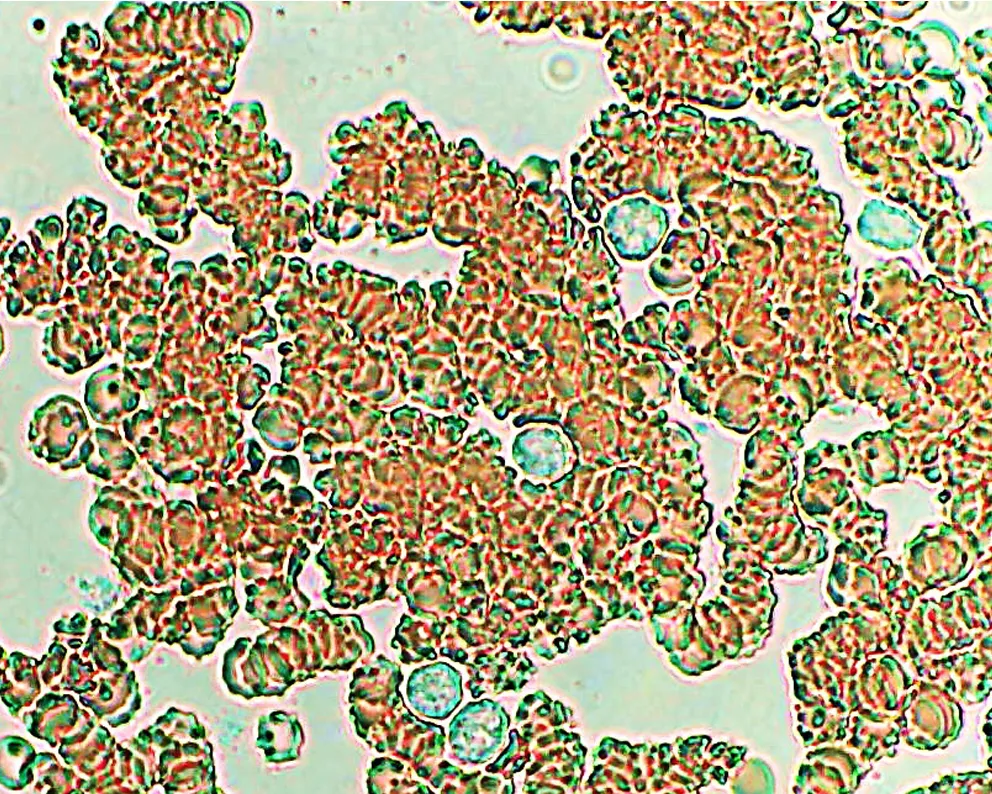
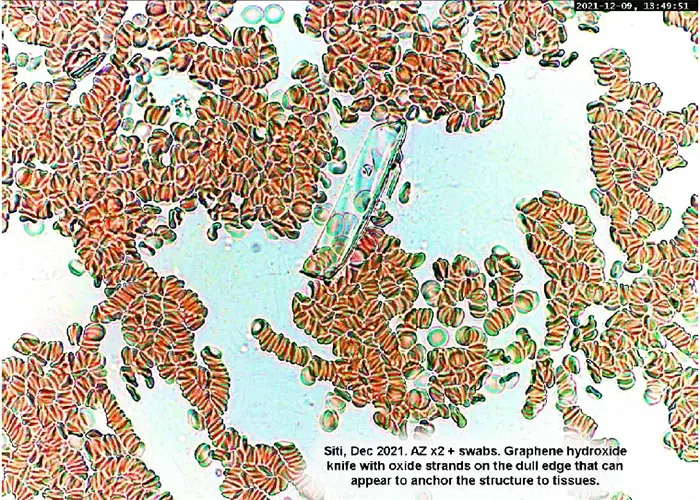
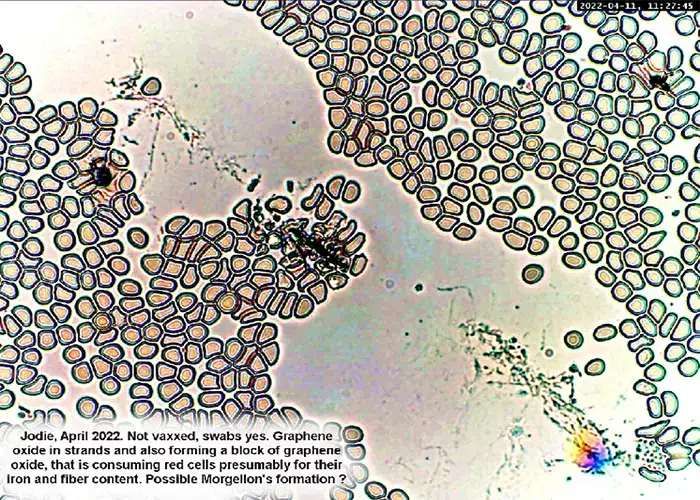
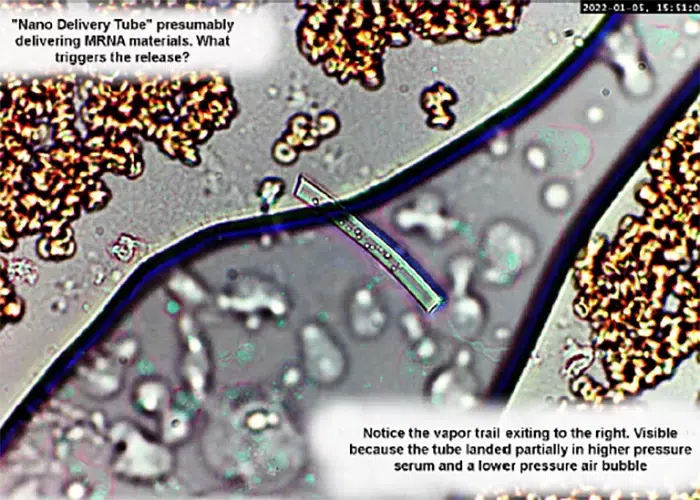
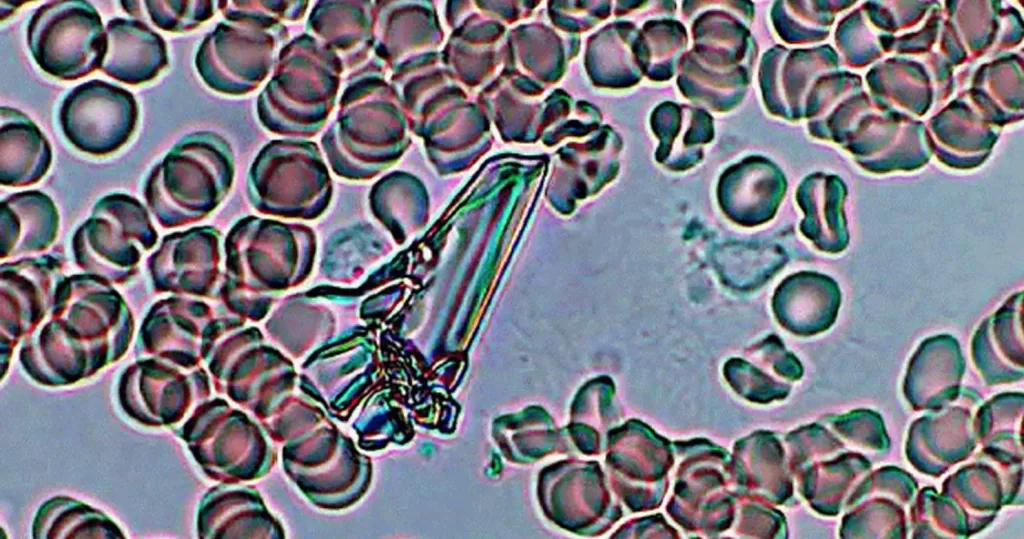
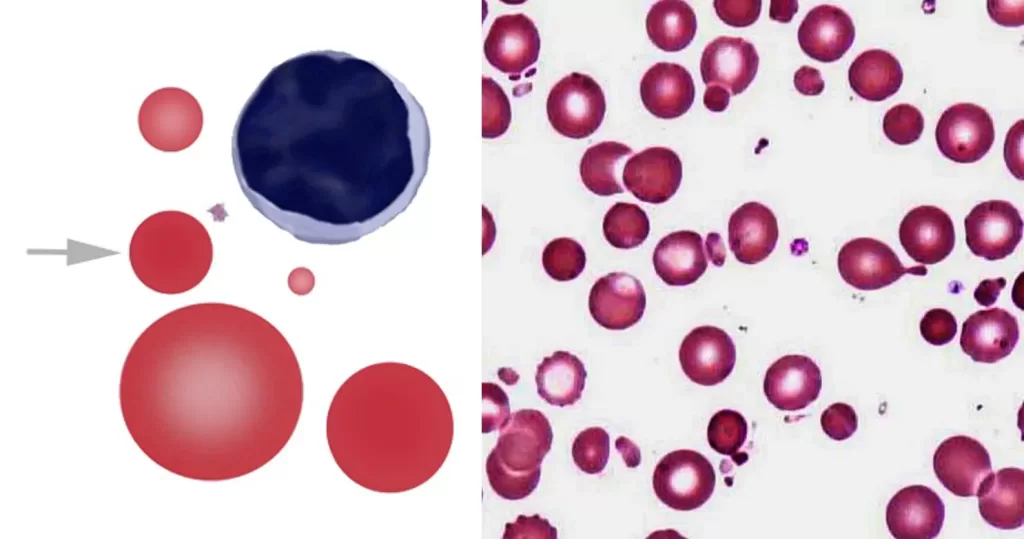
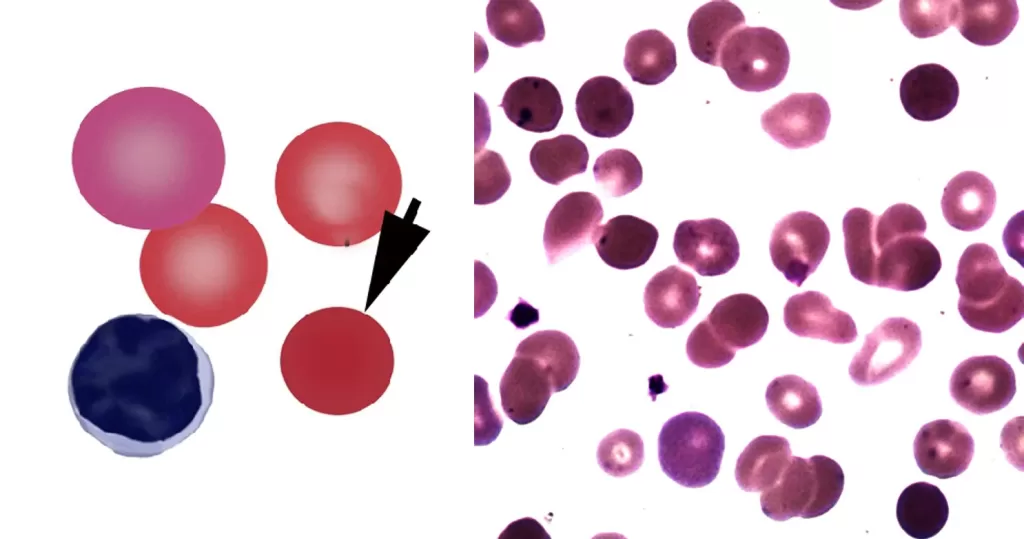
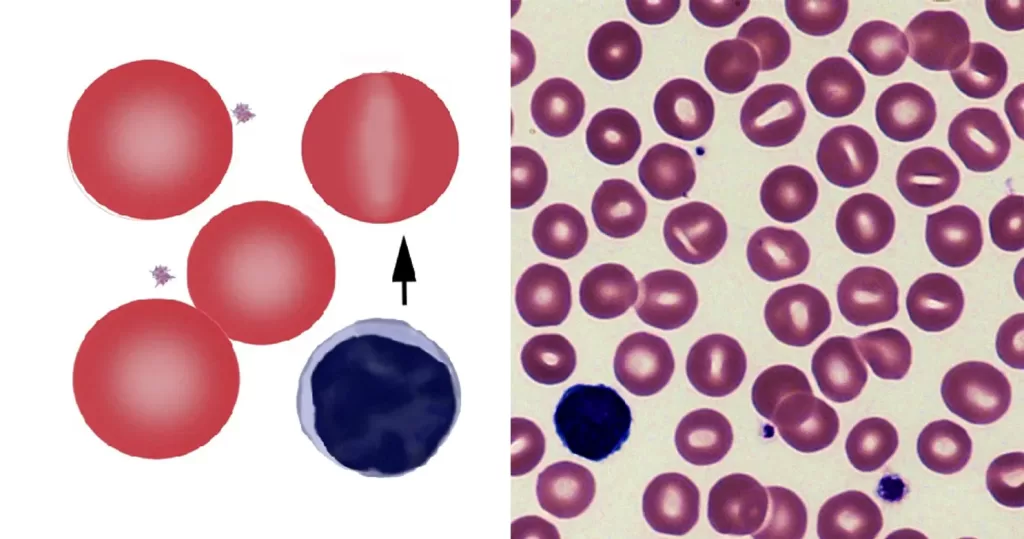
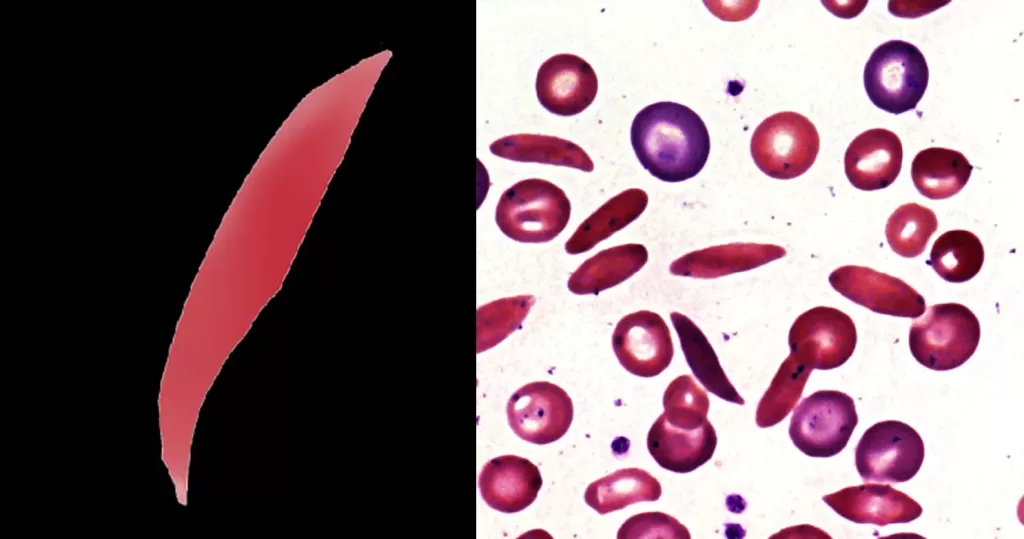
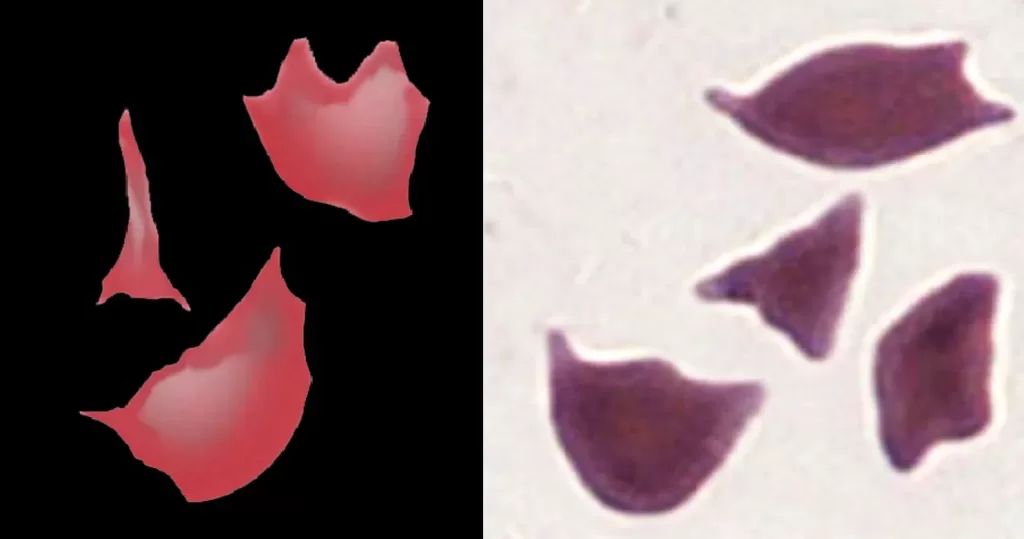
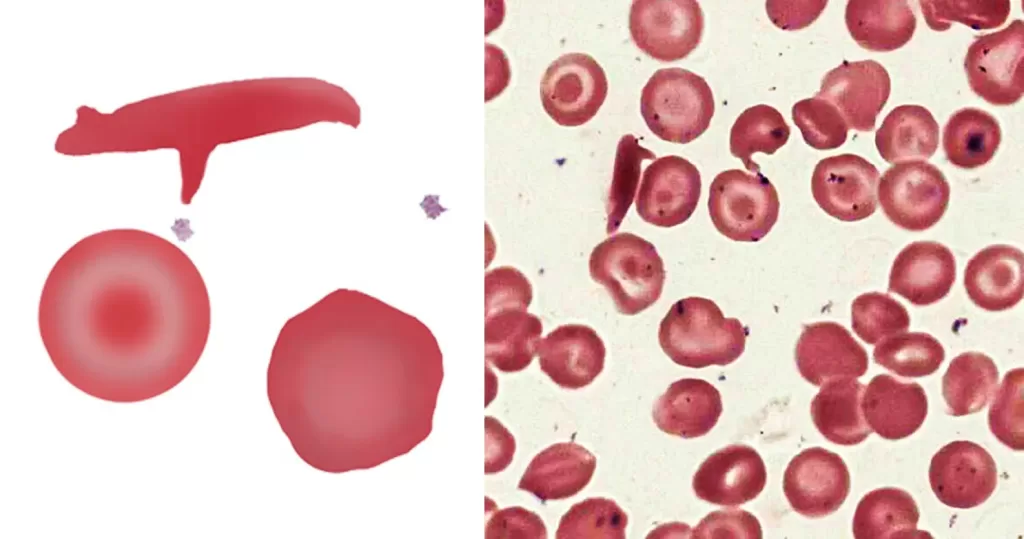
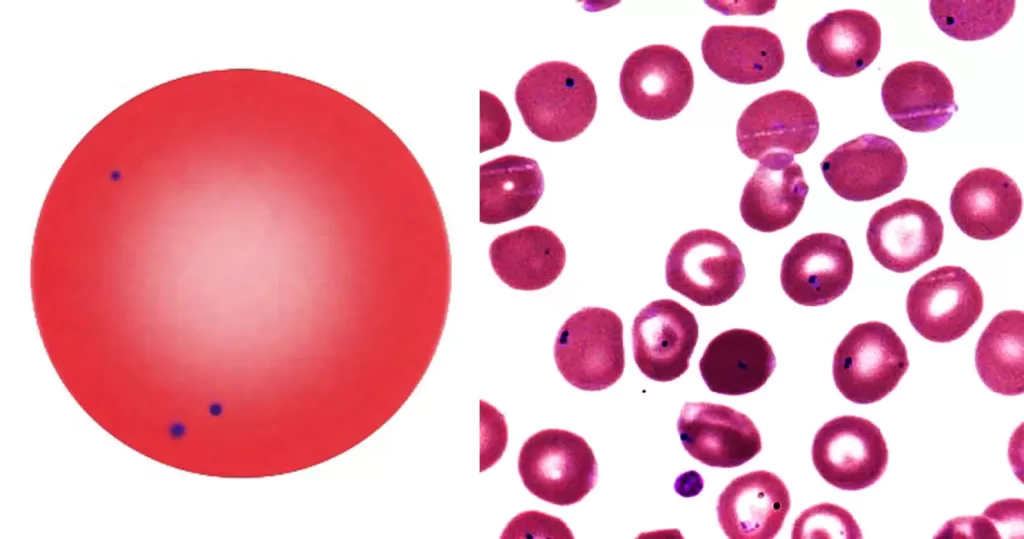
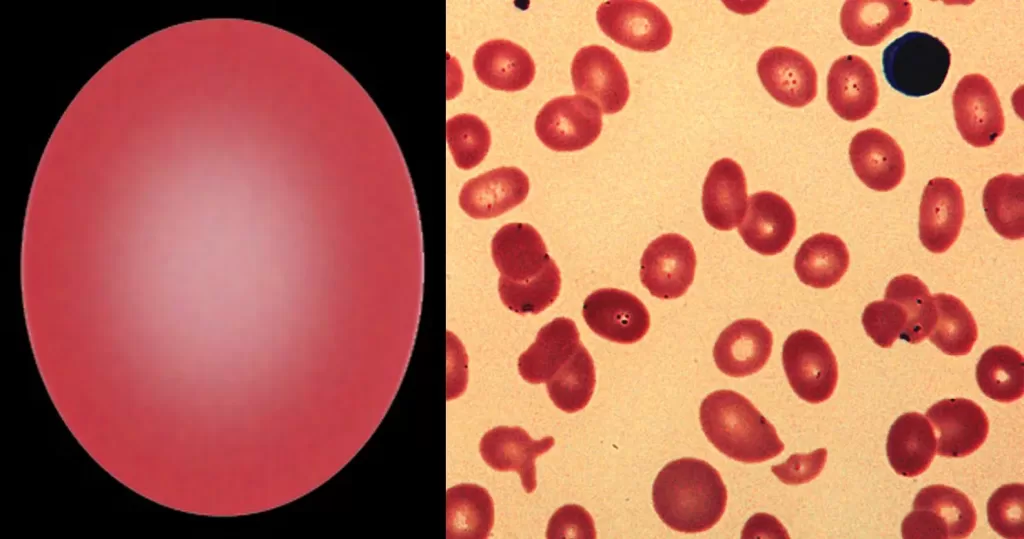
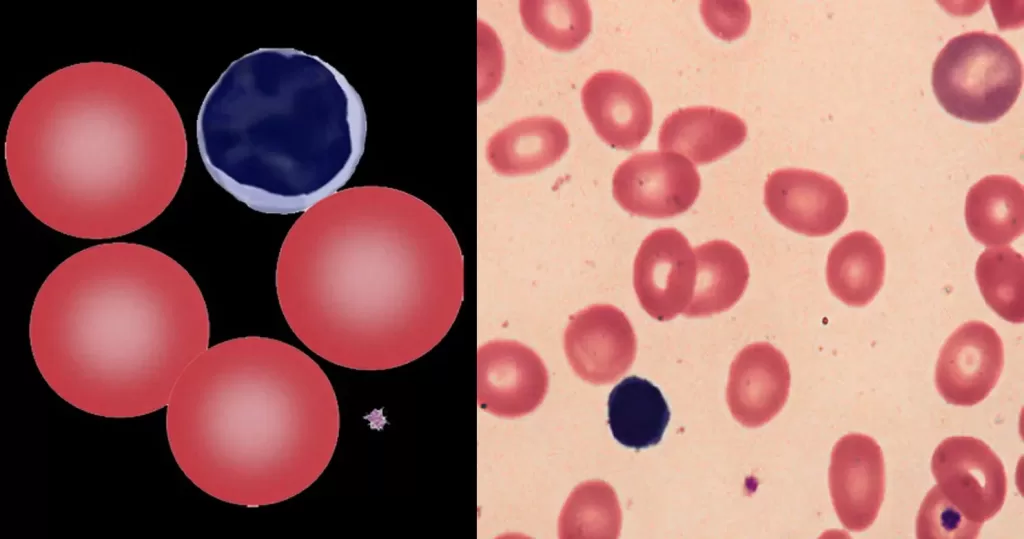
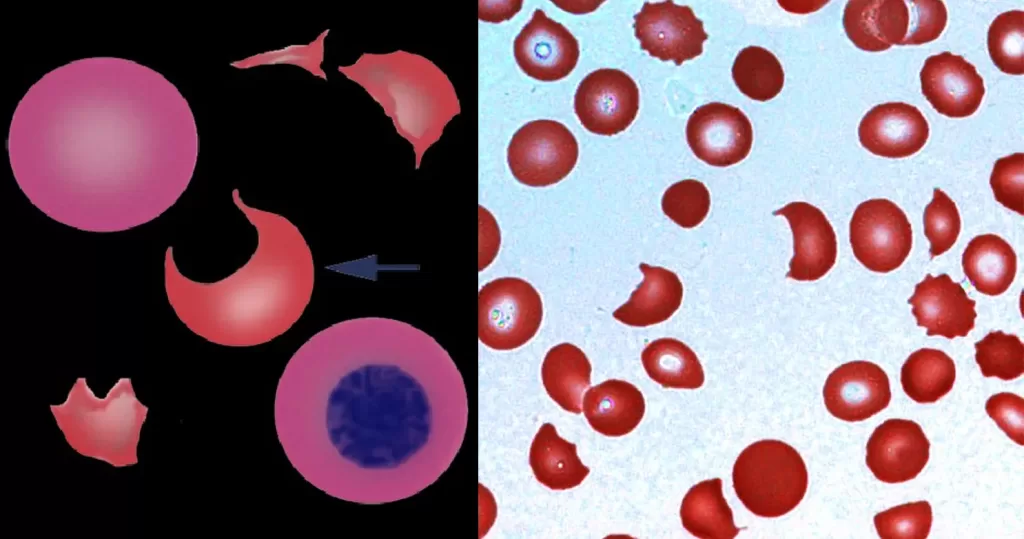
