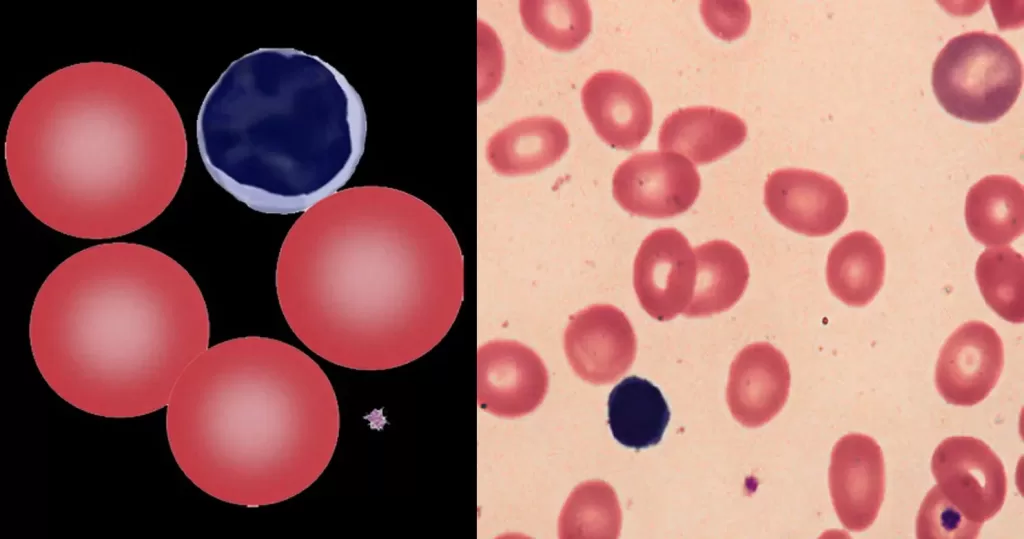
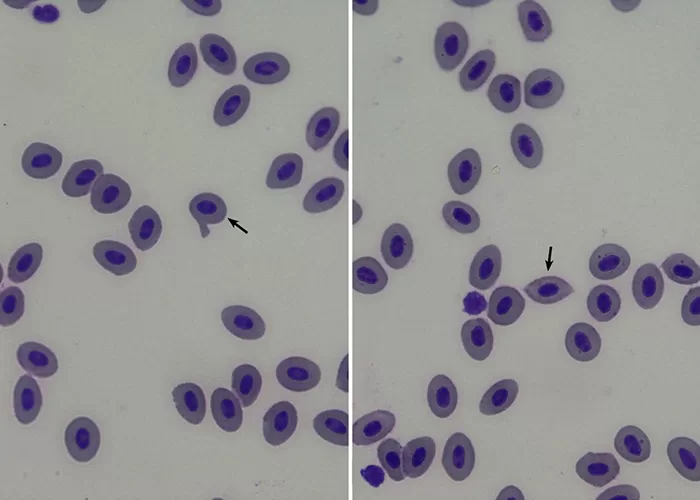
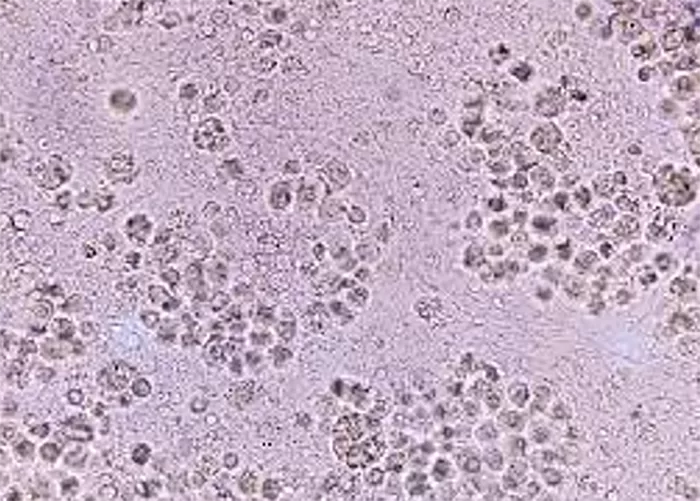
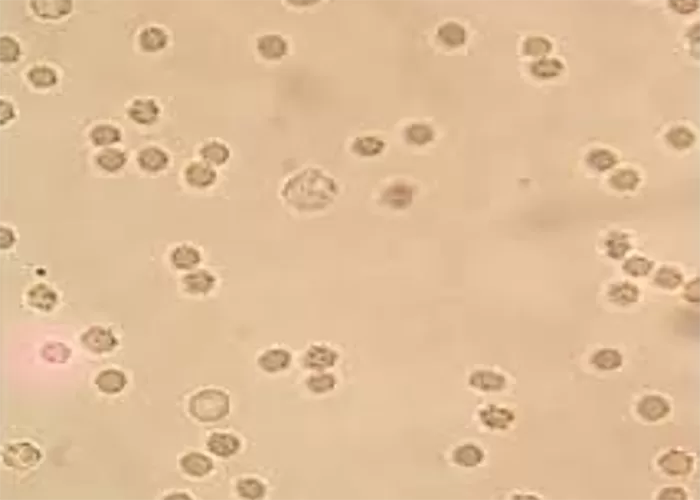
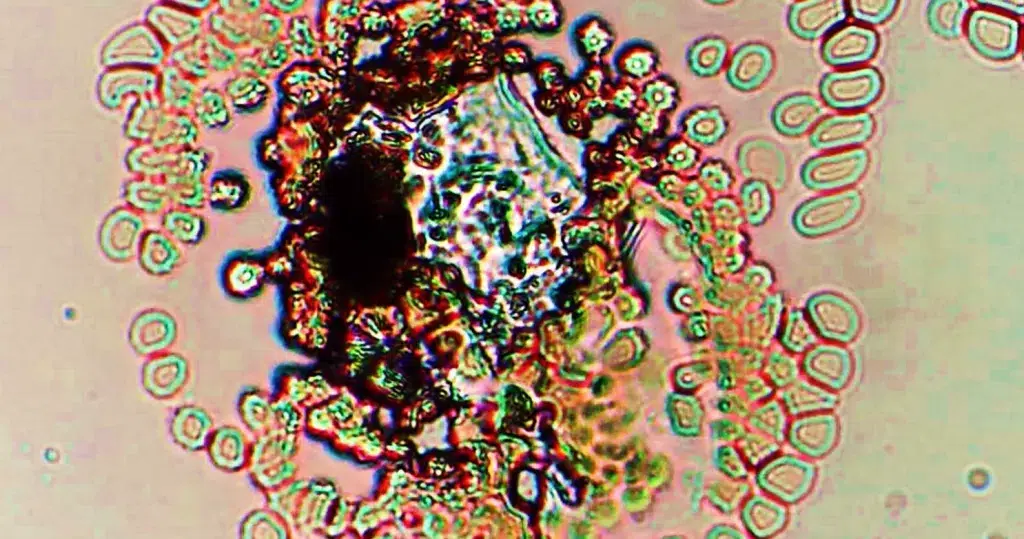
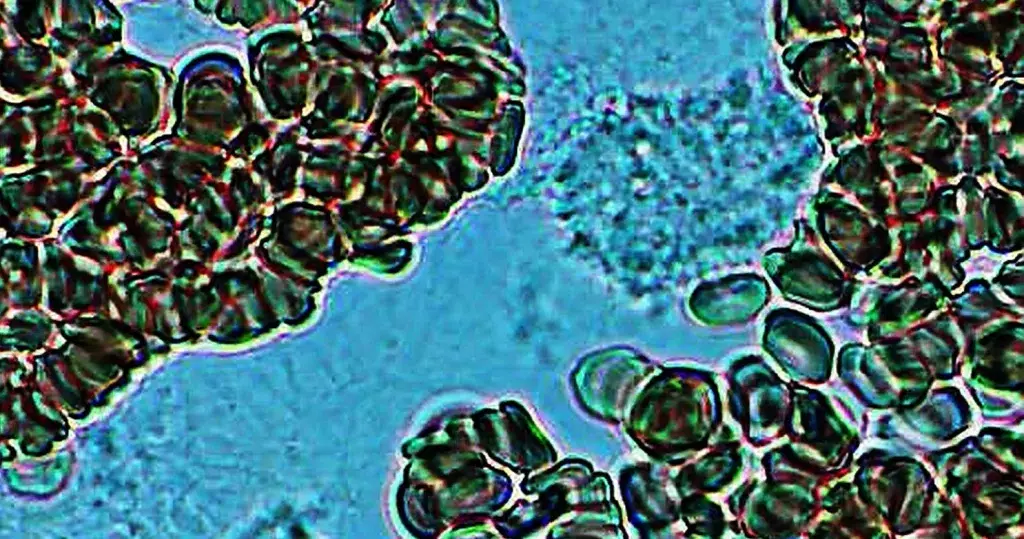
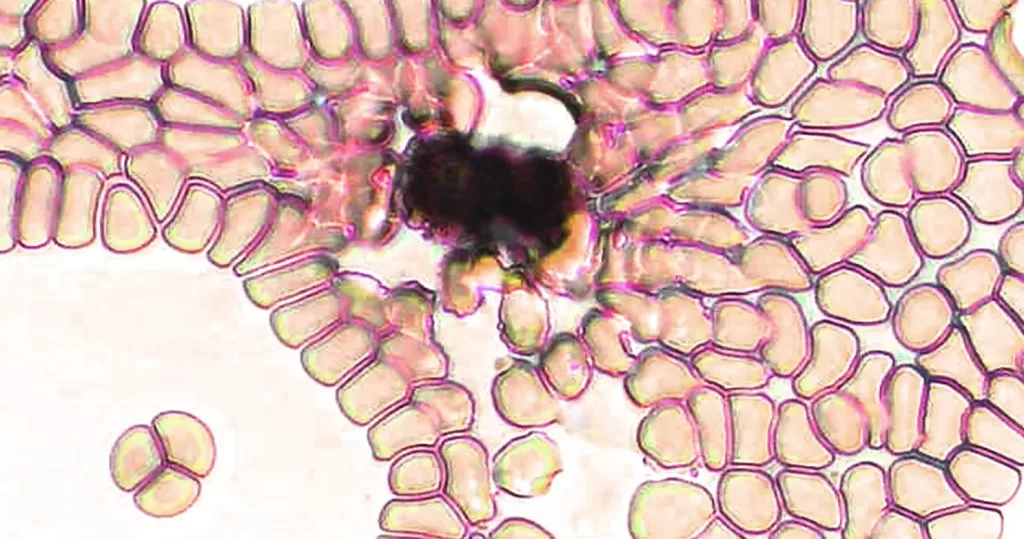
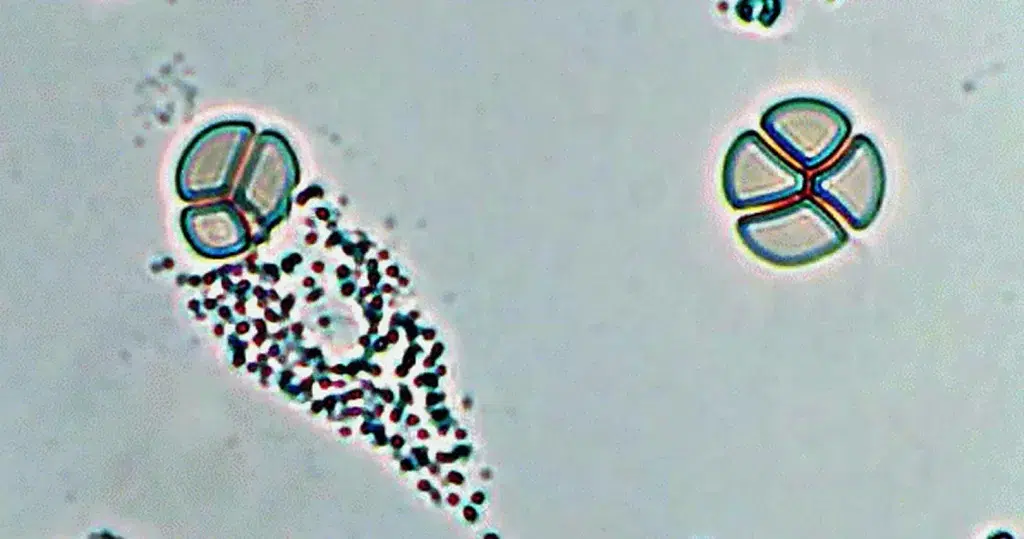
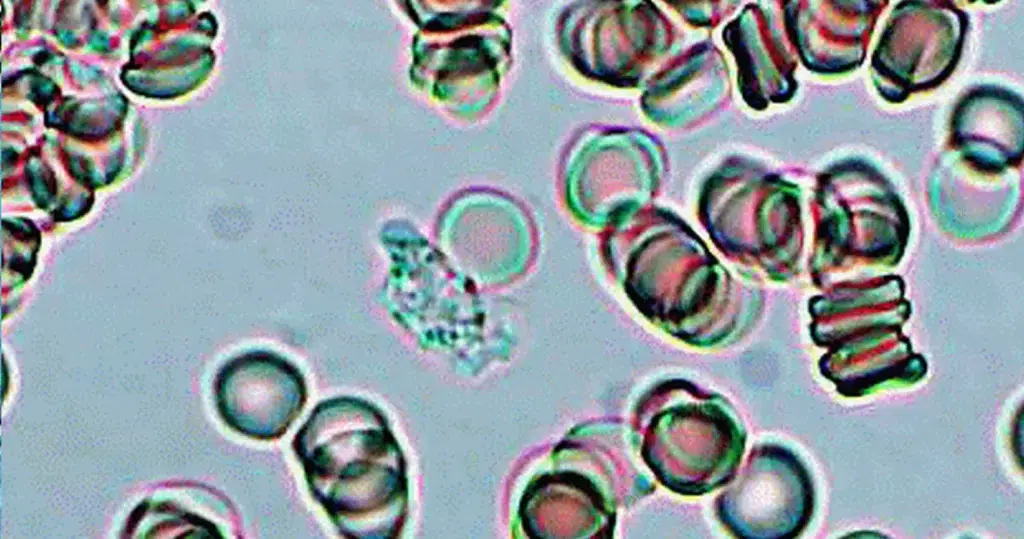
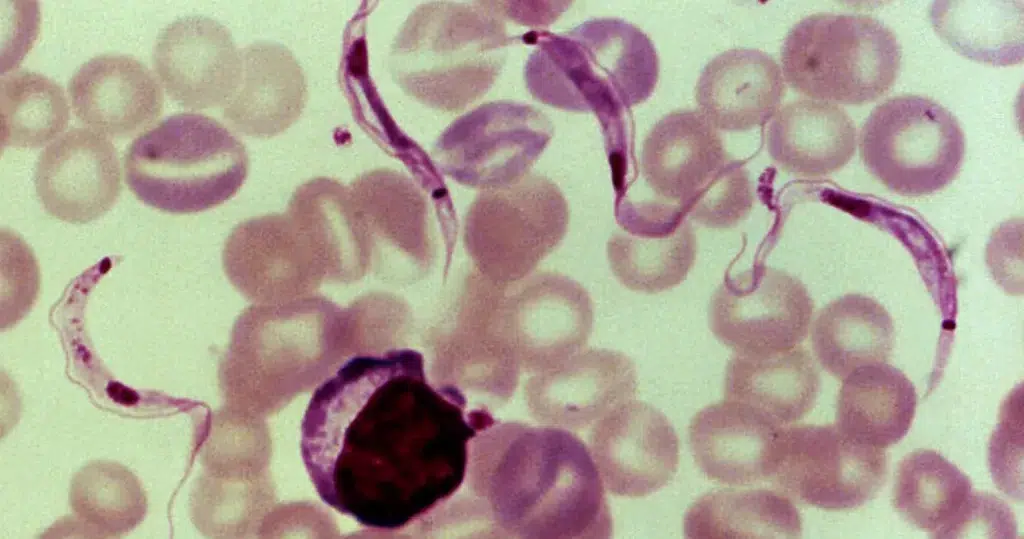
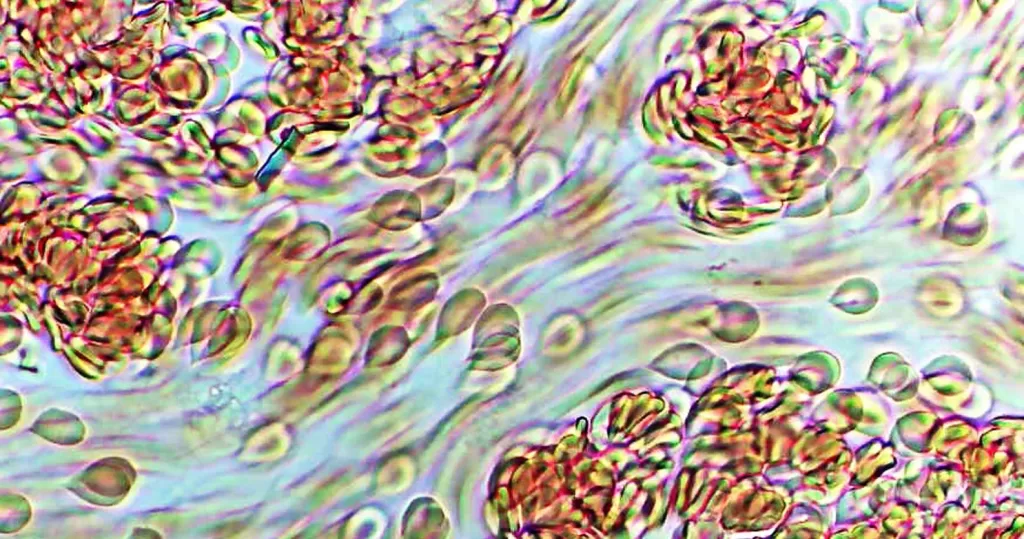
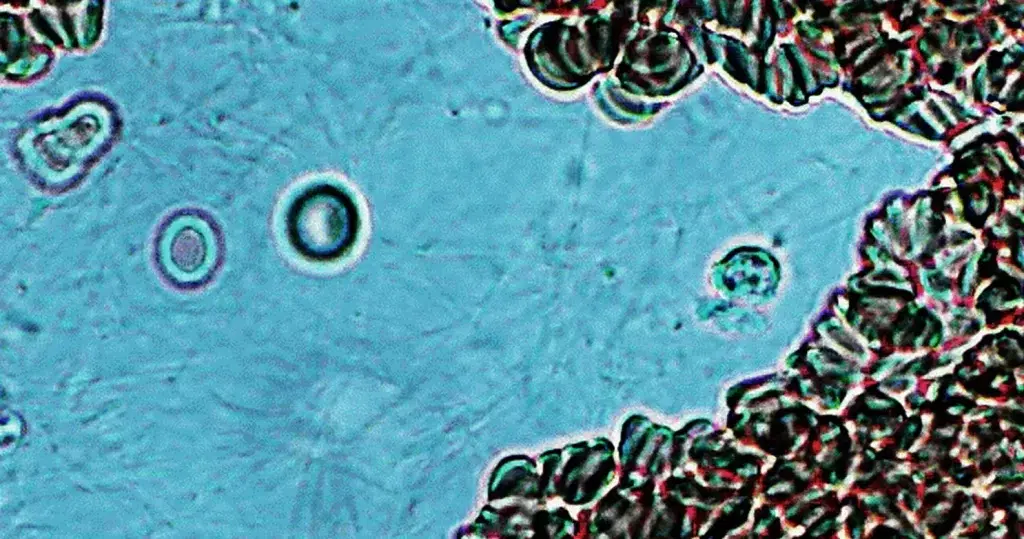
