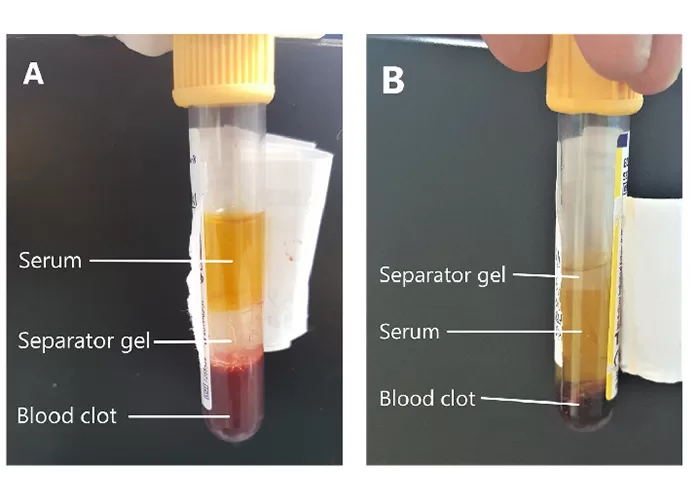
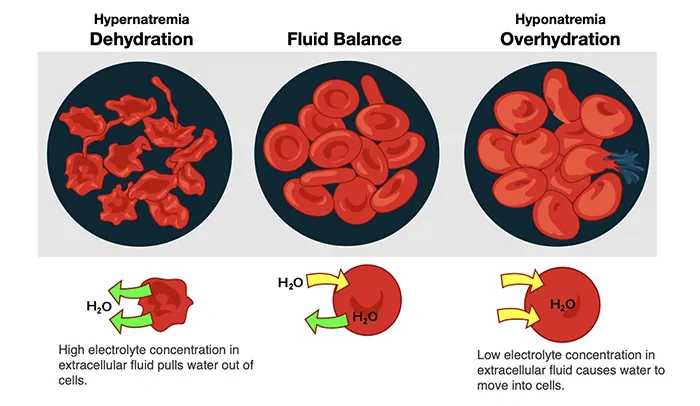
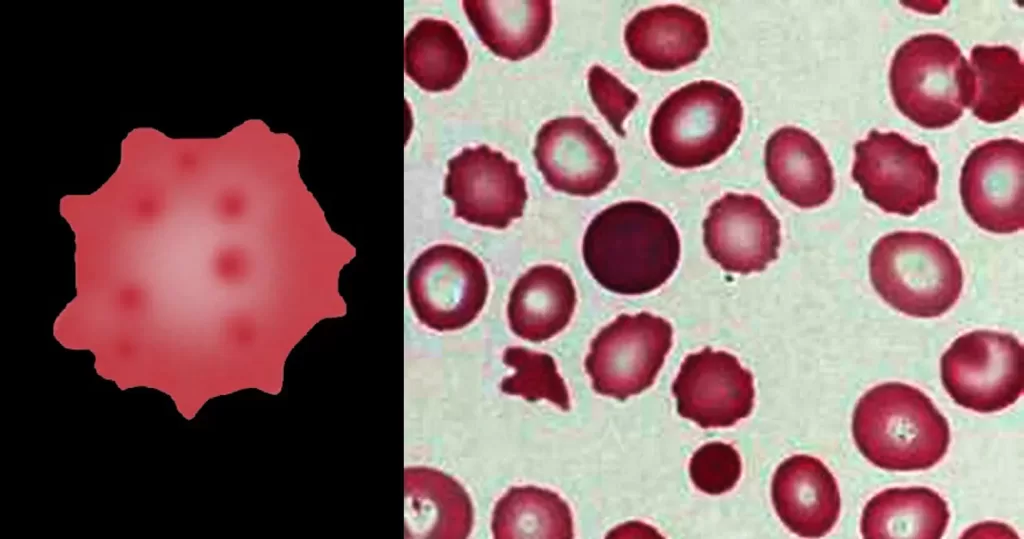
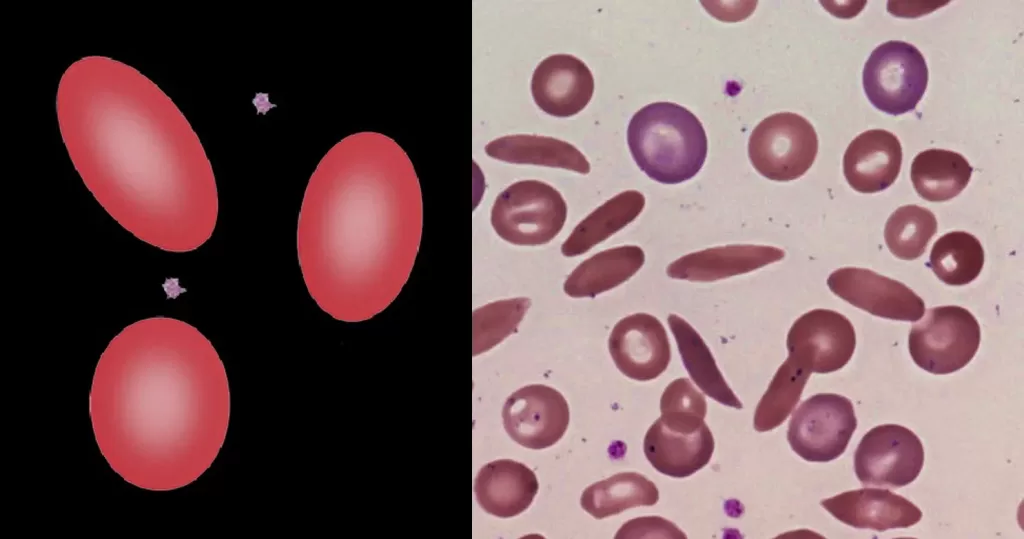
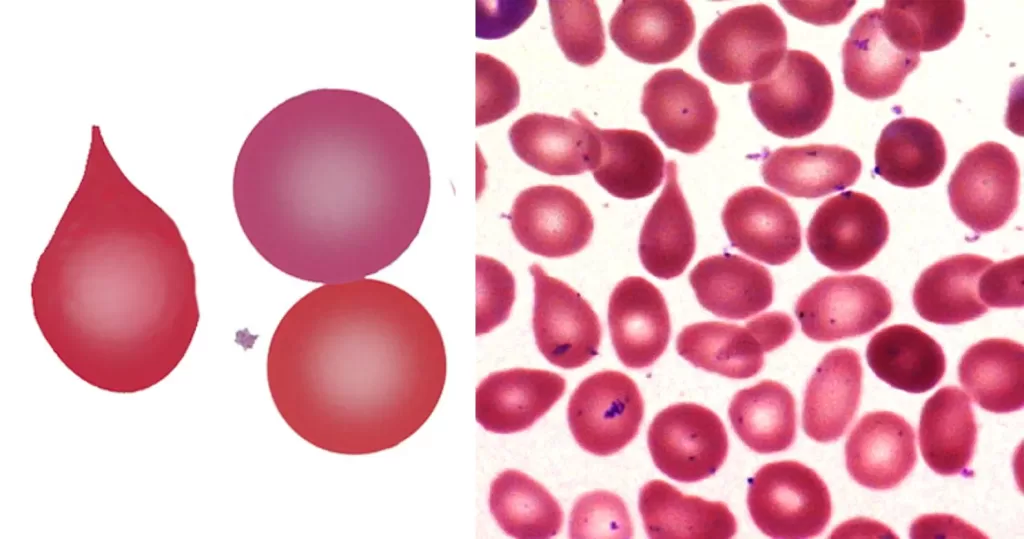
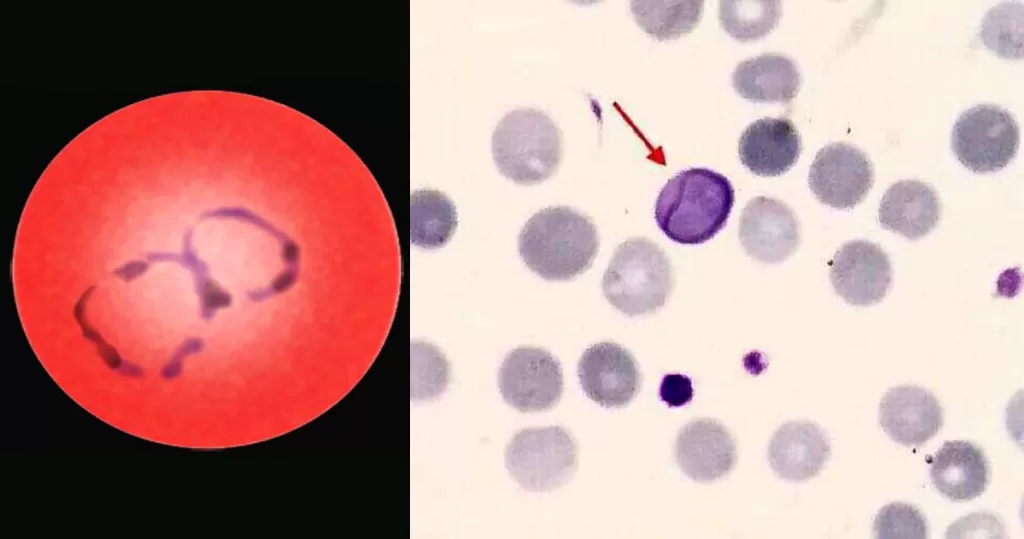