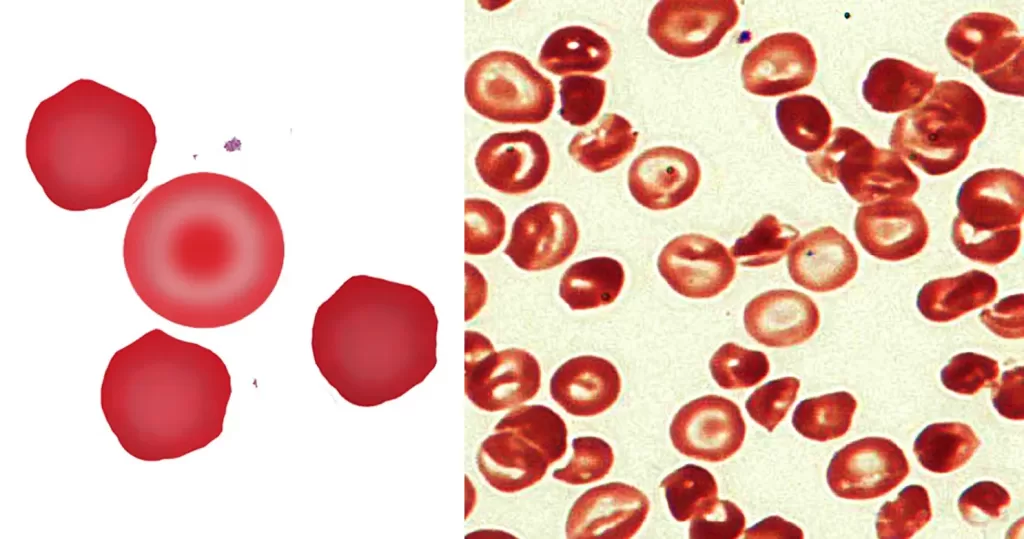
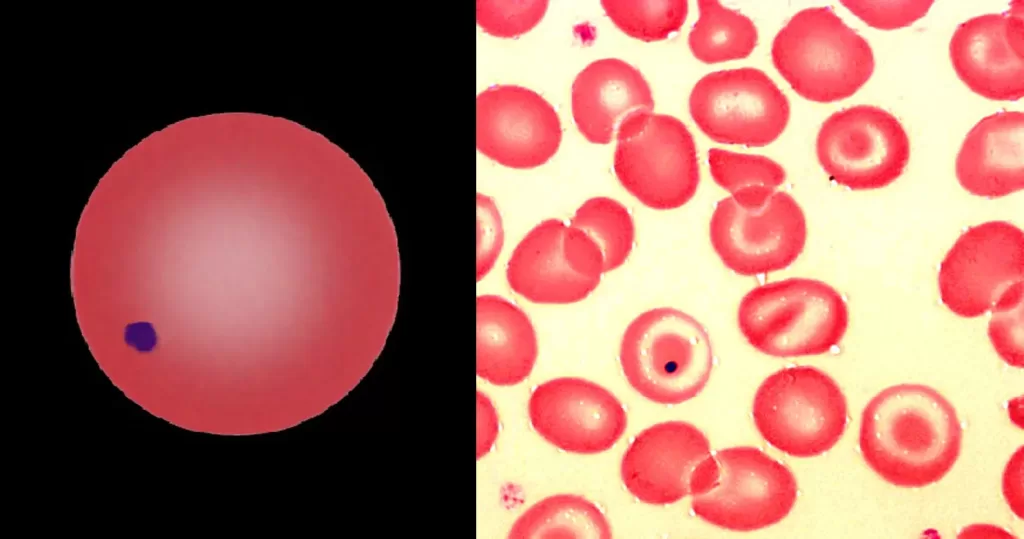
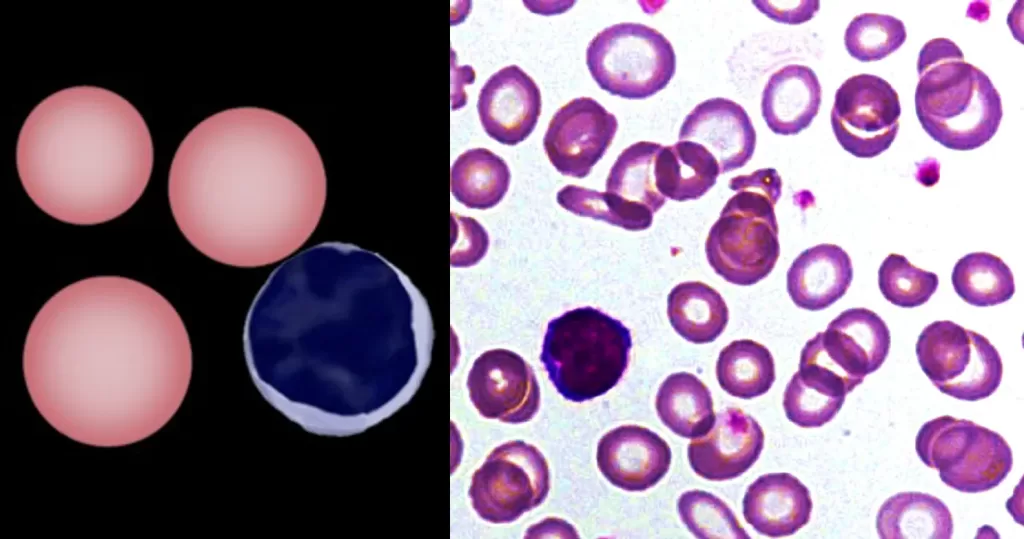
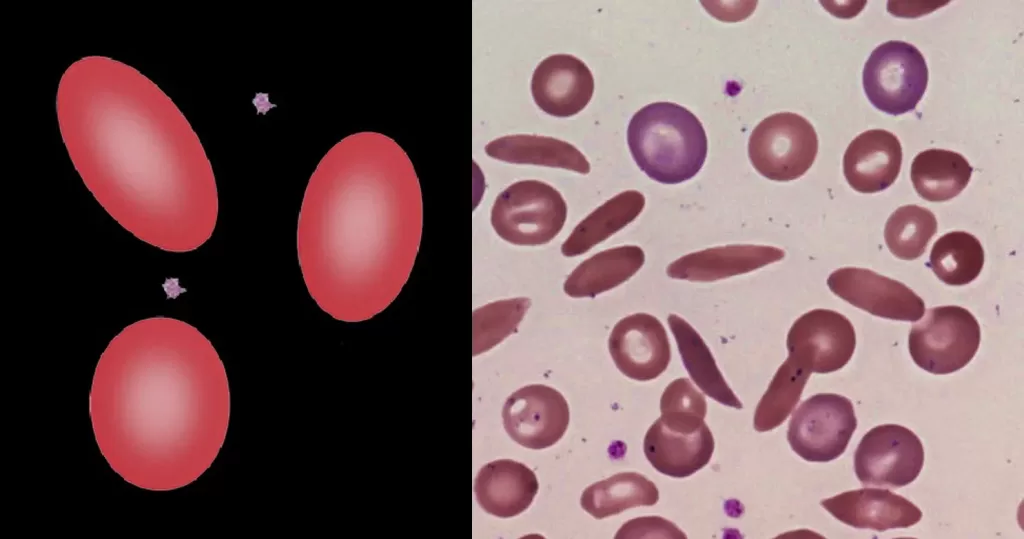
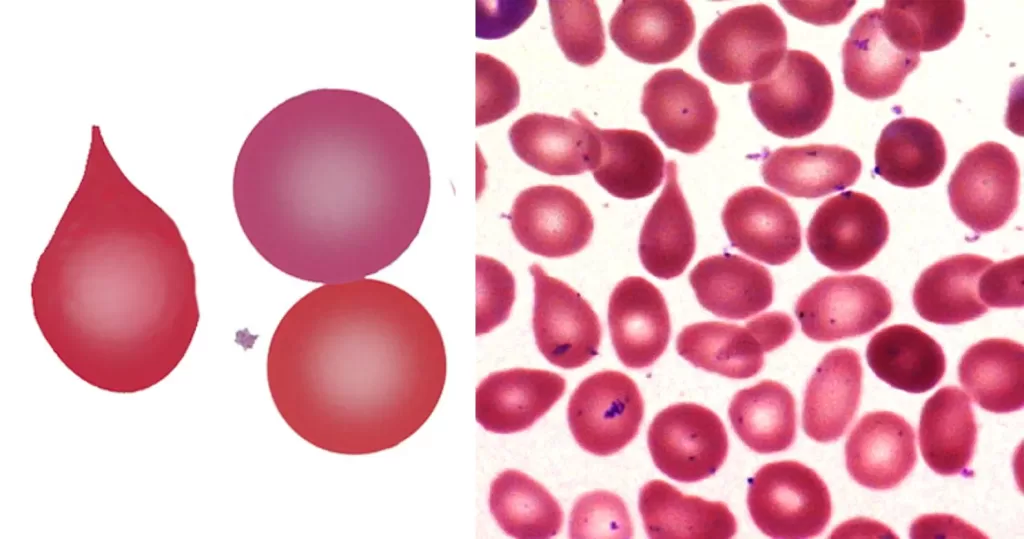
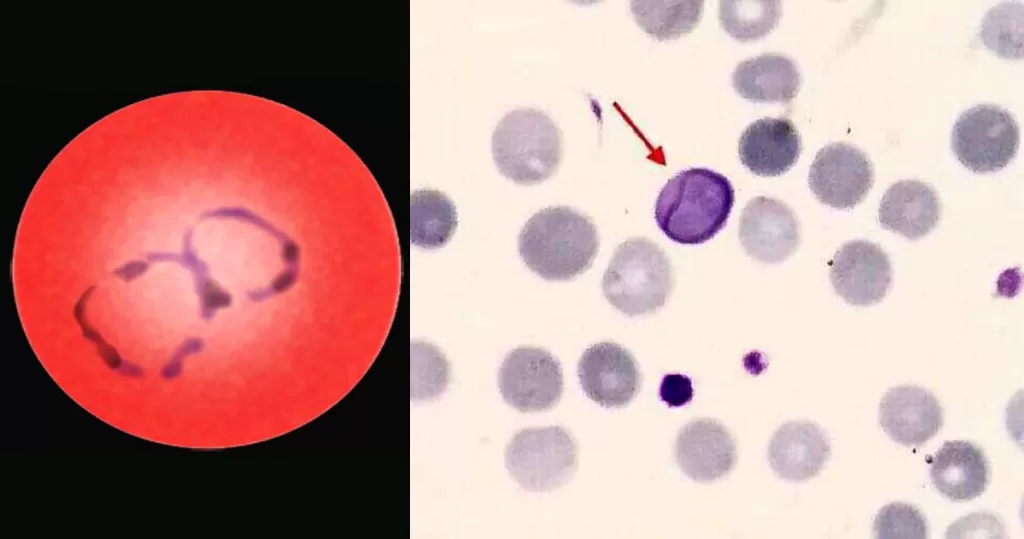
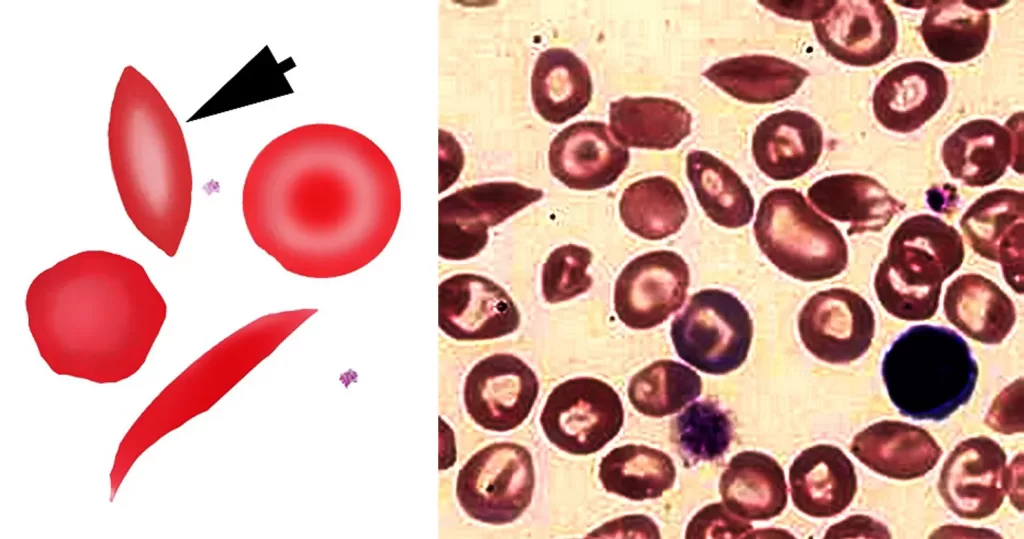
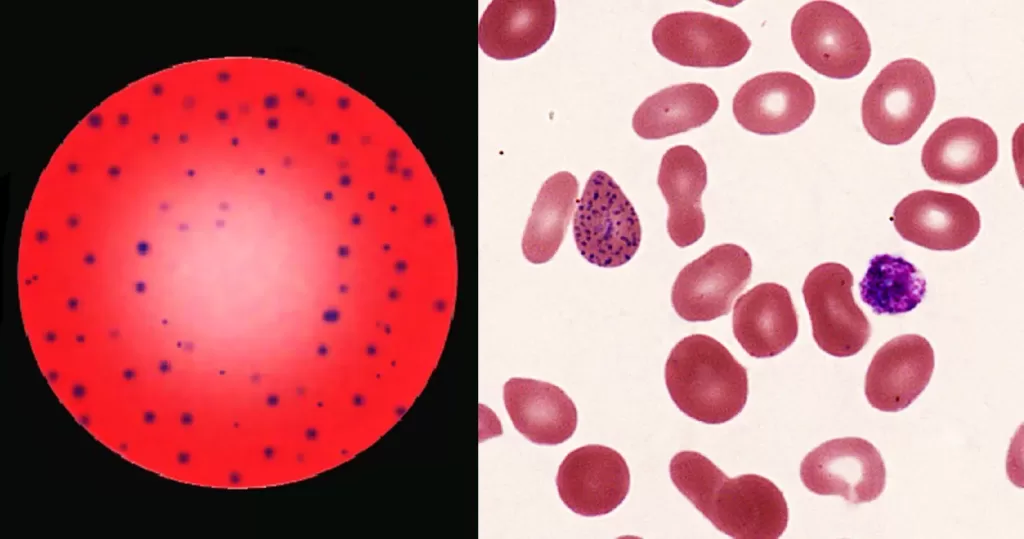
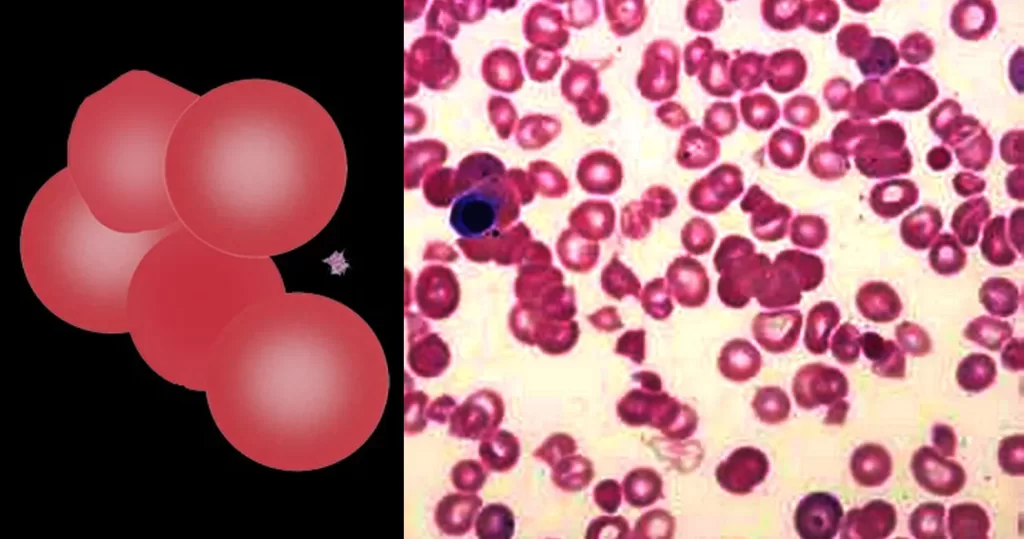
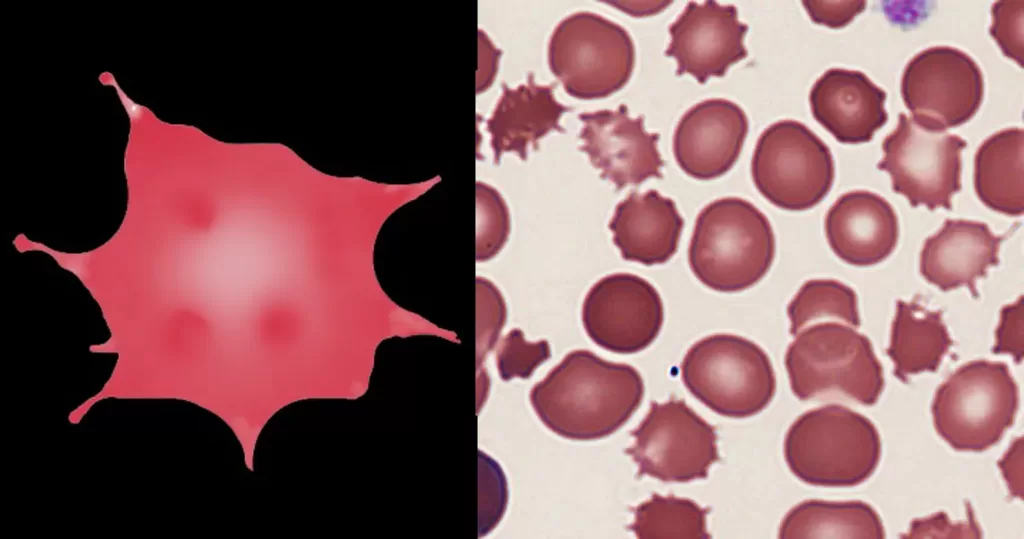
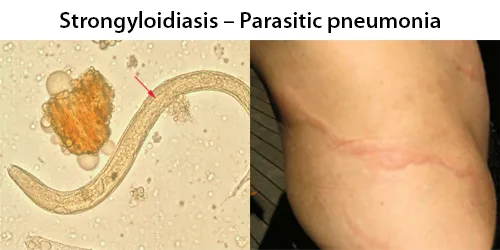
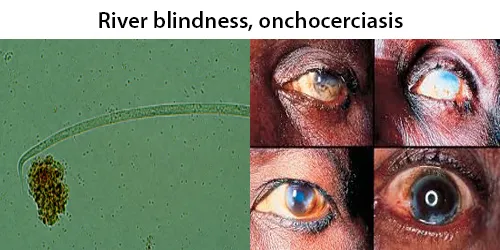
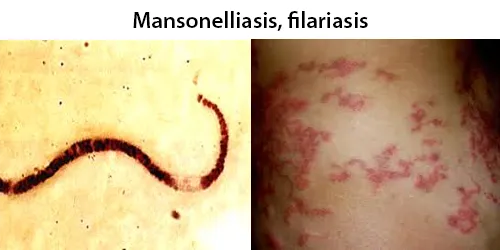
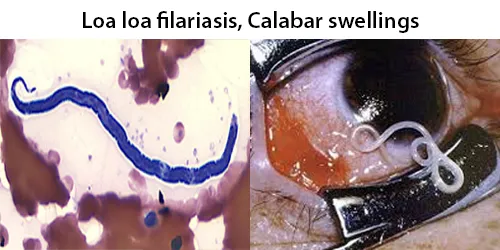
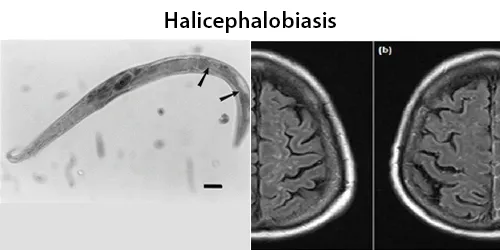