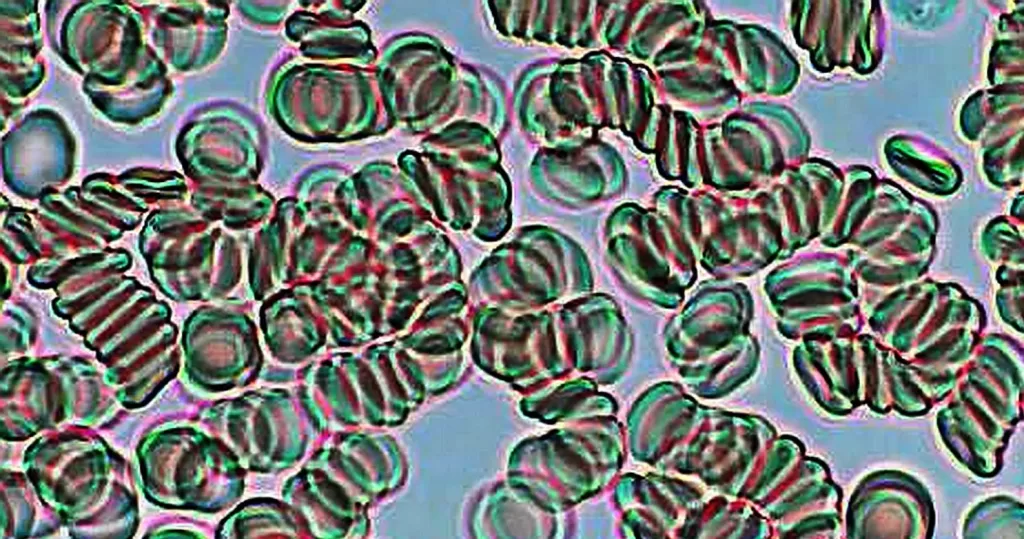
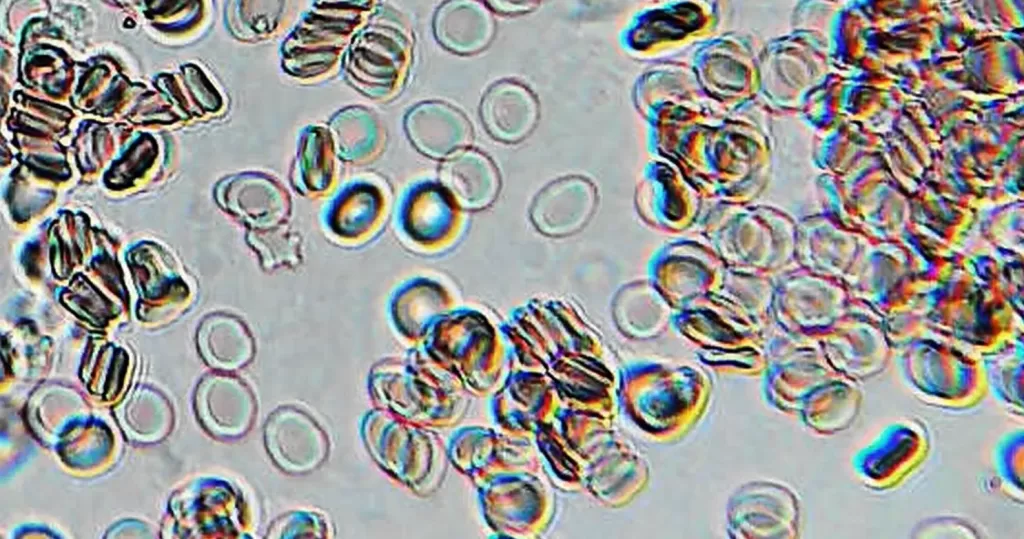
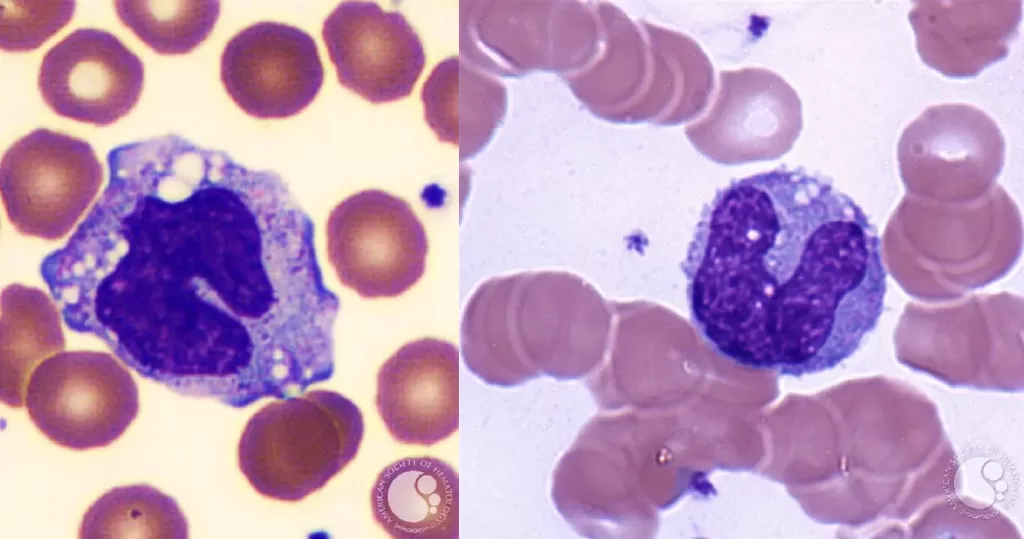
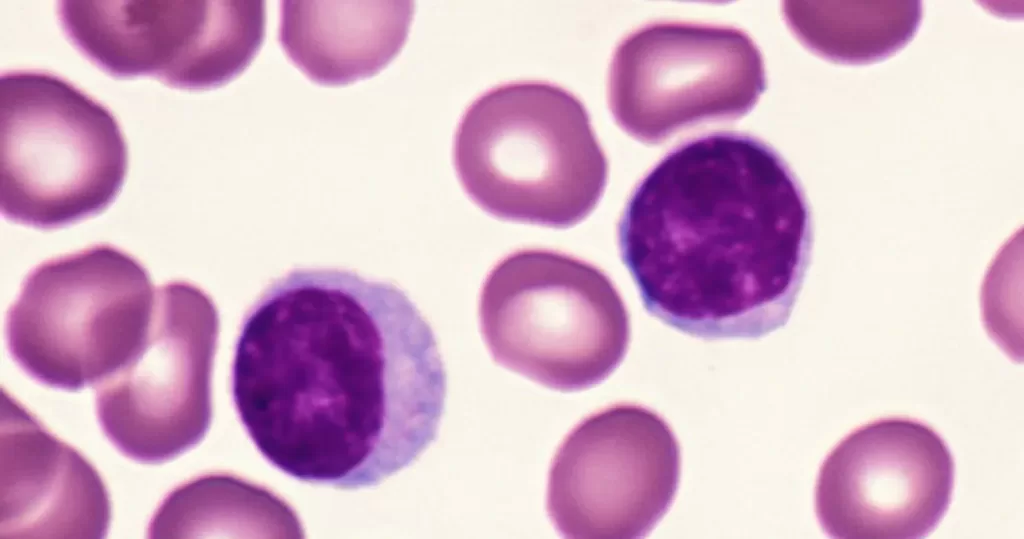
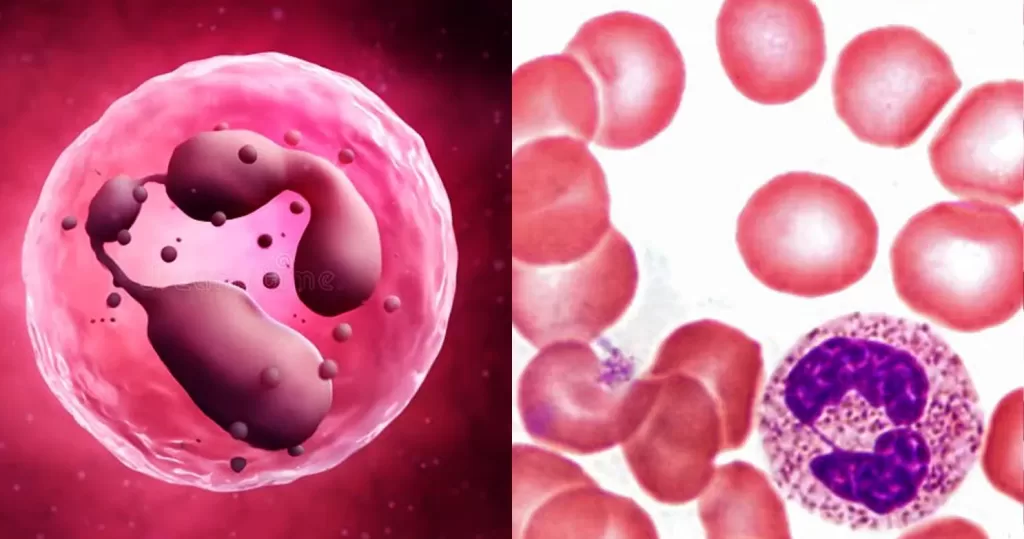
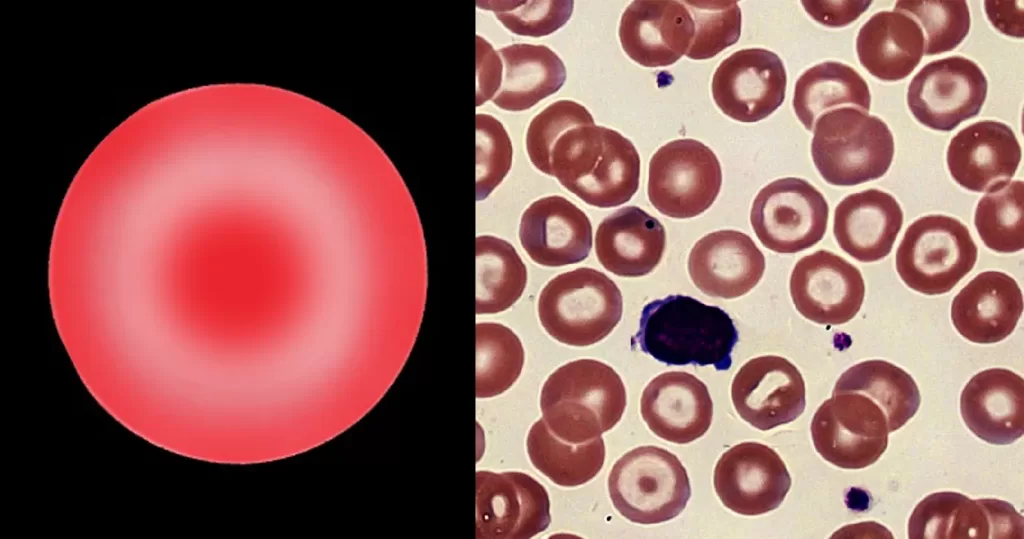
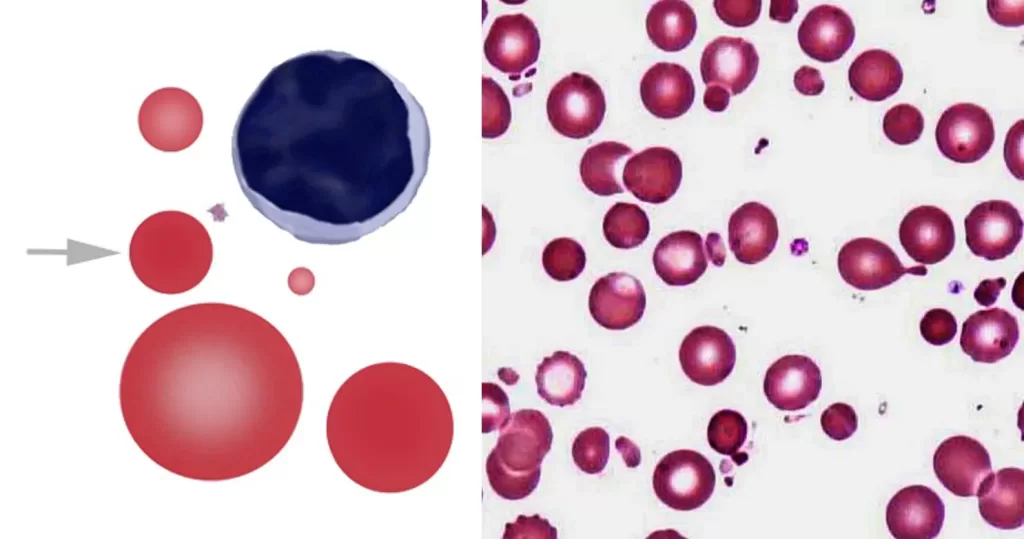
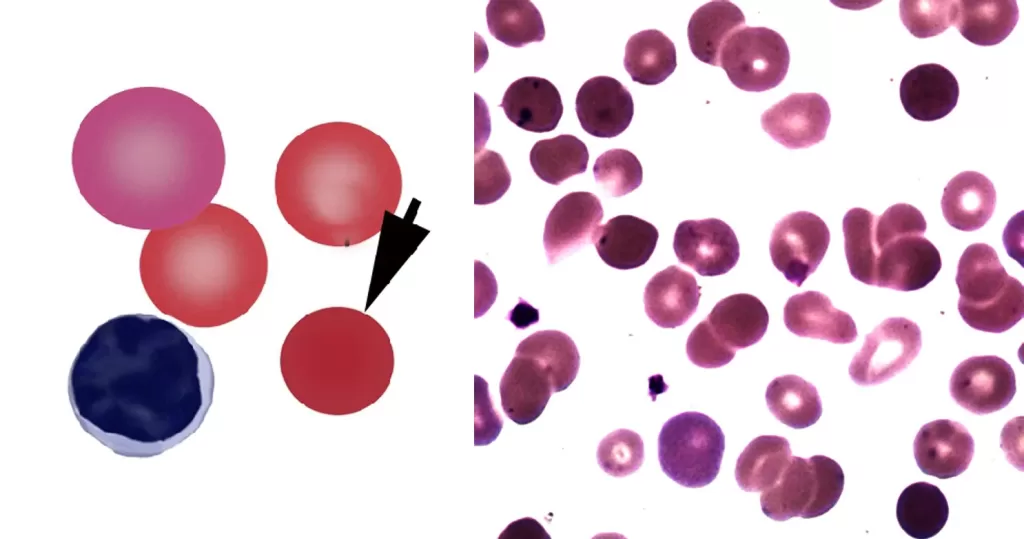
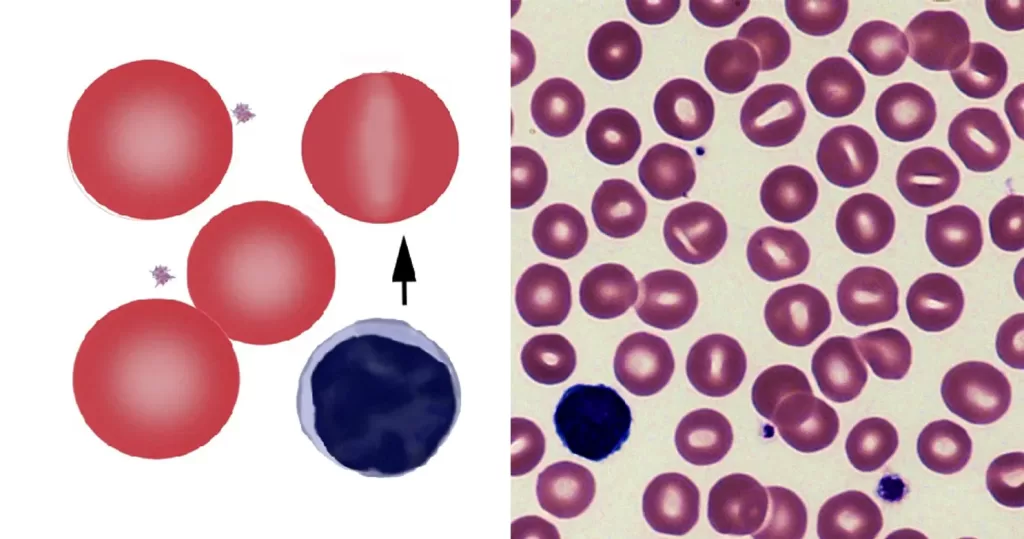
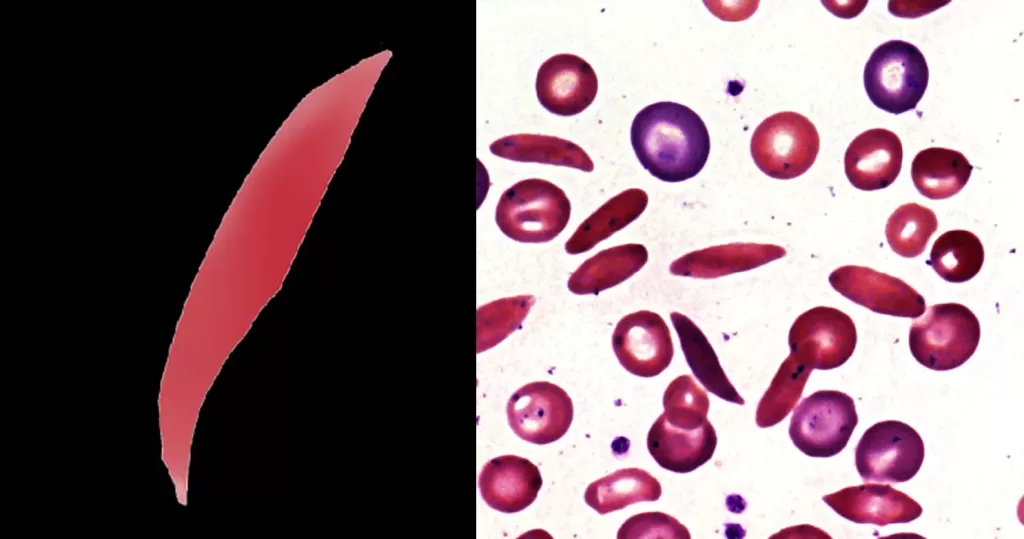
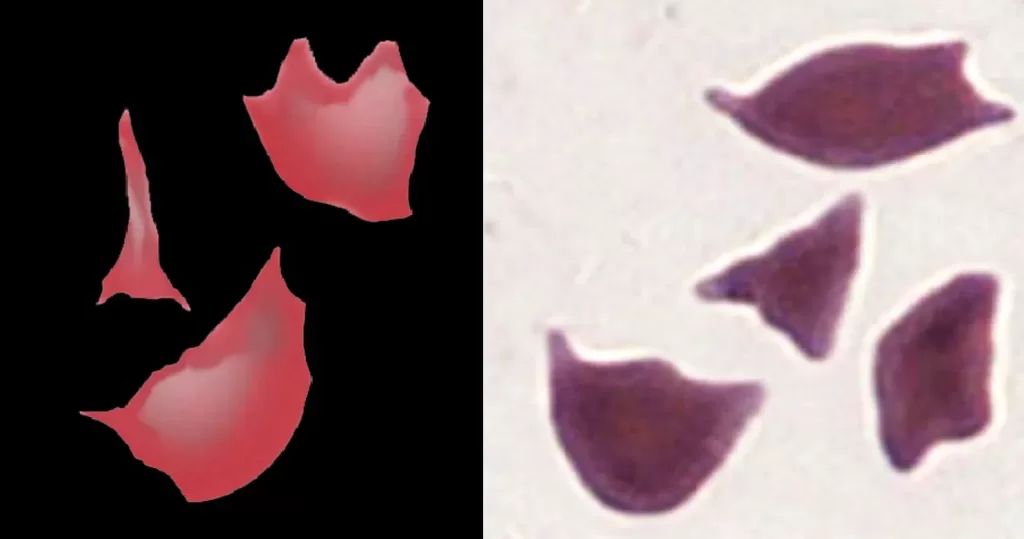
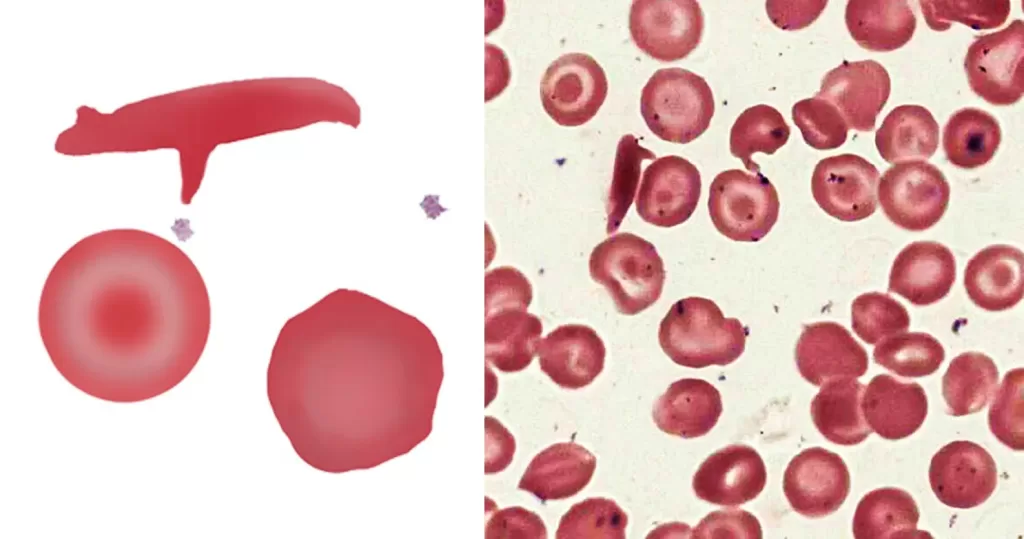