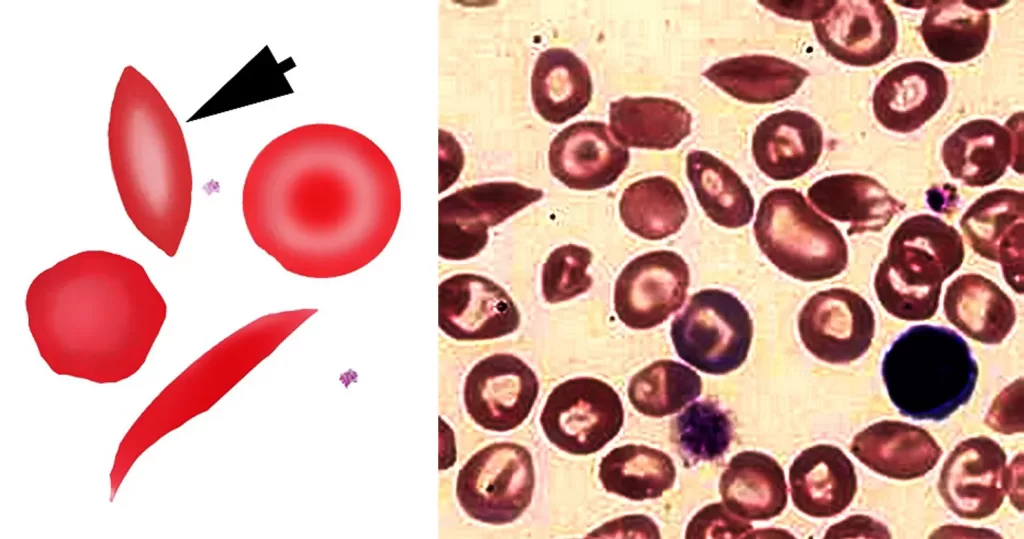
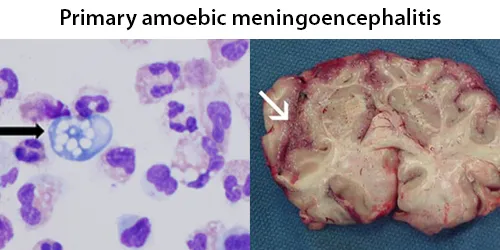
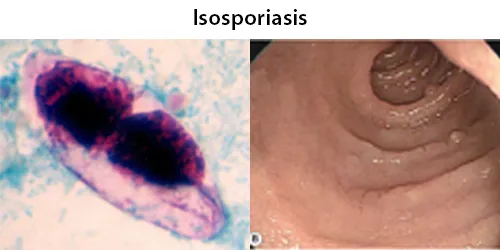
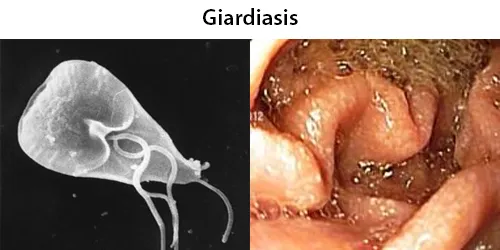
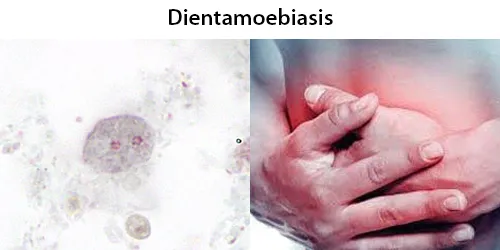
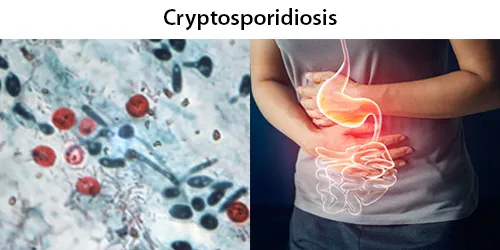
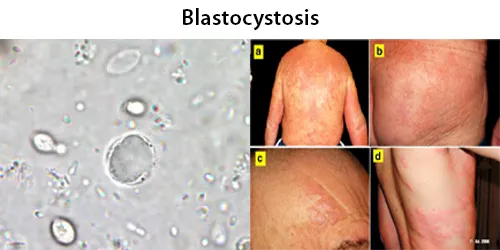