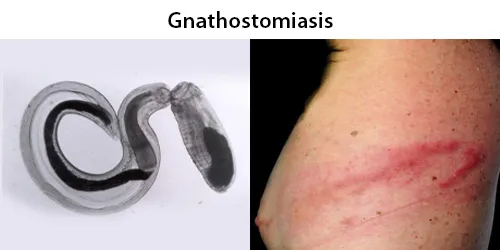
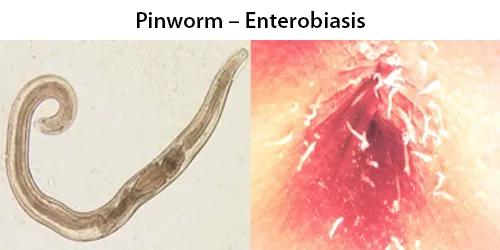
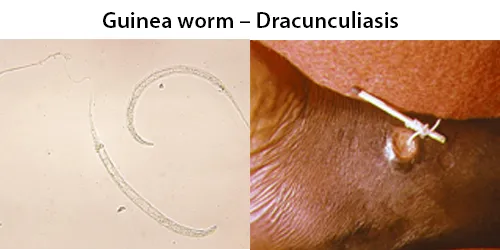
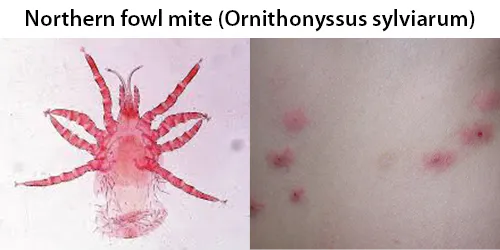
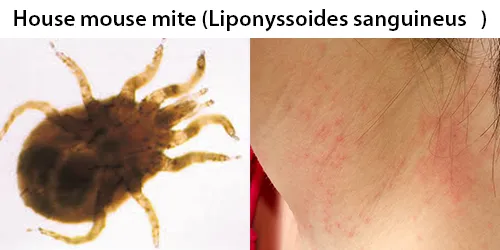
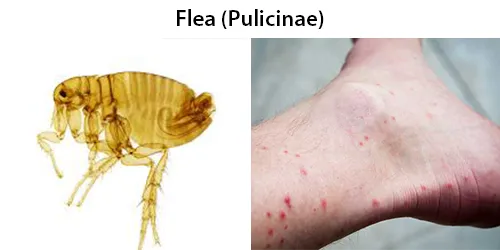
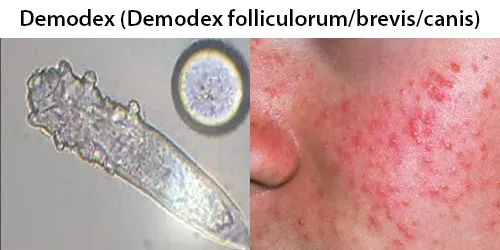
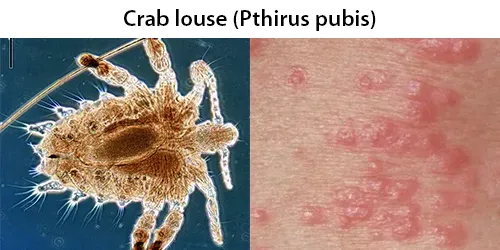
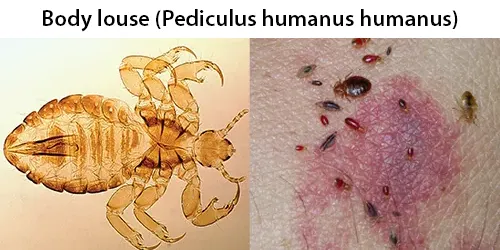
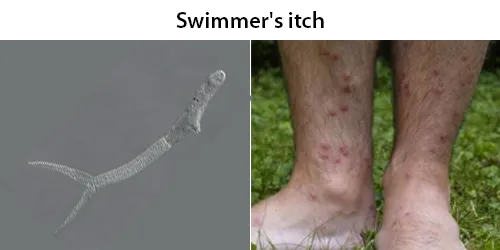
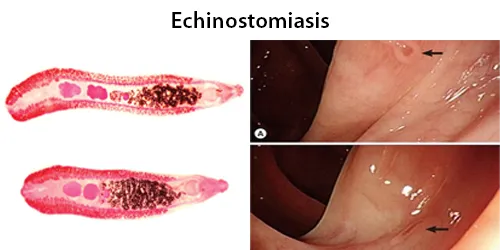
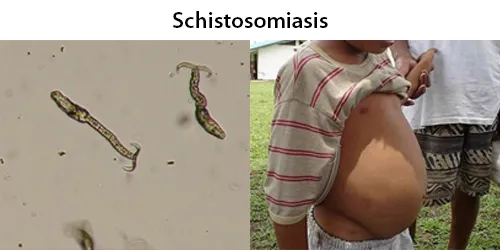
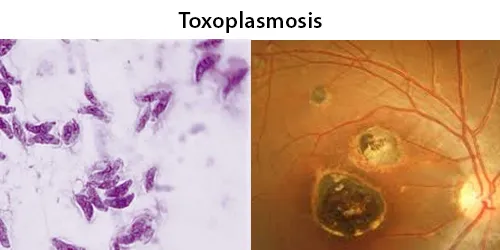
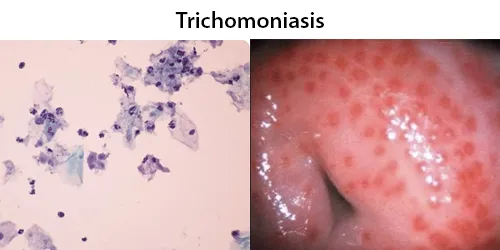
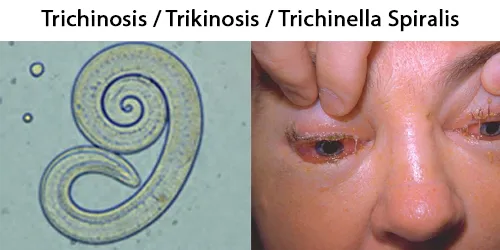