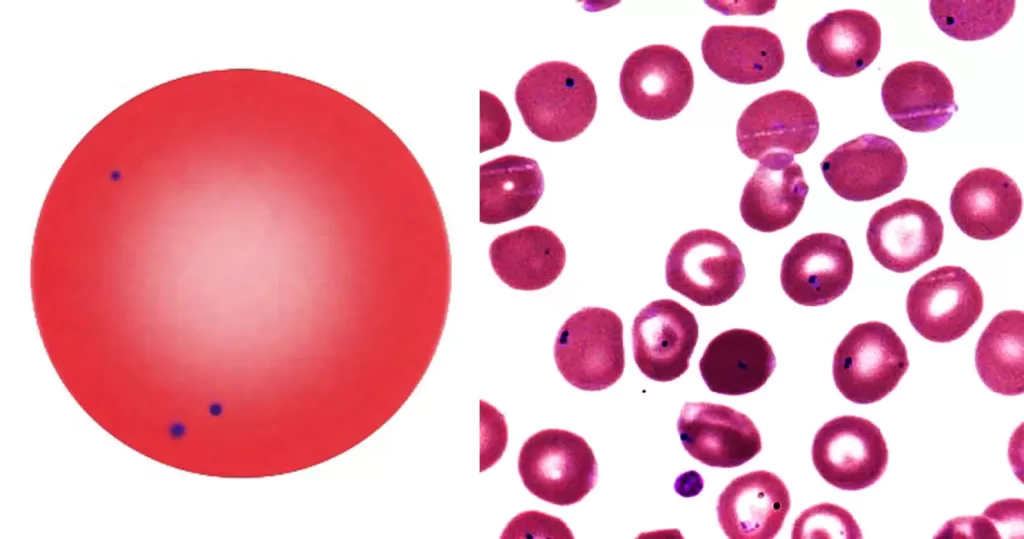
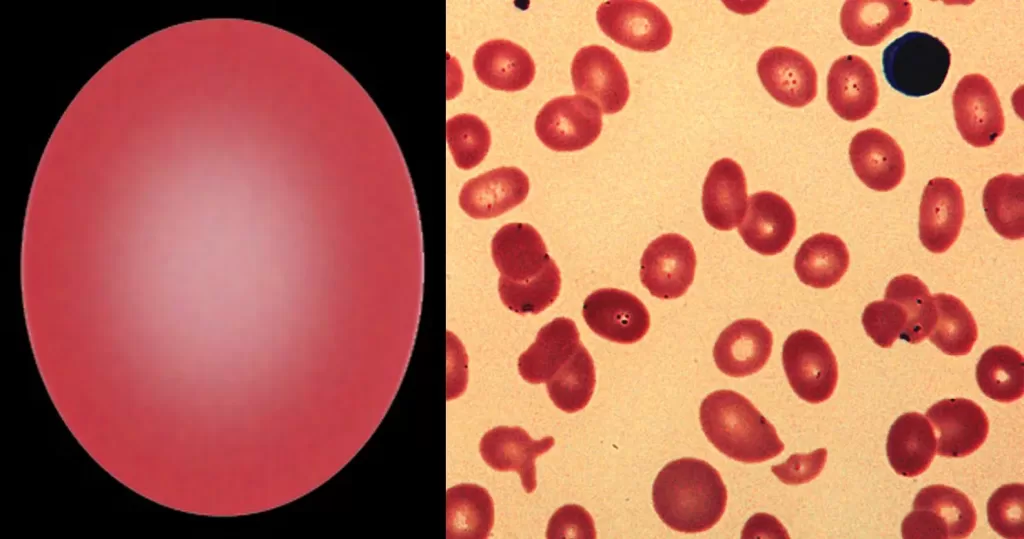
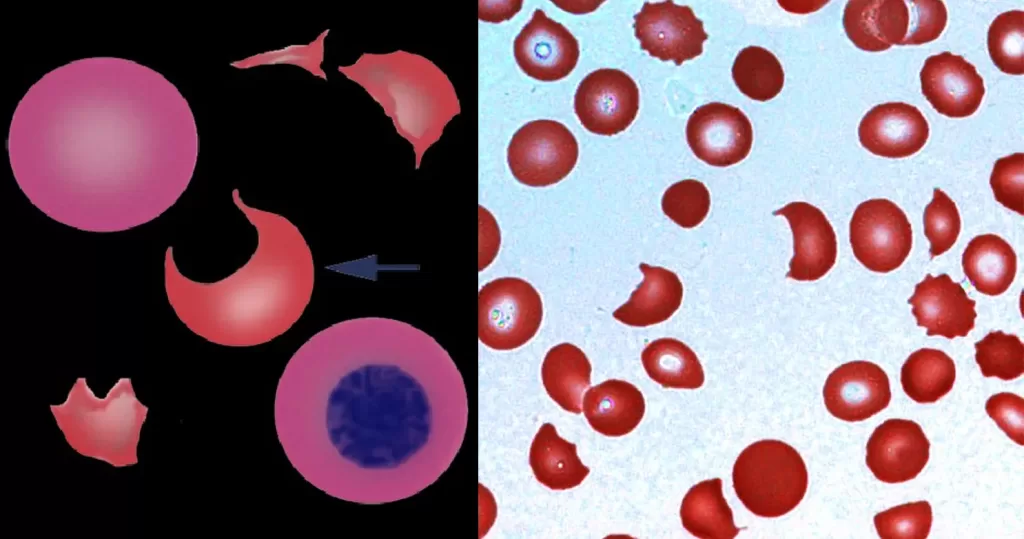
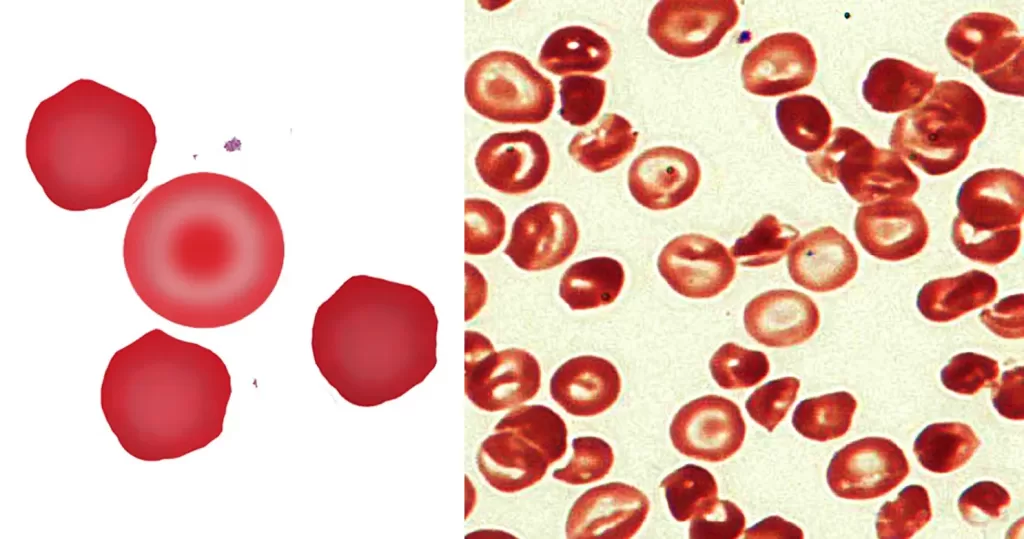
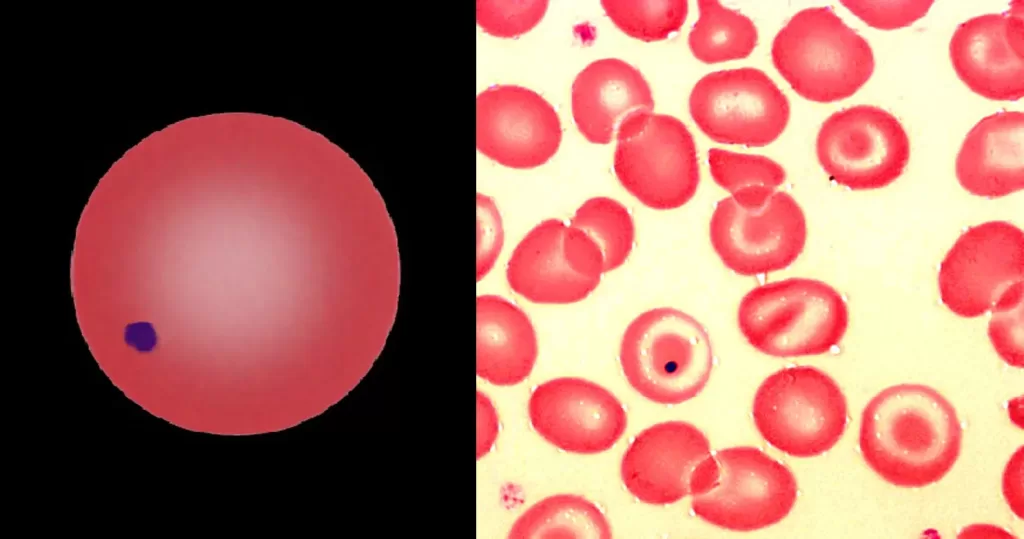
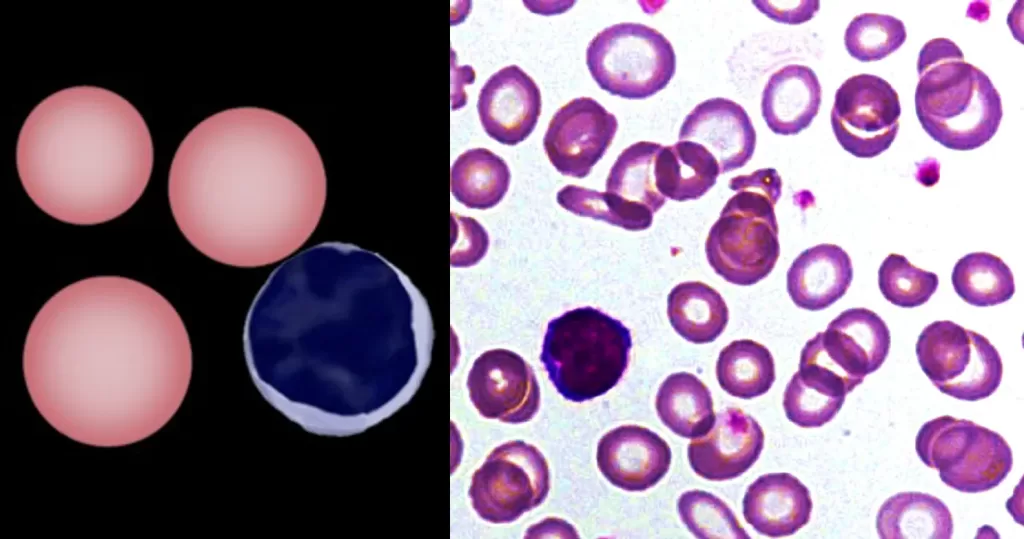
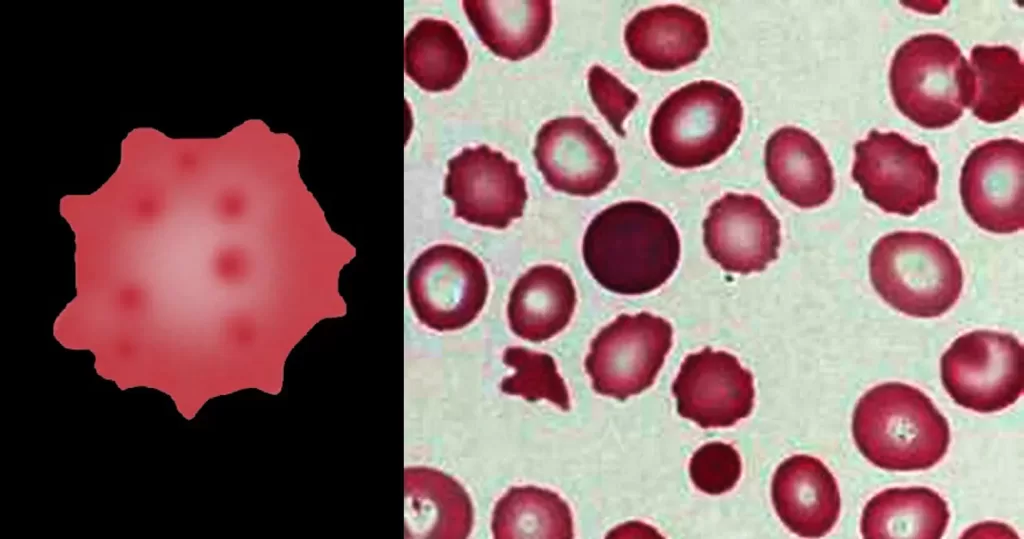
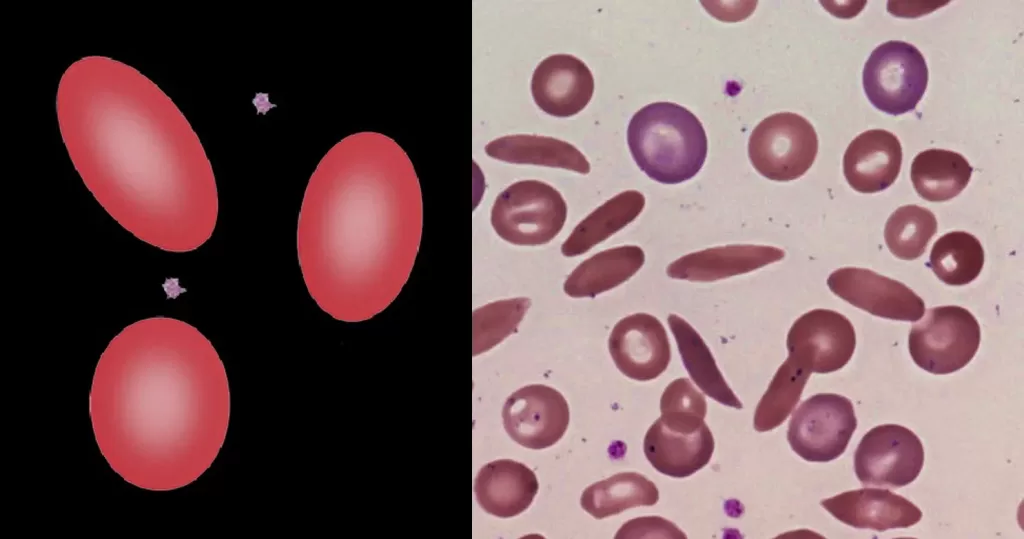
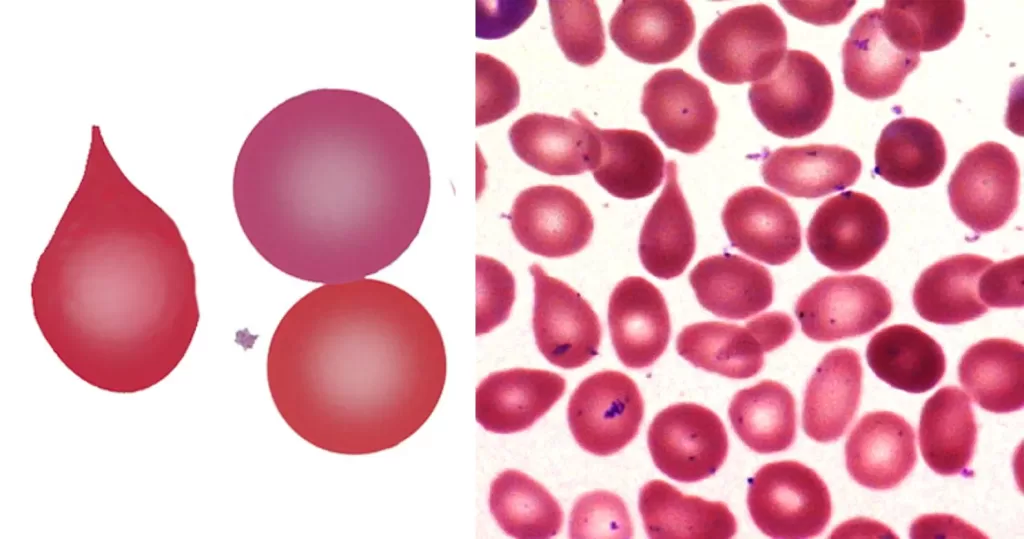
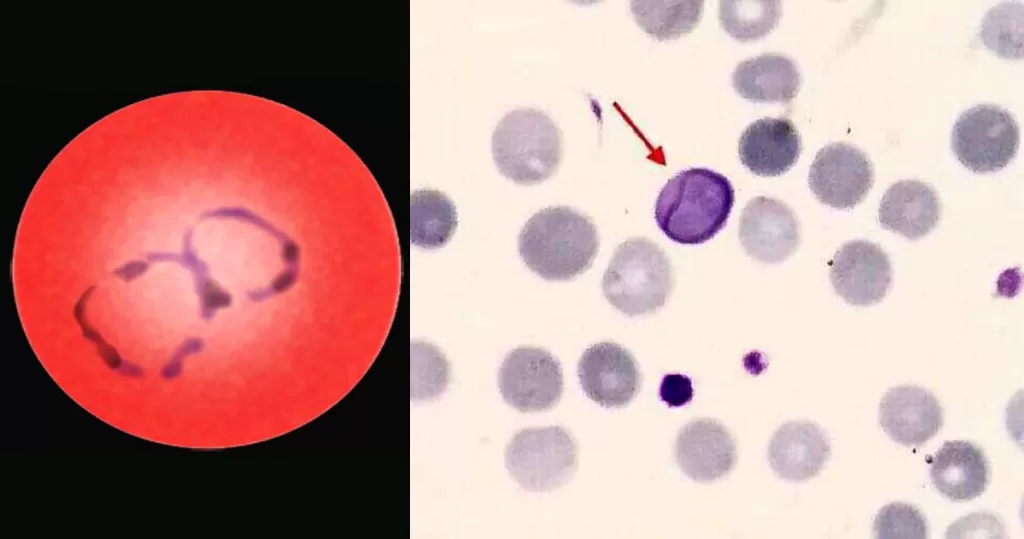
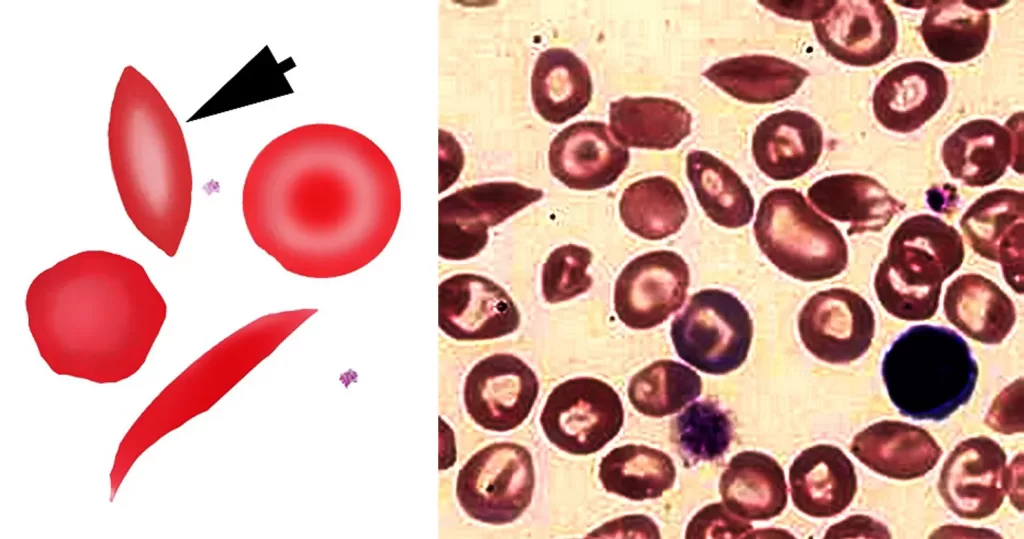
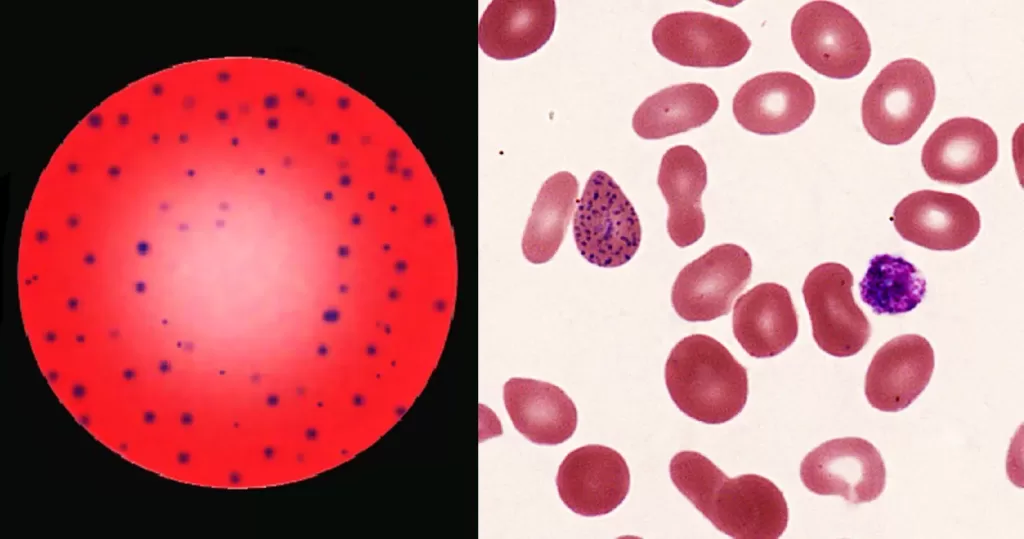
