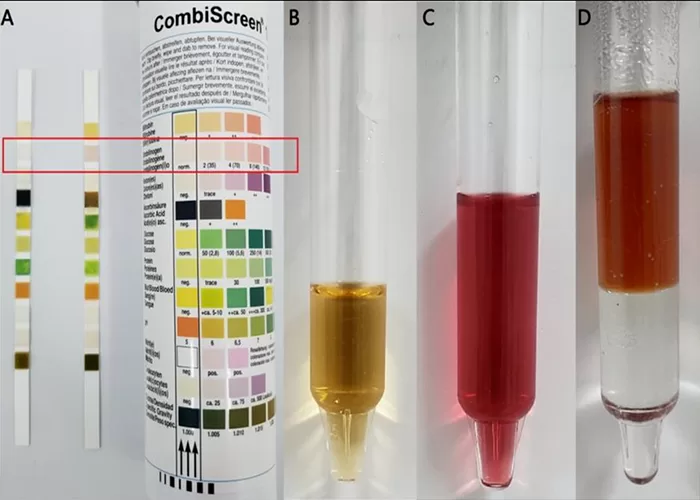
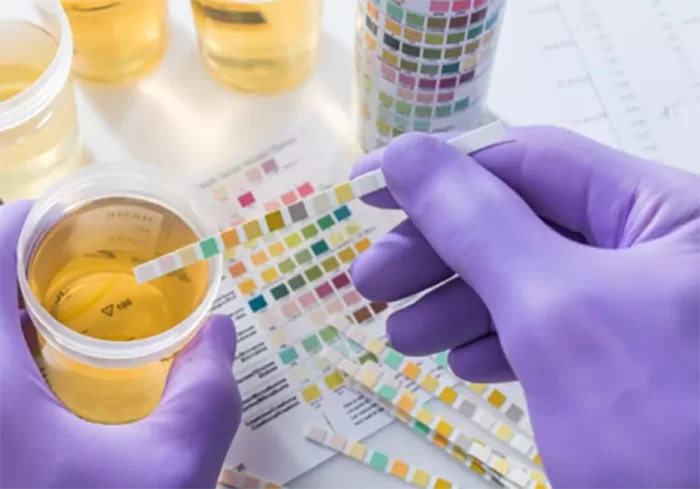
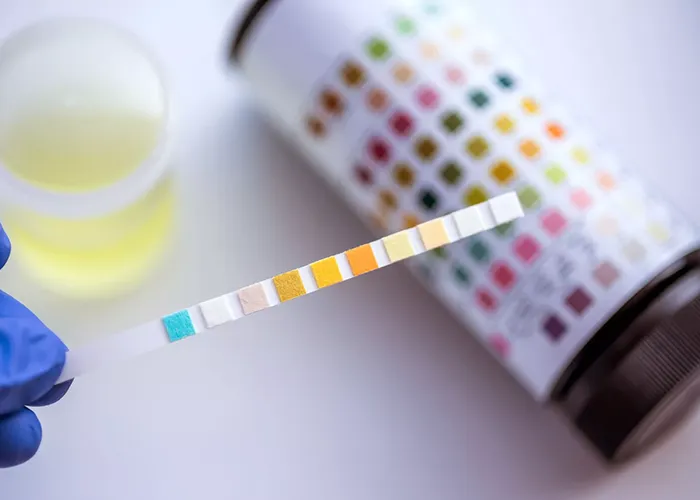
Kidney Blood Tests
BUN (Blood Urea Nitrogen)
Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) is a test that measures the amount of urea nitrogen in your blood. Urea nitrogen is a waste product formed when the liver breaks down protein. It travels through the bloodstream, is filtered by the kidneys, and is excreted in urine. If the liver or kidneys aren’t functioning properly, urea nitrogen may build up in the blood. BUN levels are used to assess kidney function and can help diagnose kidney disorders or monitor treatment effectiveness for kidney disease.
Creatinine
Creatinine is a waste product produced from the normal breakdown of muscle tissue and the digestion of protein in food. It is filtered out of the blood by the kidneys and excreted in urine. While small amounts of creatinine are always present in the blood, high levels can indicate a potential kidney problem. The serum creatinine test measures the amount of creatinine in the blood to assess how well the kidneys are functioning. This test is commonly used to check kidney health, monitor chronic kidney disease, and track kidney function changes over time. It is often part of routine health checks or used when kidney issues are suspected.

BUN / Creatinine Ratio
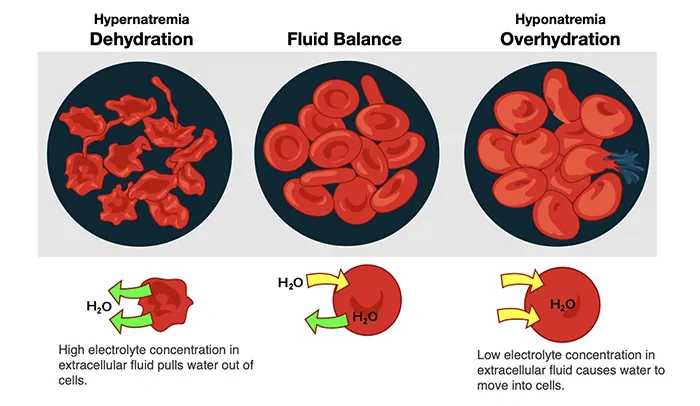
The BUN/Creatinine ratio is a blood test that compares the levels of blood urea nitrogen (BUN) to creatinine in the blood. It is used as a screening tool to help detect kidney disease and other health issues. The normal BUN/creatinine ratio typically ranges from 10:1 to 20:1. This ratio is a better indicator of kidney function than BUN or creatinine levels alone. A high ratio can suggest conditions like congestive heart failure, gastrointestinal bleeding, or dehydration, while a low ratio may indicate malnutrition or liver disease.
The BUN/Creatinine ratio calculator helps assess kidney function by comparing the levels of BUN and creatinine in the blood. Through this method, doctors can determine how efficiently your kidneys are filtering waste products from the blood and identify any underlying abnormalities.

Uric Acid
Uric acid is a waste product produced from the breakdown of nucleic acids in the body. It is normally found in the blood and urine. High levels of uric acid are commonly associated with gout, a condition characterized by painful, swollen joints due to the buildup of uric acid crystals. Elevated uric acid levels can also occur as a side effect of treatments like chemotherapy or radiation therapy. Additionally, an excessive buildup of uric acid can lead to the formation of uric acid kidney stones, which are hard deposits that can cause pain, urinary obstruction, and other health problems if they move or become lodged in the urinary tract.

Non-fasting Glucose
A non-fasting glucose test measures the level of glucose (sugar) in your blood after eating. This test differs from a fasting glucose test, which measures blood glucose after an overnight fast. Understanding non-fasting glucose levels helps identify potential issues with blood sugar regulation, such as hypoglycemia (low blood glucose) or hyperglycemia (high blood glucose), and determine if medical attention is needed.