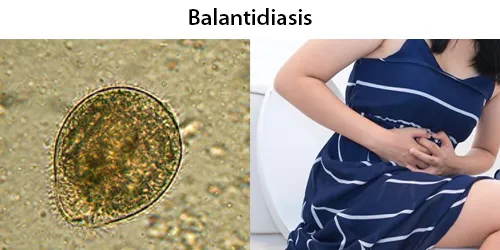
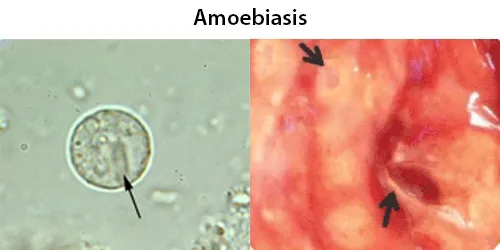
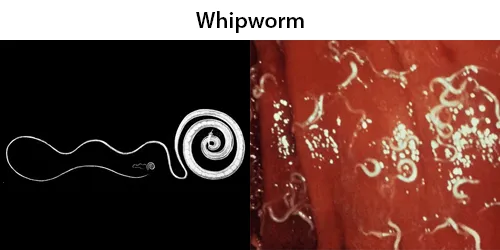
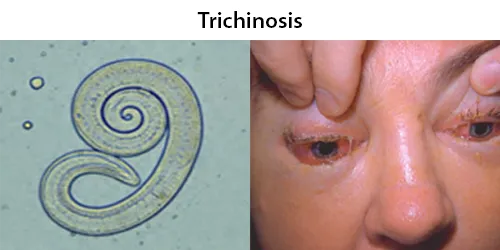
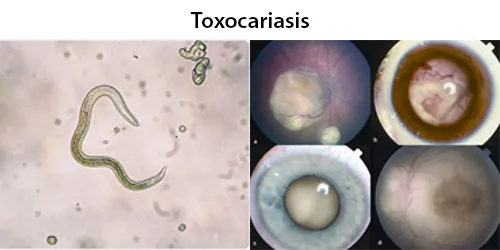
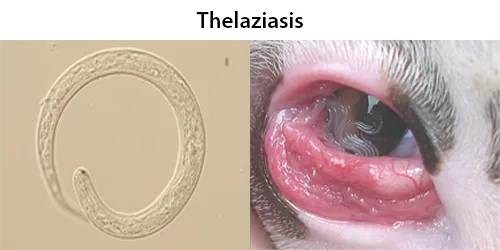
