thyroid disease or hypothalamus problems, which affect the hormones correct volume a hormone or group of hormones.
- Lifestyle and environmental factors.
- Menstrual cycle irregularities can lead to infertility. The menstrual cycle includes several phases, and problems at any one of the stages can lead to difficulty getting pregnant or to infertility.
Structural Problems
Usually involve the presence of abnormal tissue in the fallopian tubes or uterus. If the fallopian tubes are blocked, eggs are not able to move from the ovaries to the uterus and sperm is not able to reach the egg for fertilization. Structural problems with the uterus, such as those that may interfere with implantation, can also cause infertility.
Some specific structural problems that can cause infertility include:
- Endometriosis, when tissue that normally lines the inside of the uterus is found in other places,
such as blocking the fallopian tubes - Uterine fibroids, growths that appear within and around the wall of the uterus, although most women with fibroids do not have problems with fertility and can get pregnant. However, some women with fibroids may not be able to get pregnant naturally or may have multiple miscarriages or preterm labor.
- Polyps, which are noncancerous growths on the inside surface of the uterus. Polyps can interfere with the function of the uterus and make it difficult for a woman to remain pregnant after conception. Surgical removal of the polyps can increase the chances for a woman to get pregnant.
- Scarring in the uterus from previous injuries, infections, or surgery. Scarring may increase the risk of miscarriage and may interfere with implantation, thus leading to infertility.
- An unusually shaped uterus, which can affect implantation and the ability to carry a pregnancy to term.
Infections
Can also cause infertility in men and women.
- Untreated gonorrhea and chlamydia can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease, which might cause scarring that blocks the fallopian tubes.
- Untreated syphilis increases the risk for a pregnant woman to have a stillbirth.
- Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection. Chronic HPV infections or vaccines in the cervix, and surgical treatment of cervical lesions, can also reduce the amount or quality of cervical mucus. Problems with this sticky or slippery substance that collects on the cervix and in the vagina can make it difficult for women to get pregnant.
Improper Egg Maturation
Eggs may not mature properly for a variety of reasons, ranging from conditions such as PCOS, to obesity (metabolic syndrome causing excess estrogen production), to a lack of specific proteins needed for the egg to mature. An immature egg may not be released at the correct time, may not make it down the fallopian tubes, or may not be able to be fertilized.
Implantation failure
Refers to the failure of a fertilized egg to implant in the uterine wall to begin pregnancy. While the specific cause of implantation failure are often unknown, possibilities include:
- Genetic defects in the embryo
- Thin endometrium
- Embryonic defects
- Endometriosis
- Progesterone resistance
- Scar tissue in the endometrial cavity
Endometriosis
Occurs when the cells that normally line the uterine cavity, called the endometrium, are found outside the uterus instead. Studies show that between 25% and 50% of infertile woman have endometriosis and between 30% and 40% of women with endometriosis are infertile.
Endometriosis causes of infertility include the follow:
- Pelvic adhesions caused by endometriosis can cause made of scar tissue to form between nearby structures, such as between the ovary and pelvic wall. This can obstruct and affect the release of the egg after ovulation. Scarring in the fallopian tube can interrupt block the egg’s movement through the fallopian tube.
- Excess peritoneum fluids. The lining of the abdomen, which is called the peritoneum, may go through changes that affect its function: In women with endometriosis, the amount of fluid inside the peritoneum often increases. This fluid contains elements that can negatively affect the functions of the egg, sperm, and fallopian tubes.
- Chemical changes in the lining of the uterus that occur as a result of endometriosis may affect an embryo’s ability to implant properly and make it difficult for a woman to stay pregnant after conception.
PCOS
Poly Cystic Ovary Syndrome
PCOS Is one of the most common causes of female infertility. It is a condition in which a woman’s ovaries and, in some cases, adrenal glands produce more androgens (DHEA – a type of hormone) than normal. High levels of these hormones interfere with the development of ovarian follicles and release of eggs during ovulation. As a result, fluid-filled sacs, or cysts, can develop within the ovaries. Researchers estimate that 5% to 10% of women have PCOS. Research suggests that a combination of genetic and environmental factors leads to the PCOS.
POI
Primary Ovary Insufficiency
A condition in which a woman’s ovaries stop producing hormones and eggs at a young age. Women with POI ovulate irregularly, if at all, and may have abnormal levels of ovarian and pituitary hormones due to problems with their ovaries. Women with POI often have trouble getting pregnant. However, pregnancy is still possible, though rare. About 5% to 10% of women with POI get pregnant without medical treatment.