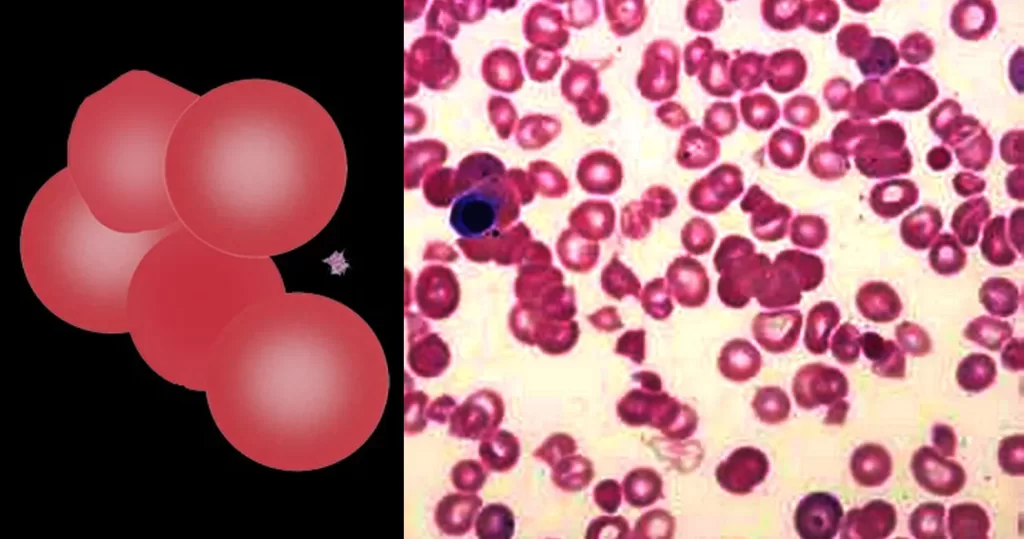
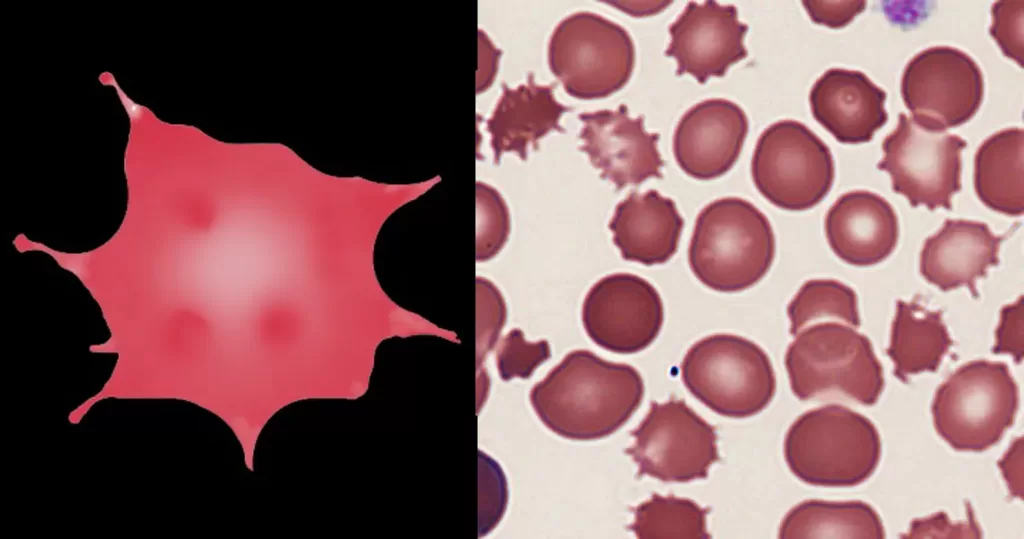
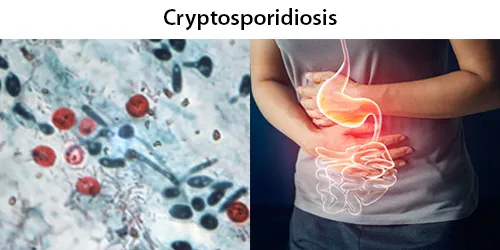
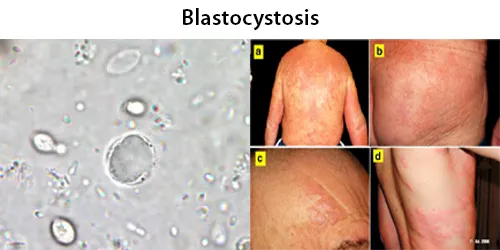
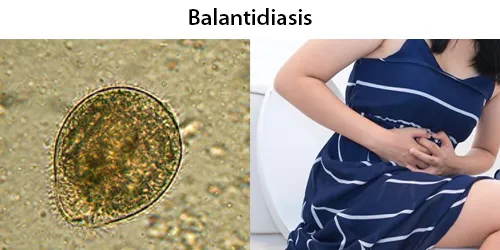
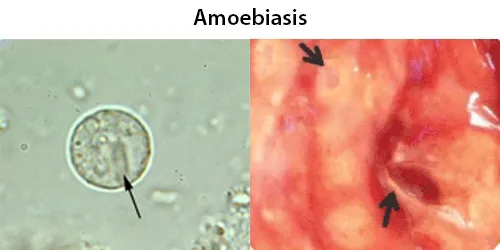
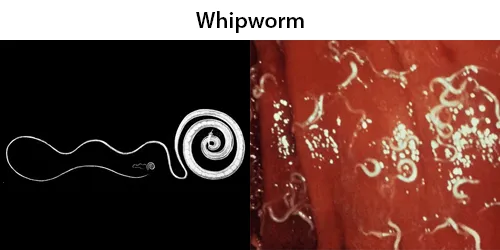
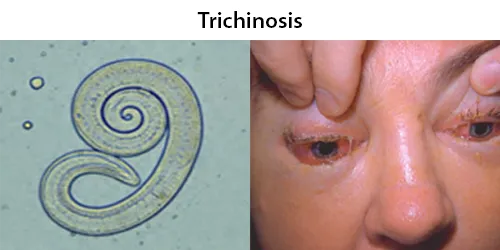
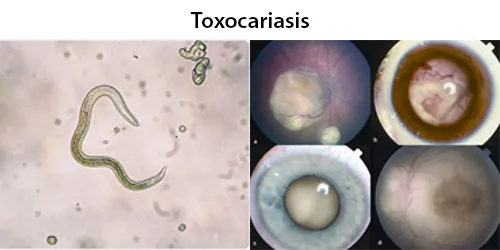
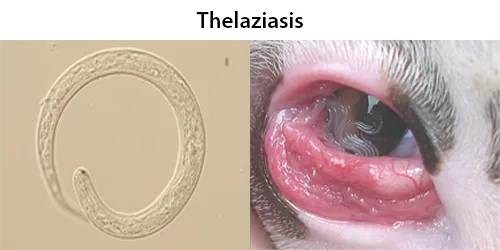
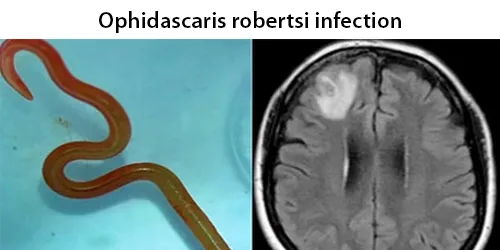
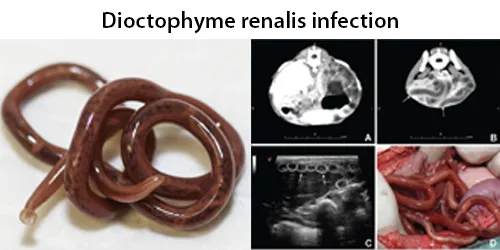