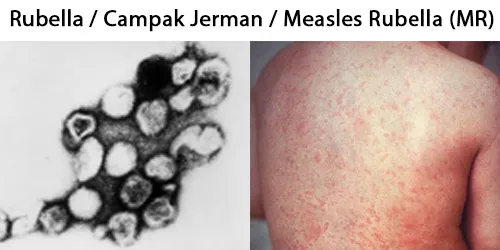
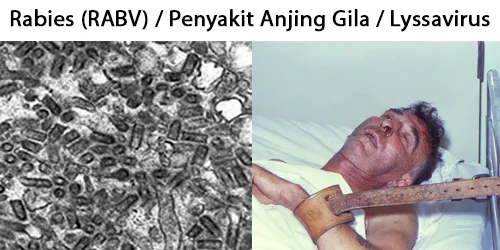
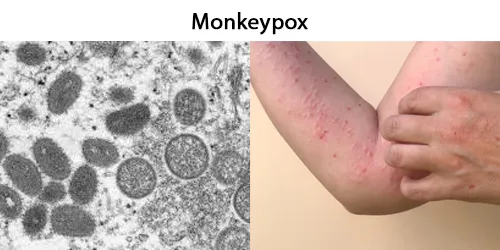
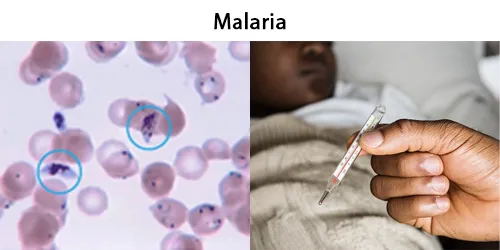
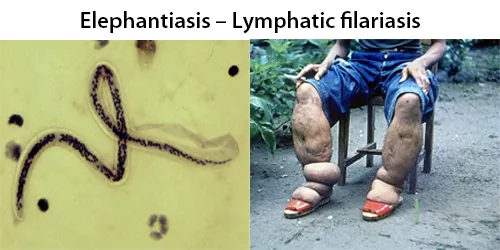
Echinocyte / Burr Cells
Always remember that echinocytes may be an artefact of blood storage or of cells on the edge of a live mount slide (artefactual echinocytosis), so look at the condition of other cells on the film and determine whether the echinocytosis is patchy in distribution. Where genuine there will usually be a significant systemic disease present. This most frequently will be renal failure.