Uterine Fibroids
Noncancerous growths that form inside the uterus. Uterine fibroids can cause symptoms in some cases, depending on their size and location. It is believed that there may be a genetic basis for fibroids formation.
Fibroids are found in 5% to 10% of infertile women. Fibroids located in the uterine cavity (as opposed to those that grow within the uterine wall) or those that are larger than 6 centimeters in diameter are more likely to have a negative effect on fertility.
Fibroids are more likely to affect a woman’s fertility if they:
- Change the position of the cervix, which can reduce the number of sperm that enter the uterus
- Change the shape of the uterus, which can interfere with the movement of sperm or implantation
- Block the fallopian tubes, which prevents sperm from reaching the egg and keeps a fertilized egg from moving to the uterus
- Interfere with blood flow to the uterus, which can prevent the embryo from implanting
Autoimmune Disorders
Cause the body’s immune system to attack normal body tissues it would normally ignore. Autoimmune disorders, such as lupus, Hashimoto’s and other types of thyroiditis, or rheumatoid arthritis, may affect fertility. Reasons involve inflammation in the uterus and placenta or medications used to treat the diseases. Both men and women can make antibodies that attack sperm or the reproductive organs.
Risk Factors
Many things can change a woman’s ability to have a baby. These include:
Age
Smoking
Excess alcohol use
Stress
Poor diet
Athletic training
Being overweight or underweight
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
Health problems that cause hormonal changes, such as polycystic ovarian syndrome and primary ovarian insufficiency
Covid-19
Diagnosis
Interview (Use Hormone Testing form to complete exam questions.)
- Medical history
- Lifestyle
- Sex life
- STDs past or present
- Surgeries, especially lower regions, including circumcision
- Injuries
- Exercise
- Smoking, recreational drugs, Rx drugs
- Libido
- Menstruation, frequency, duration, blood volume, cramping, etc.
- Menopause, family history, etc.
- Awakened at night to urinate
- Urine stream strong or weak
Causes of Female Infertility
- Anatomical or genetic abnormalities
- Systemic or neurological diseases
- Infections / STDs
- Trauma to the groin or other areas of the body
- Gonadotoxic radiation therapy
- Endocrine disruptors such as plastics, estrogen, soy products, etc.
- Surgeries
- Emotional trauma
- Stress
- Malnutrition
Risk Factors discussion:
- Smoking
- Drinking alcohol
- Being overweight or obese or being underweight
- Sexual history, especially sexually transmitted infections
- Malnourishment
- Exposure to chemicals
- Covid-19
BSI standard exam and detox program with live blood analysis, with genital and abdomen exam
Including: Thyroid, Hormone Female, Vaginal swab (if needed)
Prescription. BSI Clinics may suggest a large variety of remedies, based on interview, test results, and examination. Prescriptions are based on the chart below, and prescribed as needed.
Female Sex Hormones Combinations Tests
- Albumin (hormone transport) (If requested)
- Testosterone Total
- Testosterone Free
- Free testosterone percentage *
- Bio-available testosterone *
- Estrogen / Estradiol
- Progesterone
- Estrogen / Progesterone Ratio *
- Luteal phase length calculation (if needed)
- Dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEA) (Adrenal glands product)
- 17-OHP (Adrenal glands product)
- Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
- Luteinizing (LH)
- FSH / LH Ratio *
- Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin (SHBG)
- Prolactin (PRL)
Additional (optional)
- Cortisol Stress Hormone (optional)
- Cortisol / DHEA Ratio (optional) *
* Available with the complete package, cannot be tested individually.
Master Glands Hormone Combinations Tests
(These control the sex hormones, and all interrelated bodily functions)
- TSHs (Thyroid-stimulating hormone)
- T3 (Total Triiodothyronine)
- FT3 (Free Triiodothyronine)
- T4 (Total Thyroxine)
- FT4 (Free Thyroxine)
- FT3 / FT4 Ratio *
- IPTH (Parathyroid hormone)
* Available with the complete package, cannot be tested individually.