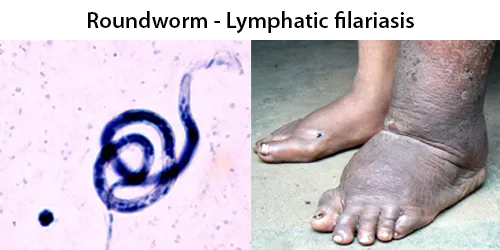
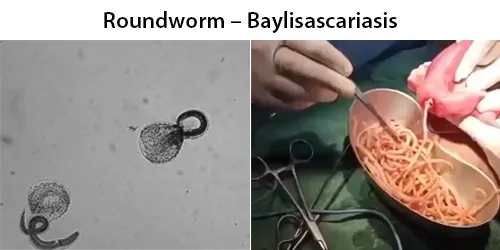
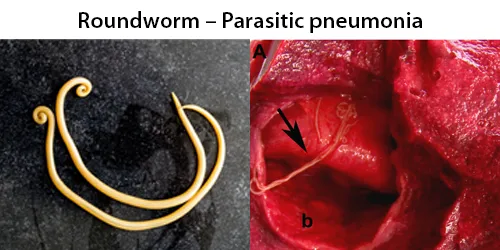
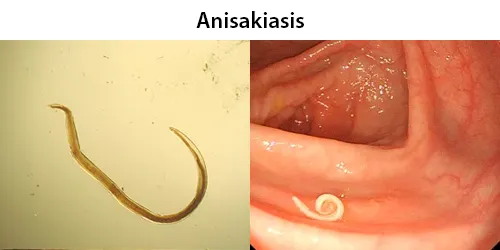
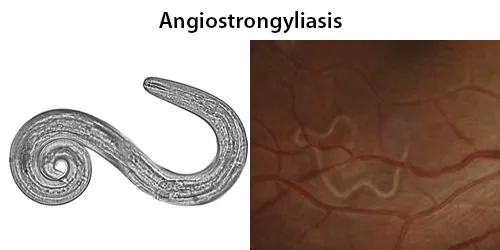
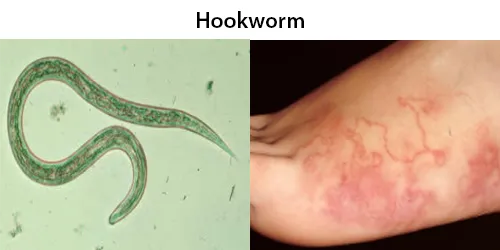
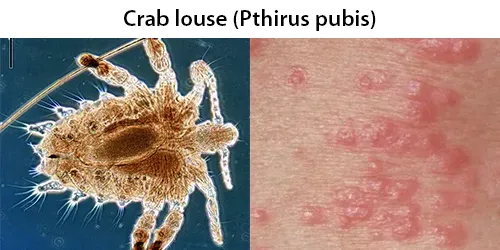
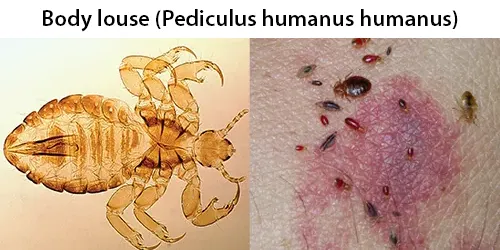
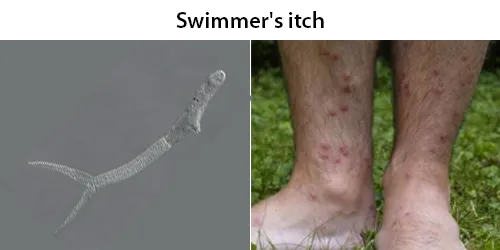
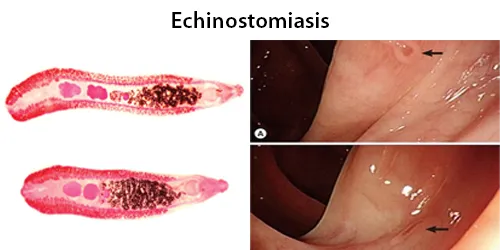
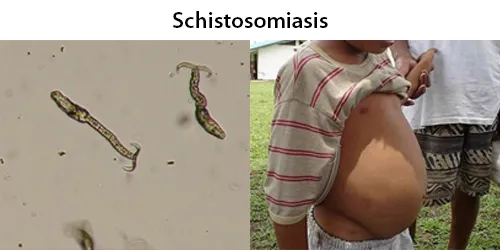
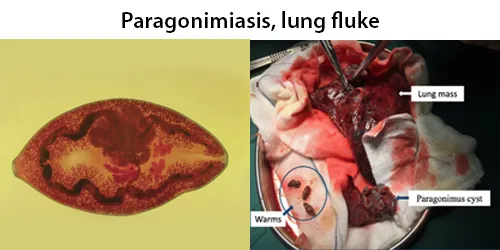