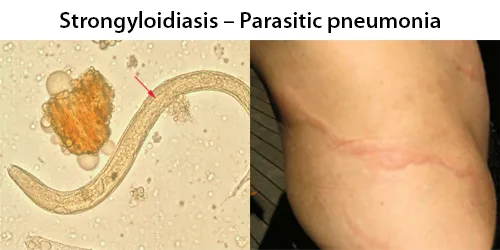
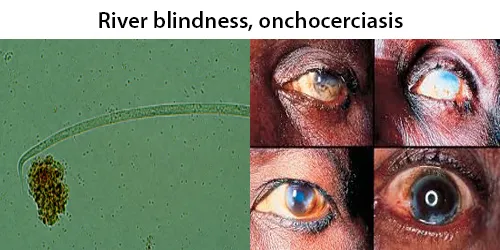
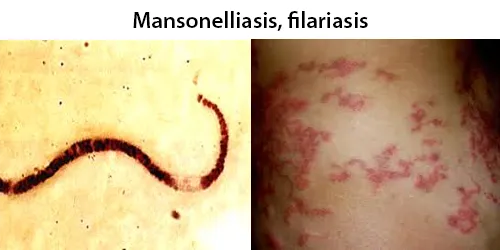
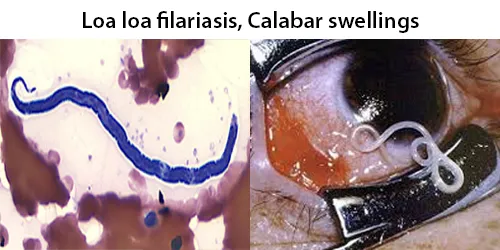
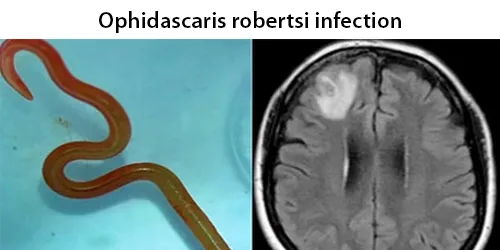
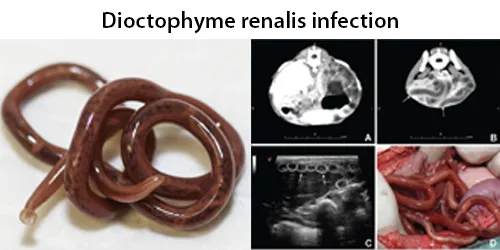