https://haematologyetc.co.uk/index.php?title=Echinocytes
Artefact
- Prolonged storage of sample before spreading
- Glass/Ph effect
- Slow drying
Energy depletion
- Pyruvate kinase deficiency (note that the cells also resemble acanthocytes – the abnormal forms being prominent only after splenectomy). See Clinical Image.
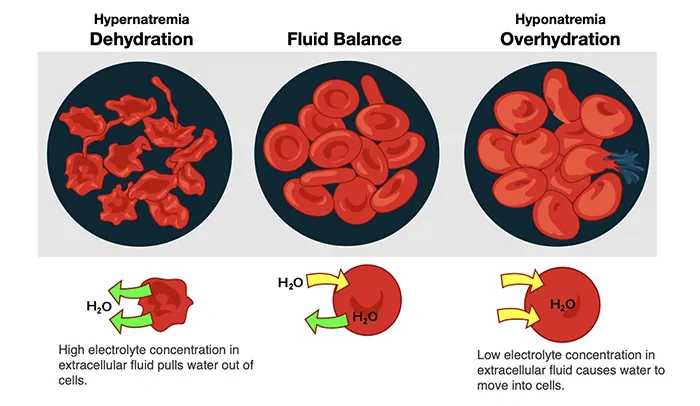
Altered hydration
- Renal failure
- Electrolyte imbalance
- Diuretic treatment
- Altered membrane composition
- Drugs (doxorubicin)
- Snake venom (CV-19 inoculations)
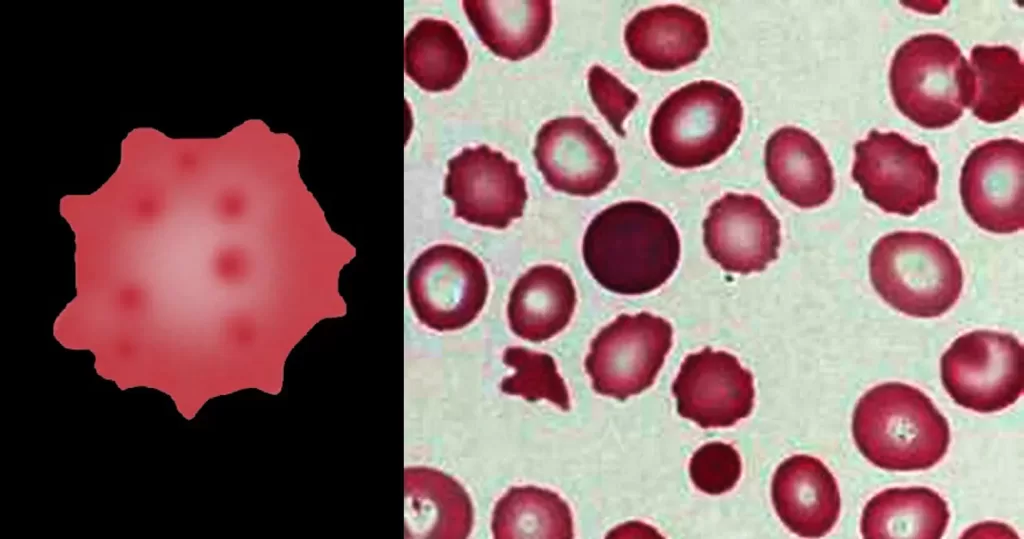
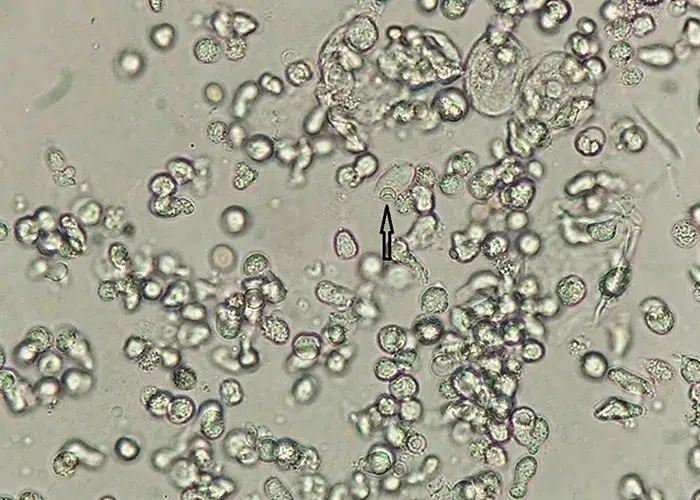