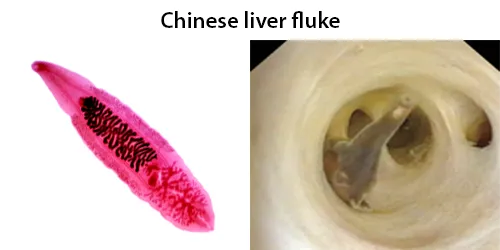
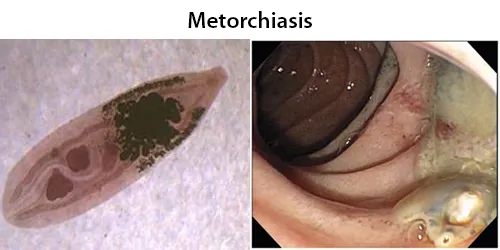
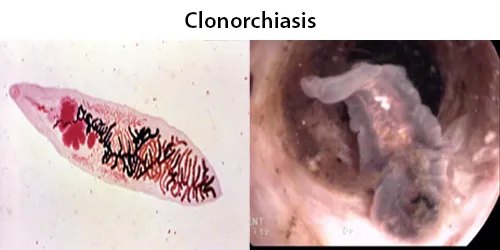
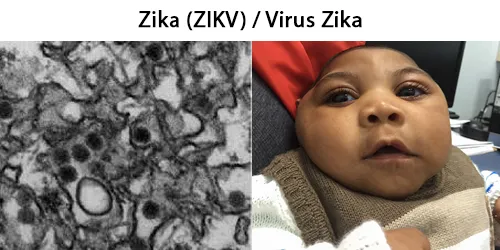
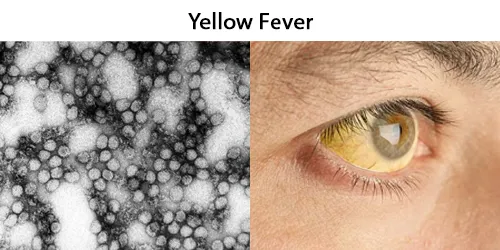
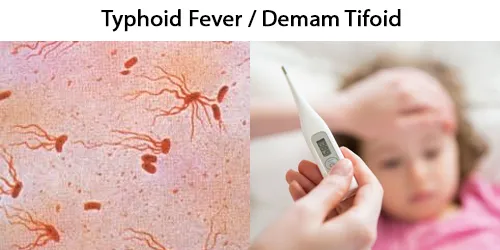
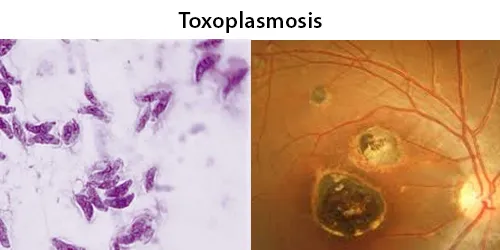
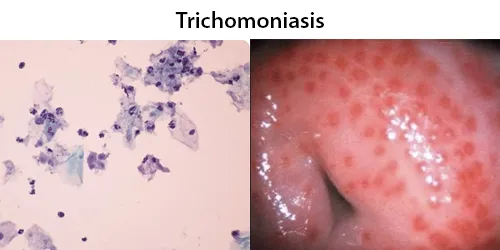
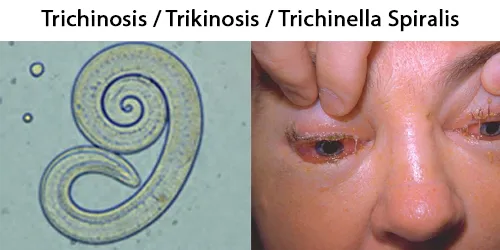
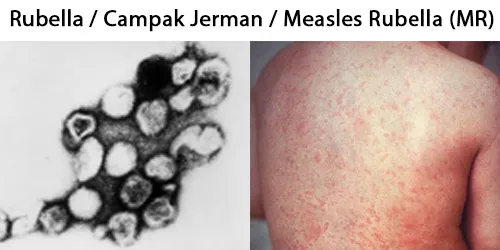
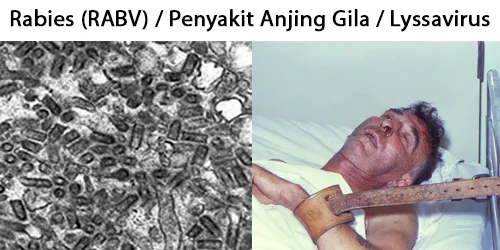