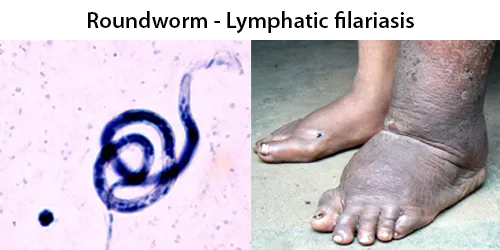
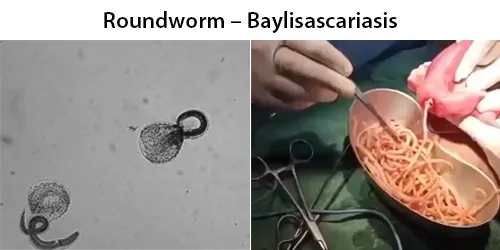
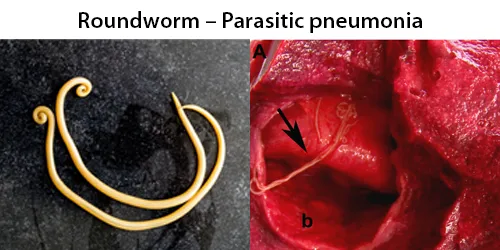
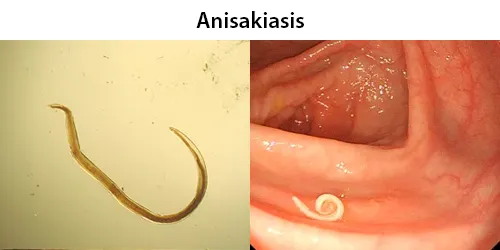
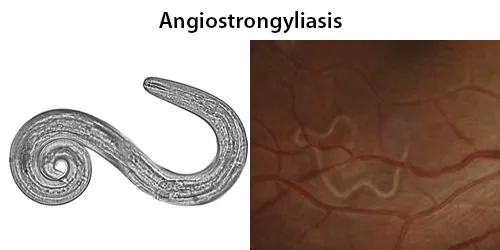
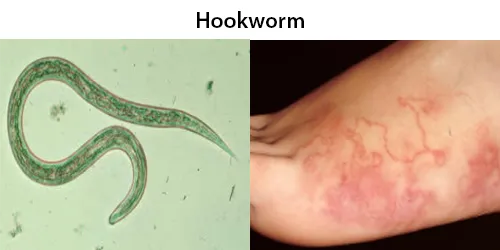
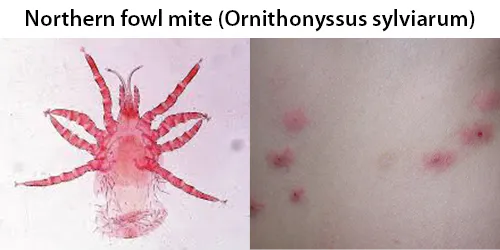