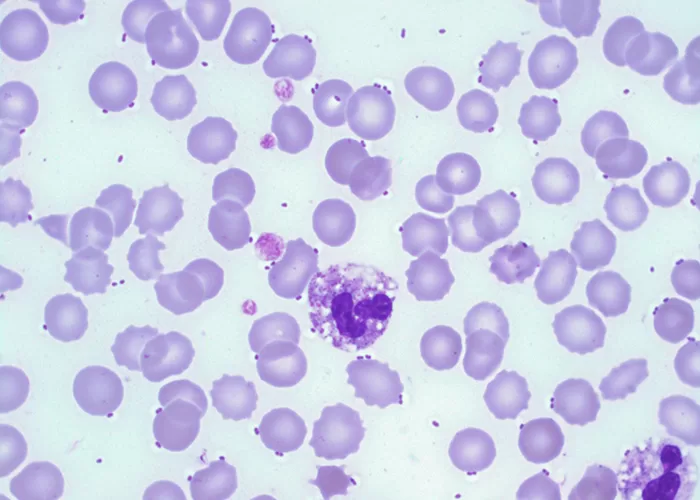
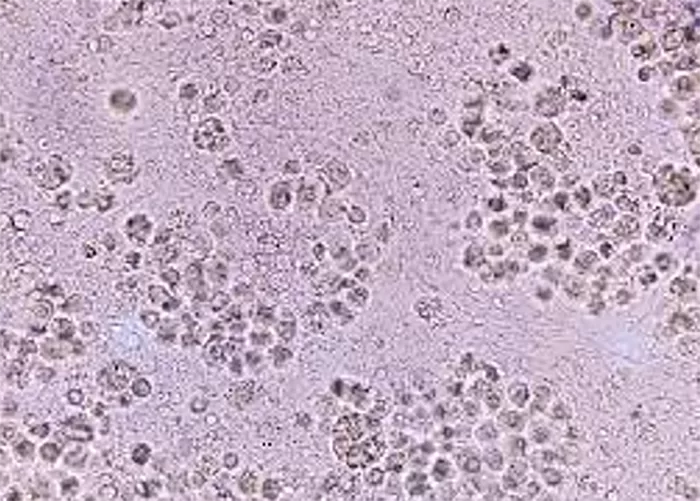
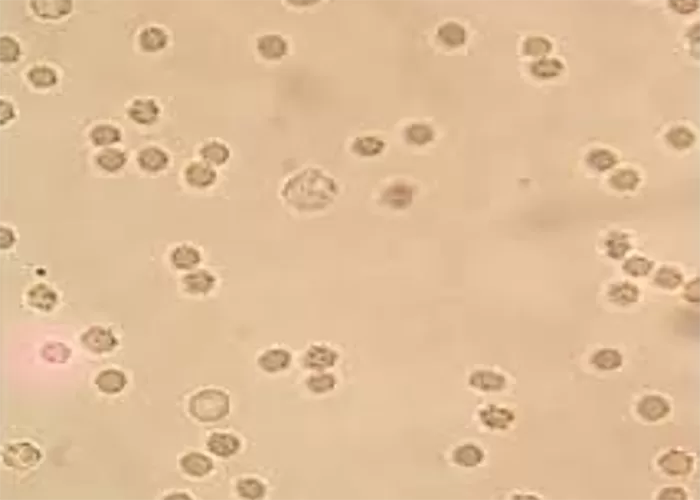
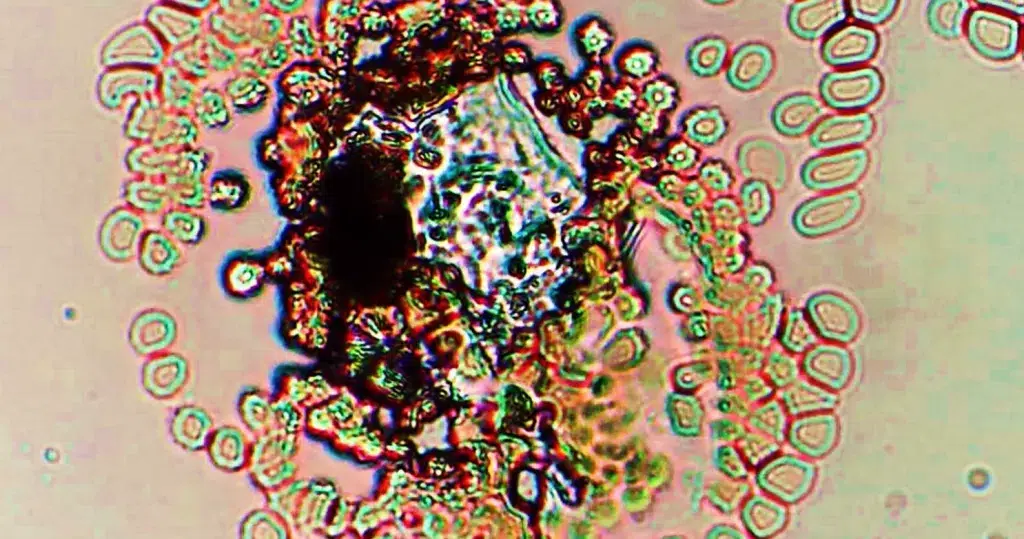
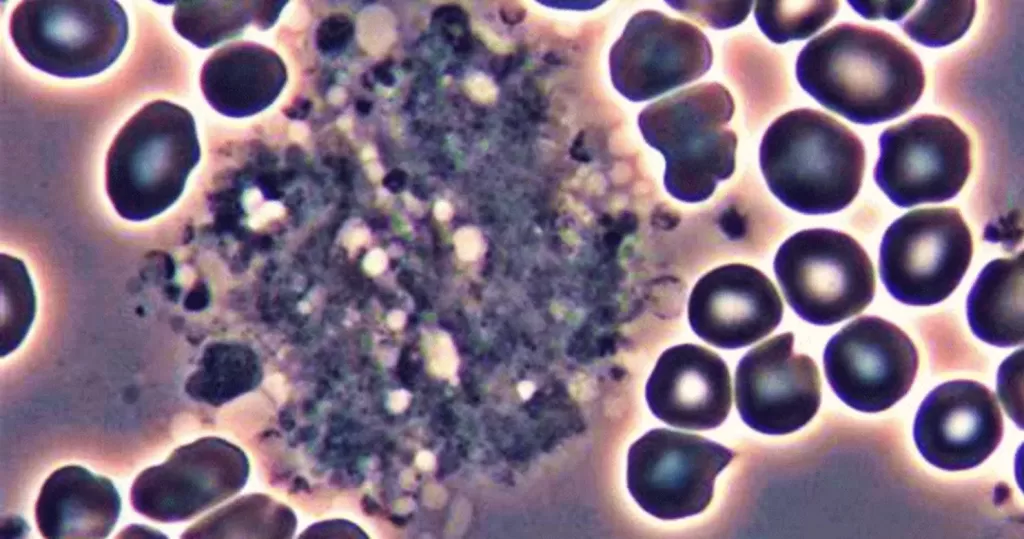
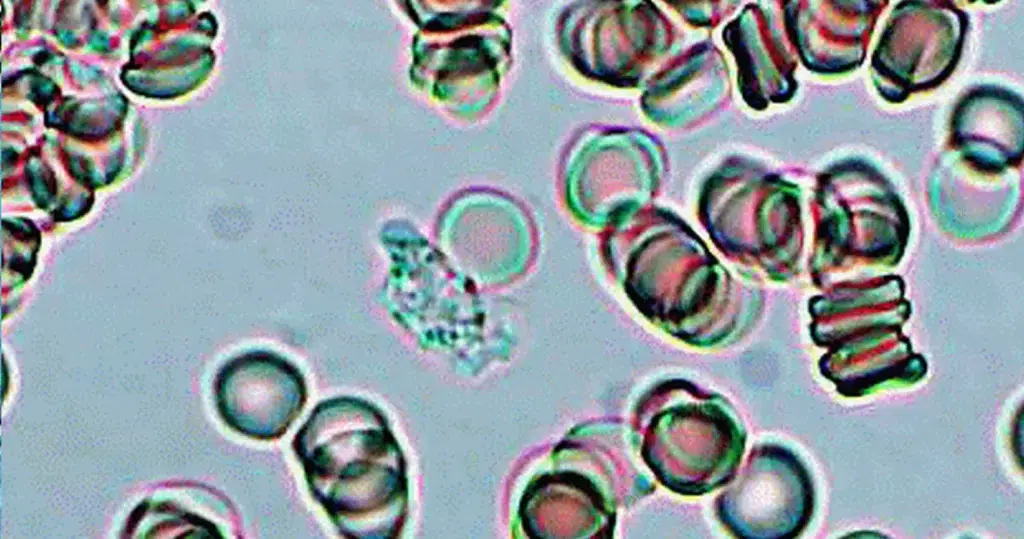
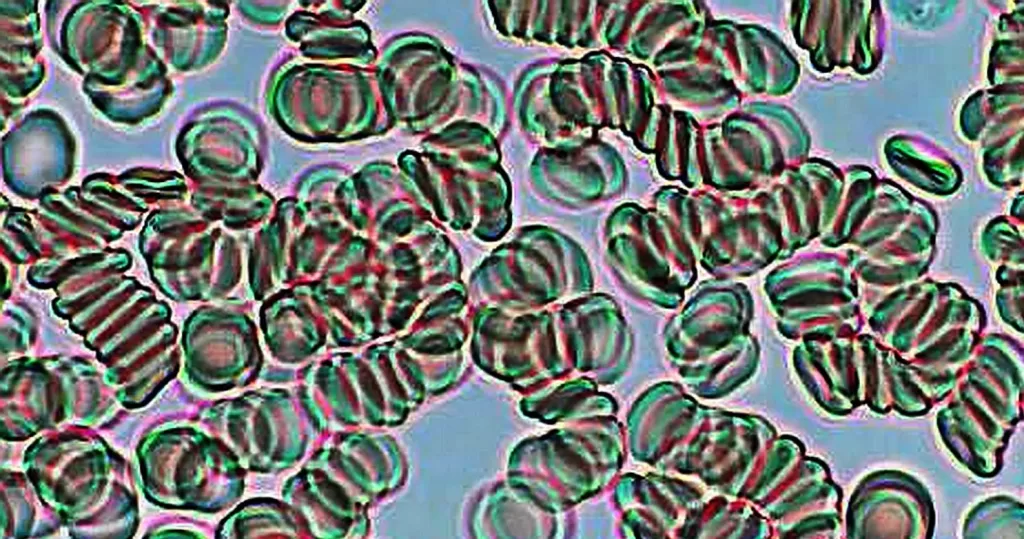
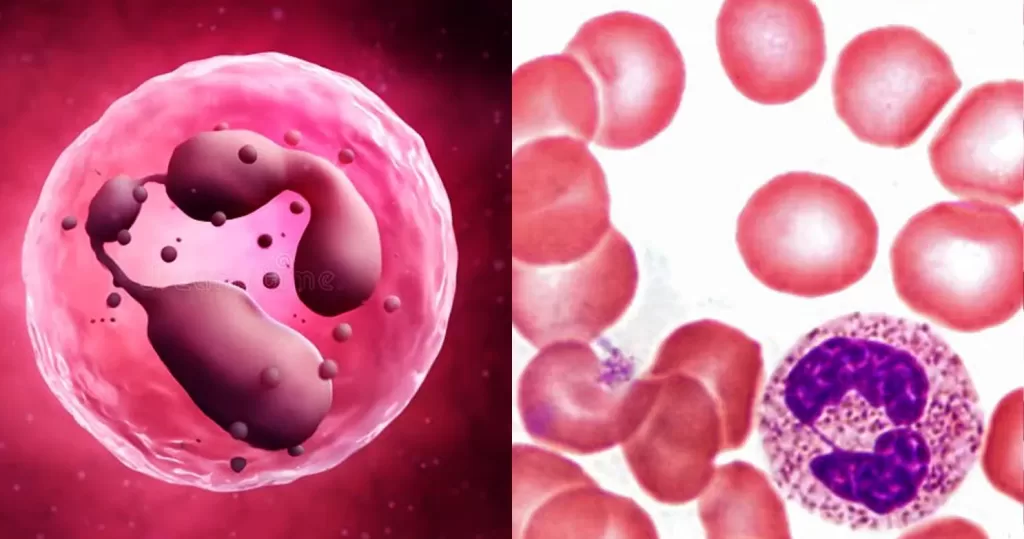
Un-stained stem cells with burr cells with highly clotted red cells. Indicative of an acidic condition.
Only consider this condition if the cells appear far within the sample. If these cells appear near the very edge of the live sample slide, then burr cells should be ignored, as exposure to oxygen and dehydration can also cause this condition.