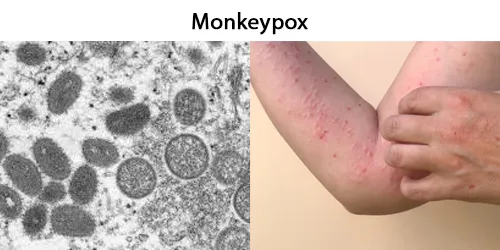
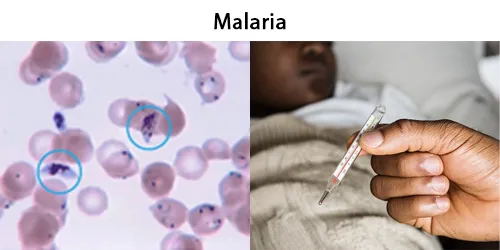
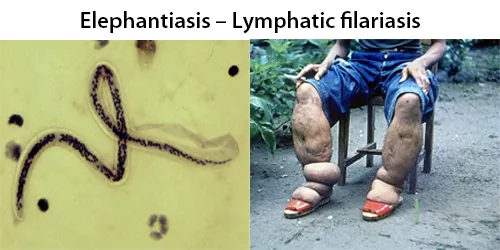
Macrocytes
Morphological evidence of any accompanying disease should actively be sought. Most frequently these causes are B12 or folate deficiency, myelodysplasia, or liver disease.
https://haematologyetc.co.uk/index.php?title=Macrocytic_Red_Cells
Impaired cell division (nutritional or metabolic)
- Vitamin B12 deficiency (most commonly due to impaired absorption)
- Folic acid deficiency (most commonly dietary deficiency)
Impaired cell division (drug)
- Cytotoxic e.g. hydroxycarbamide
- Immunosuppressive e.g. azathioprine
Defective cell formation
- Most frequently myelodysplasia (also seen in congenital dyserythropoiesis, aplastic anaemia or post stem-cell transplant)
Other causes
- Alcohol and liver disease: excess cell membrane lipid
- Hypothyroidism. Likely caused by reduced cell division
- Drugs and medication, causing macrocytosis through various mechanisms