Suggested MEDICINES and THERAPIES, FEMALE HORMONES and MOOD PROGRAM : HOME CALENDAR
Modify and follow as long as needed, stop when results are obtained
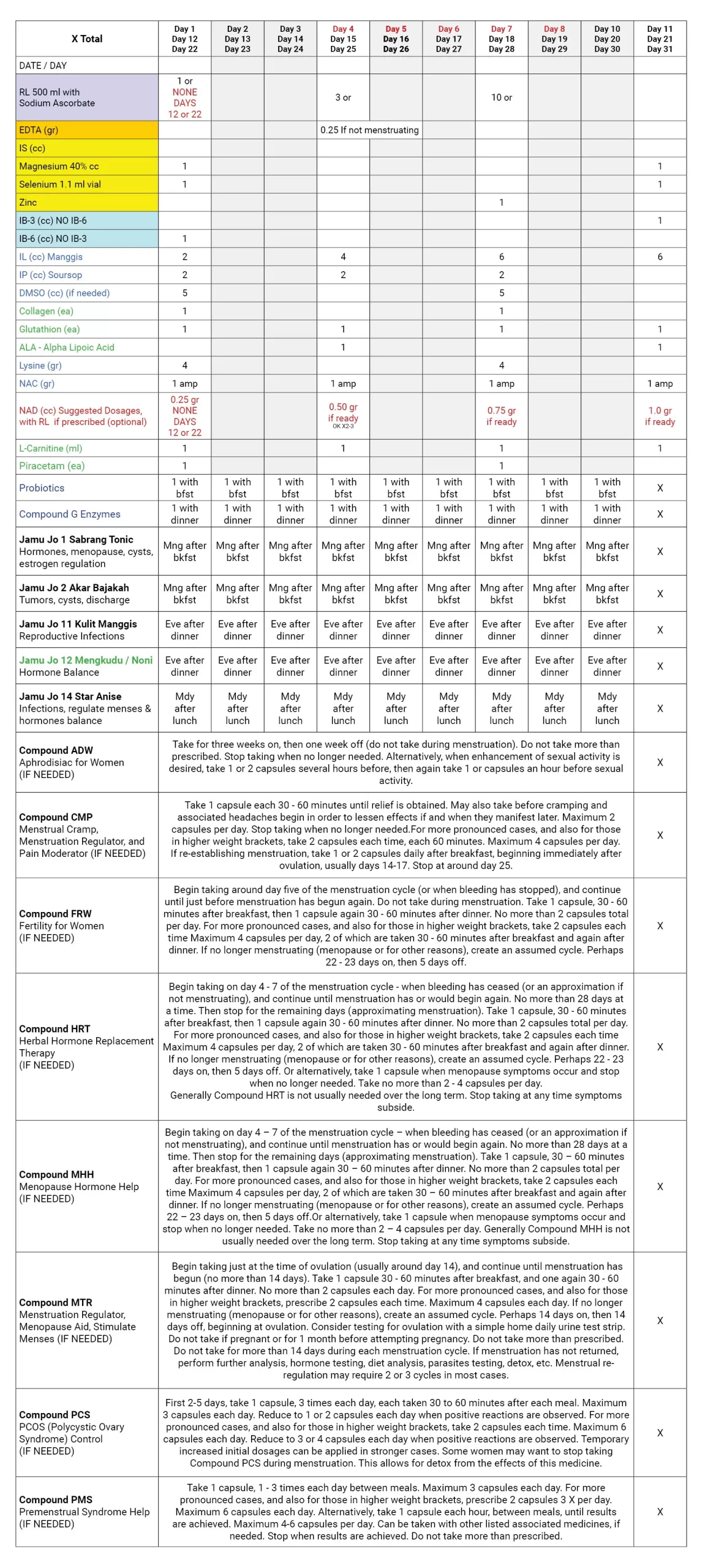
Medicines and Therapies that may be prescribed.
Words of Encouragement
Modern drugs usually do not cure a problem and tend to cause addiction and other side effects. Lifestyle changes may be required for optimal healing to occur. In some cases, surgery may be beneficial, such as in the case of polyps or fibroids.
The patient must carefully monitor her therapy, changes in libido, mood, diet etc. It’s very important to concurrently follow the infusion and oral medications schedule, while limiting conventional medicines intake. Of course, diet and exercise are paramount. Frequent stimulation of the genital region is advised.
Remember: The body only heals during deep sleep and rest. The patient must be patient, rest, and get impact exercise too. Therapies prescribed by BSI for infertility may vary greatly from patient to patient. And Patience is advised, healing can take time.