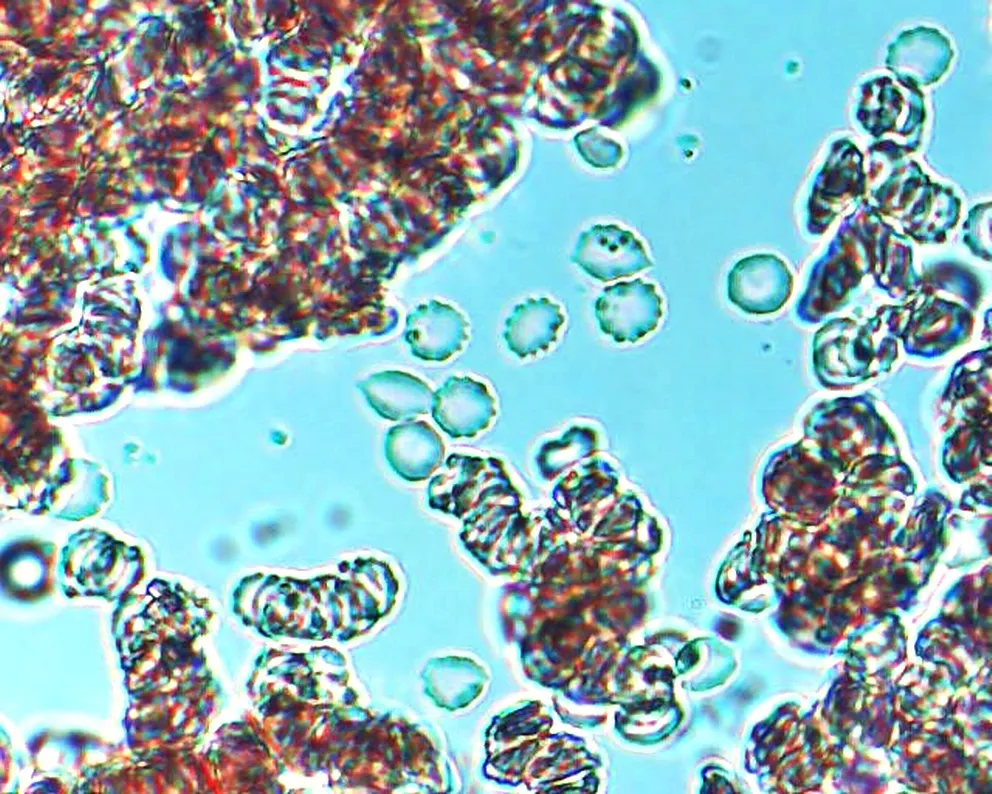
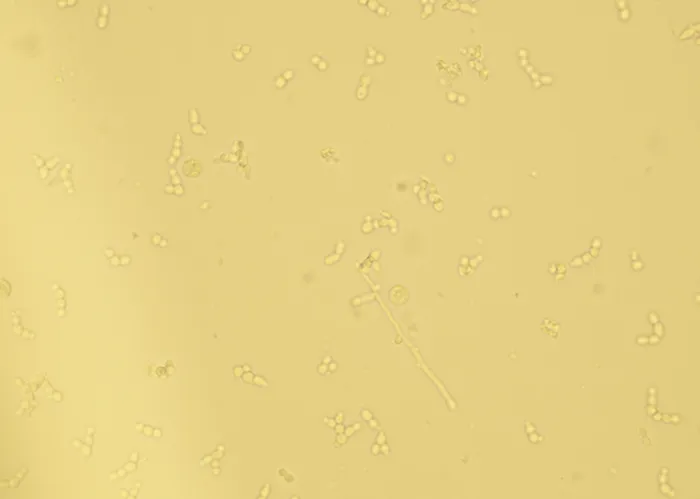
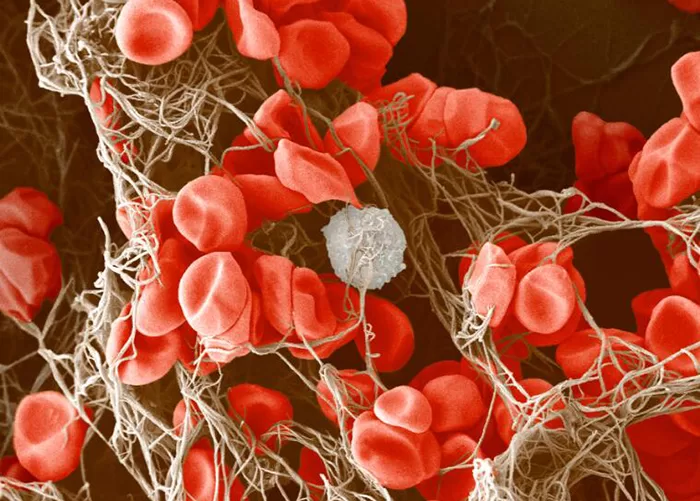
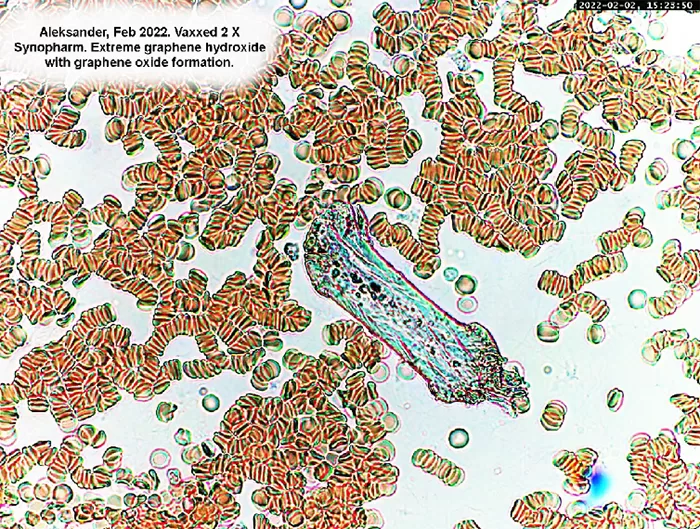
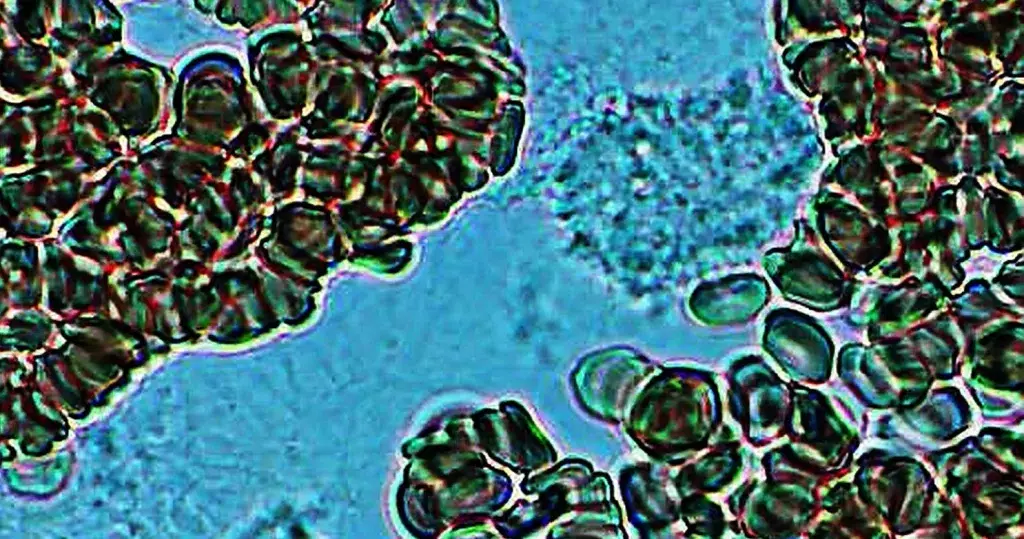
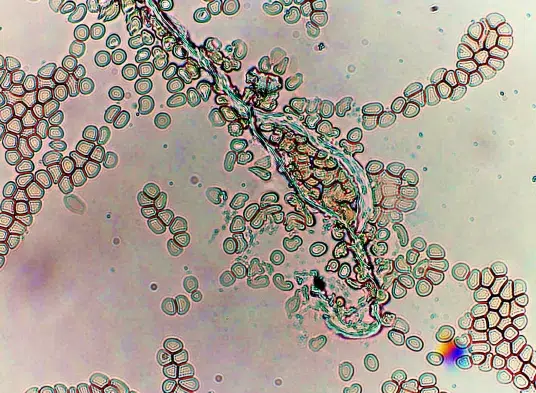
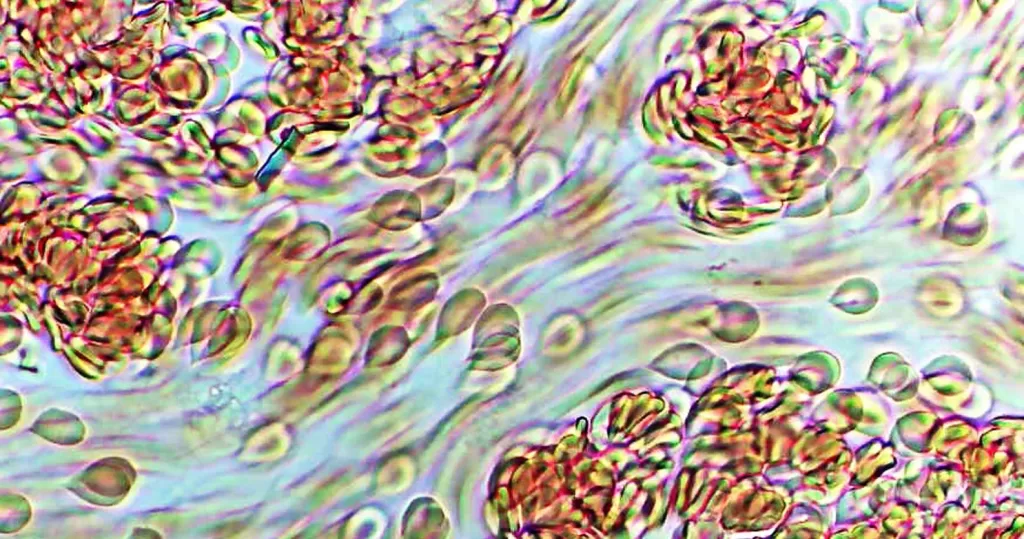
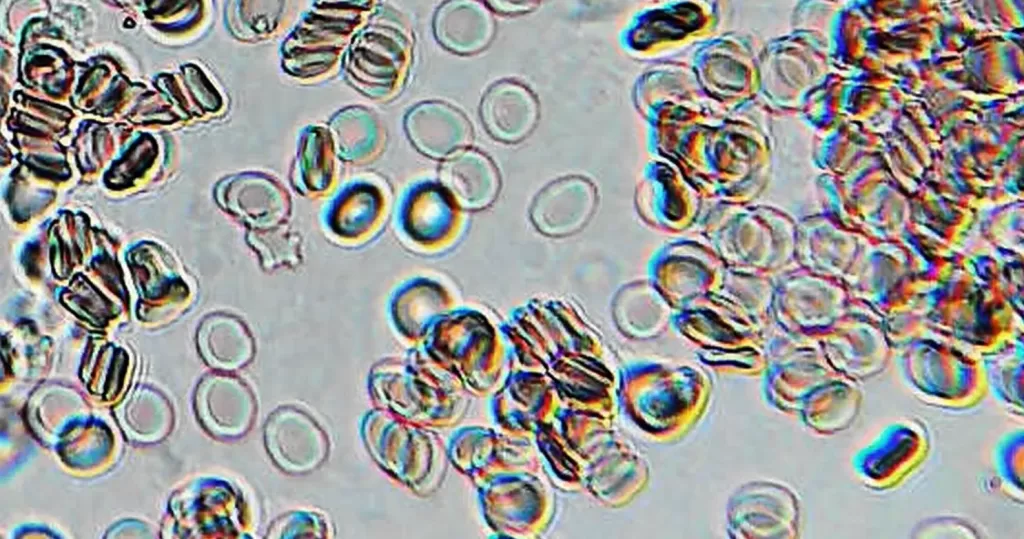
Burr cells with boat-shaped cells.
Together this condition would indicate a possible serious blood disorder and exposure to heavy toxins, such as street or prescription drugs, etc.
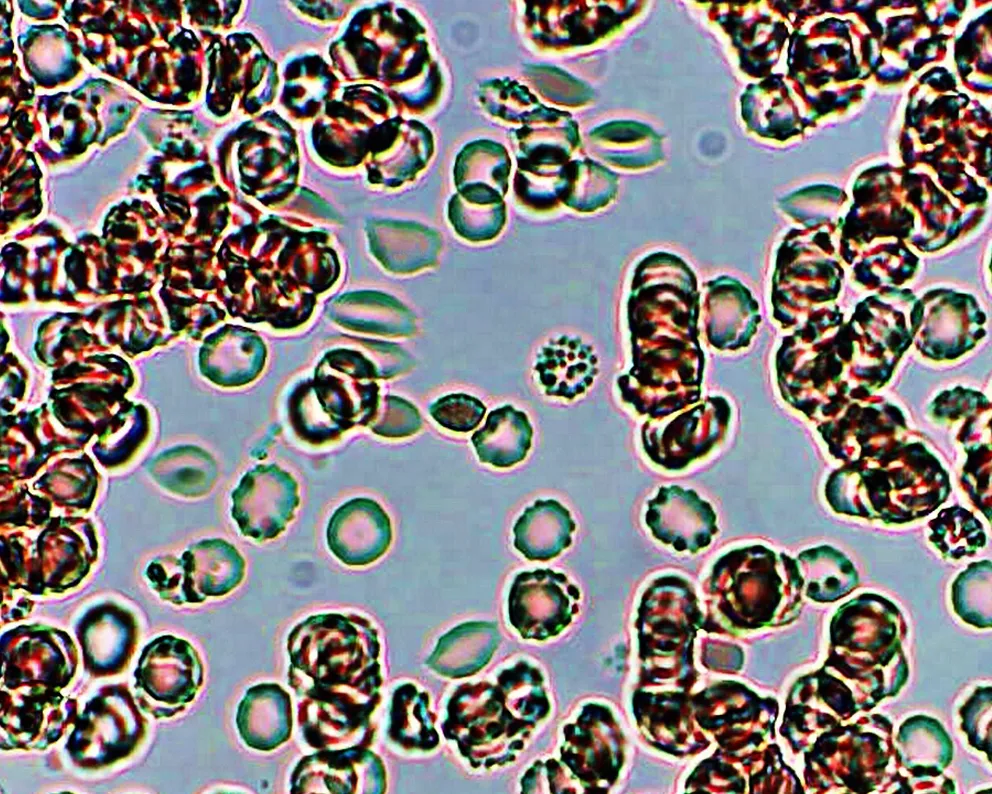
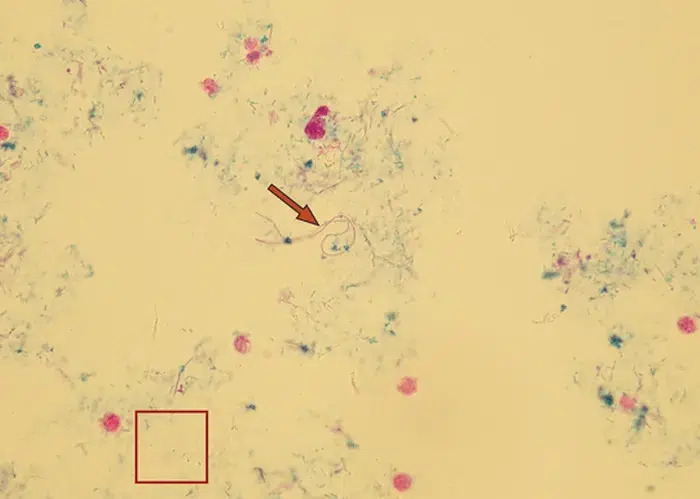
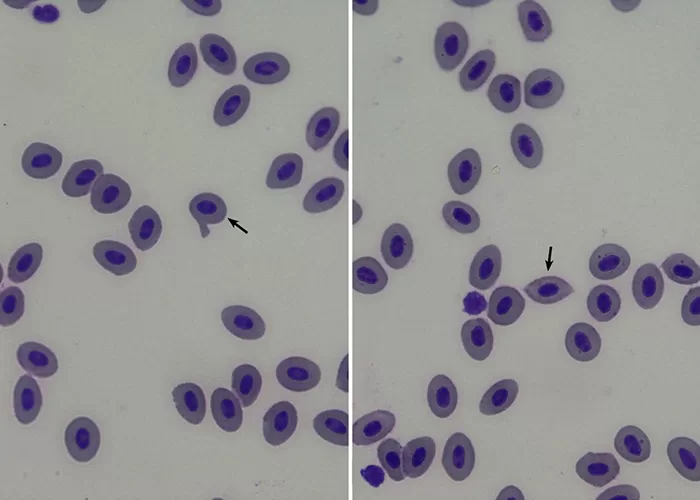
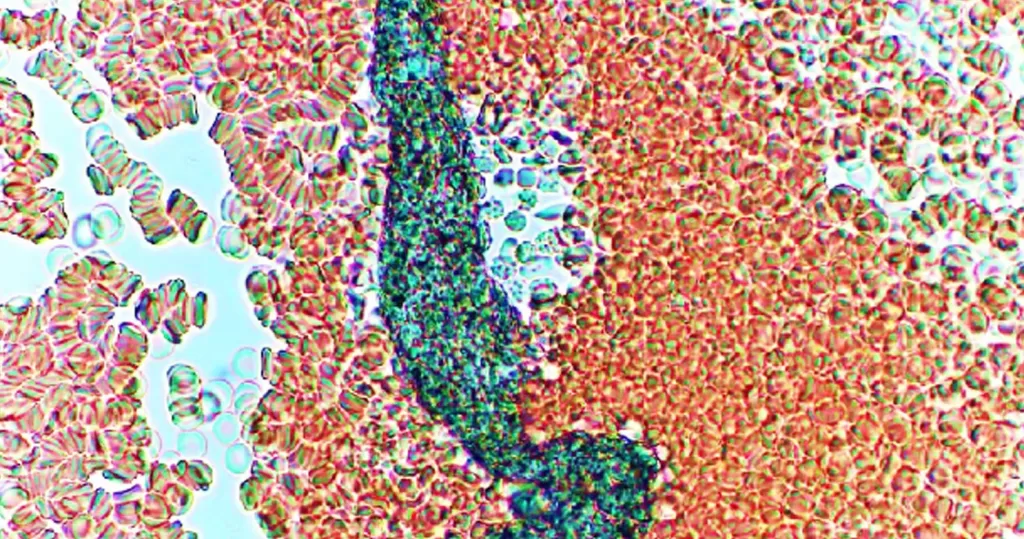
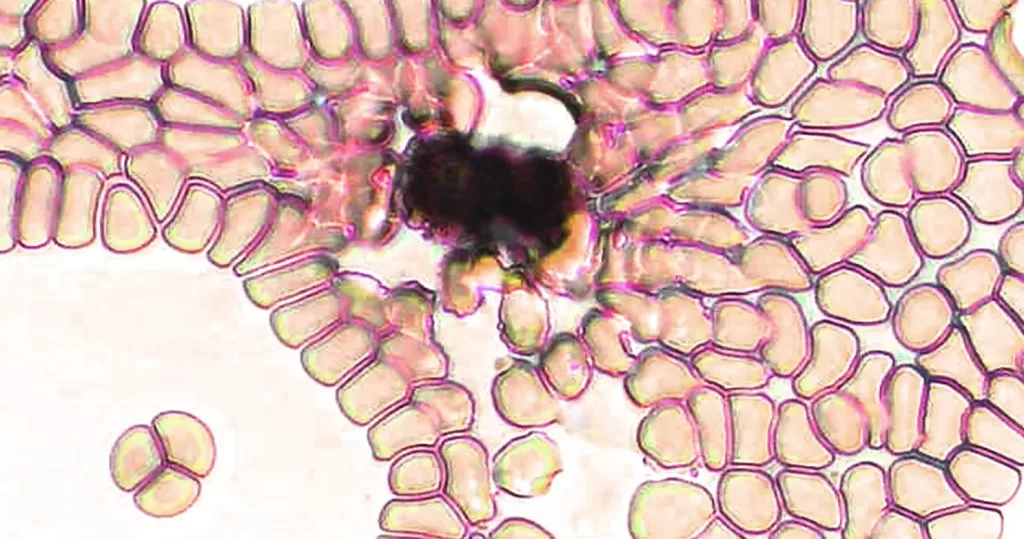
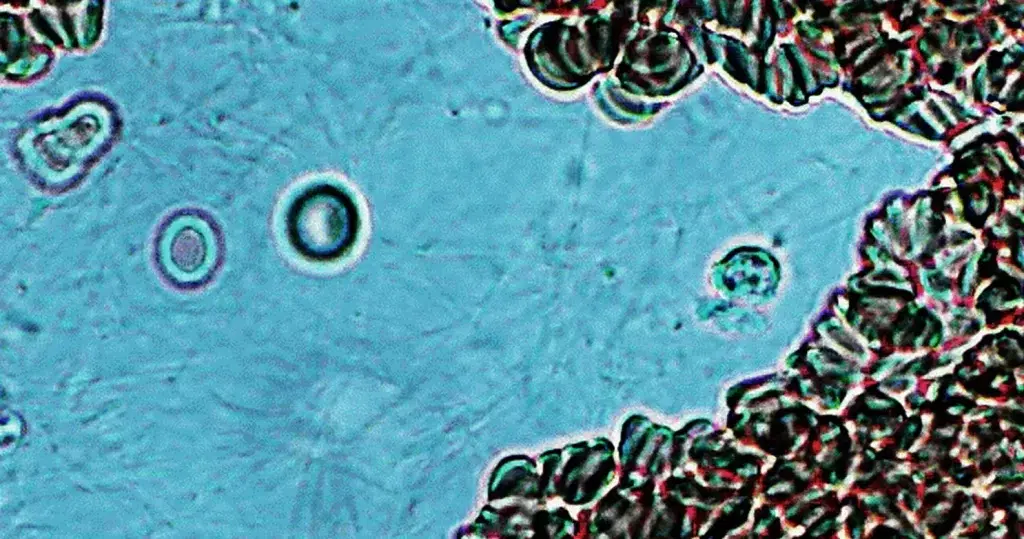
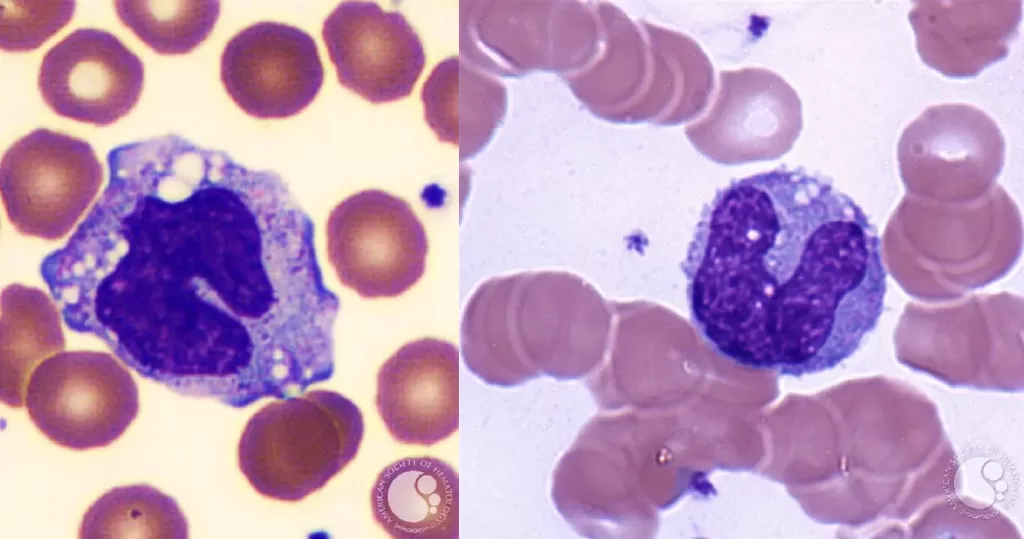
Very sick blood. Many Burr cells in non-differentiated Roulleux. Note also the internally-broken, or burst neutrophil cells.
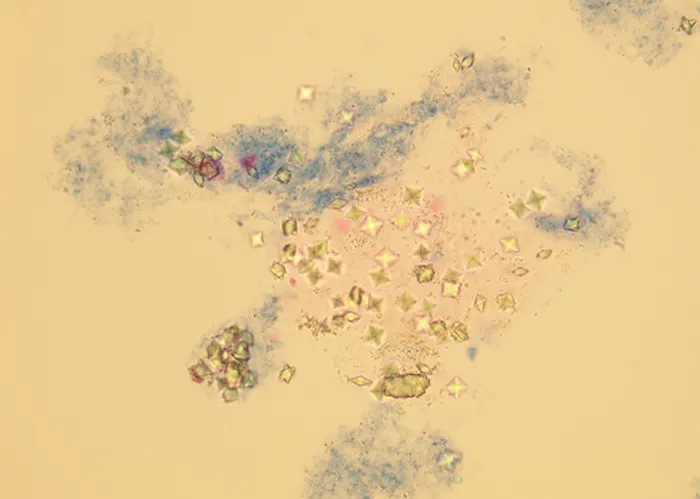
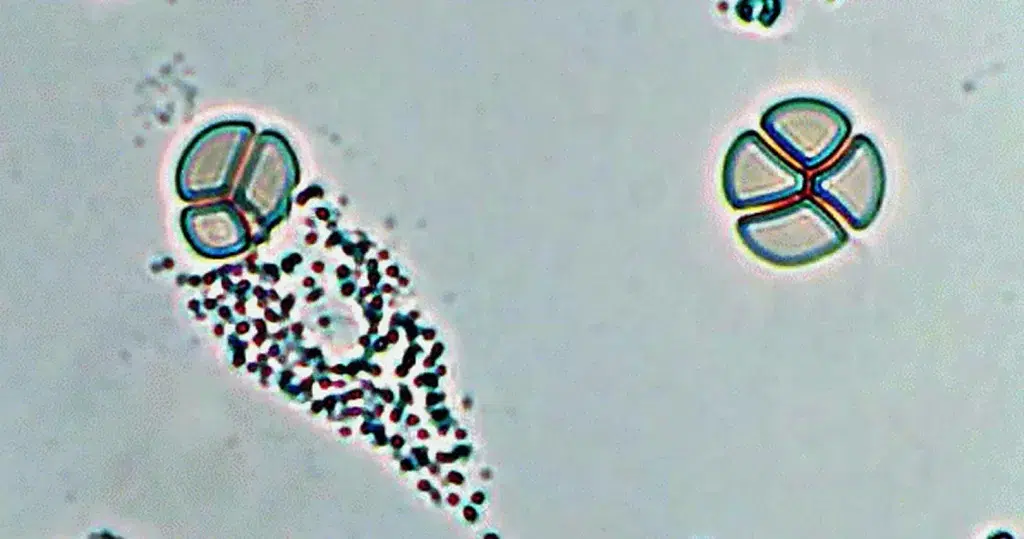
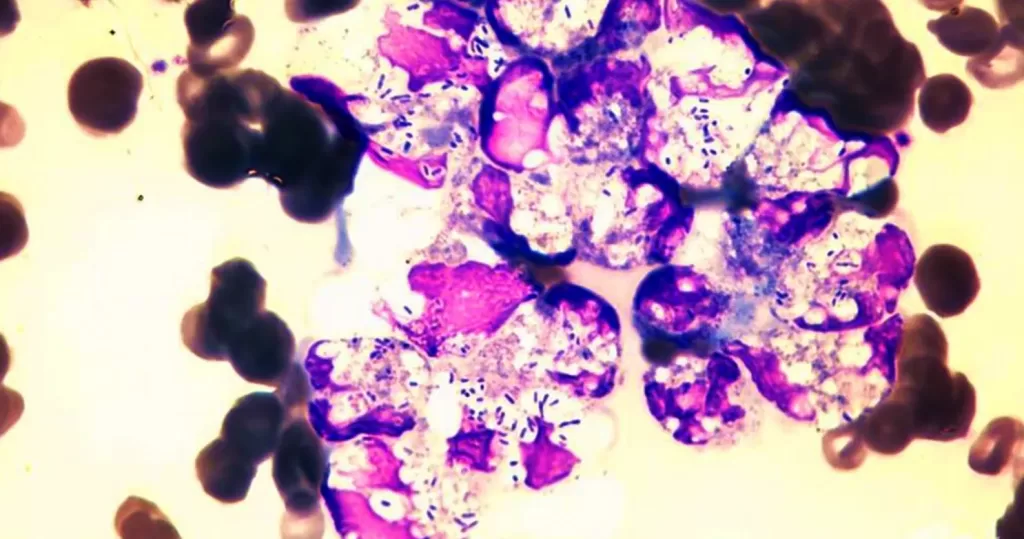
This would occur in heavy radiation, both ionizing and non-ionizing. Also heavy chemical contamination.