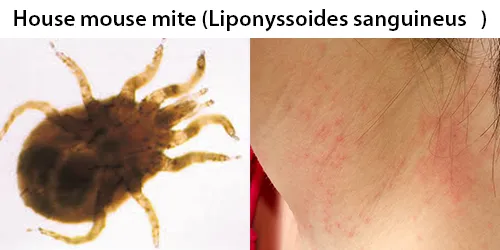
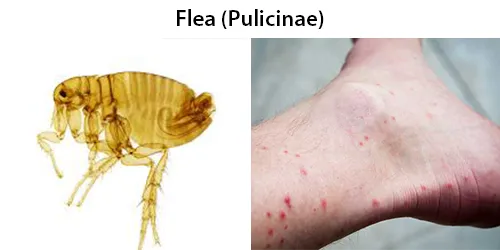
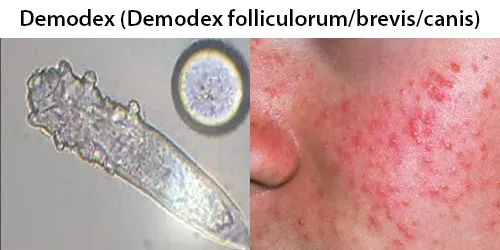
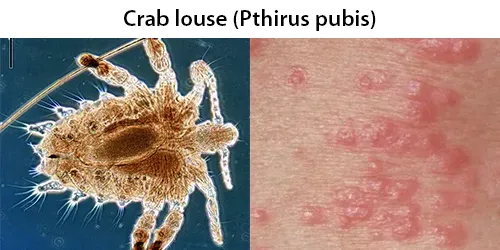
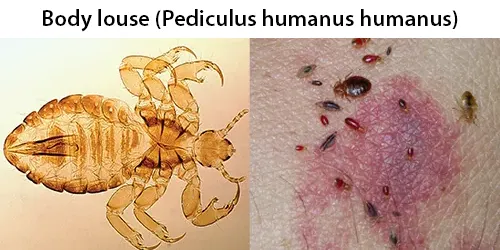
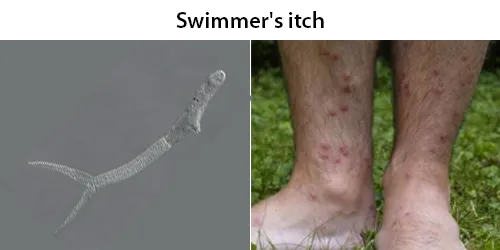
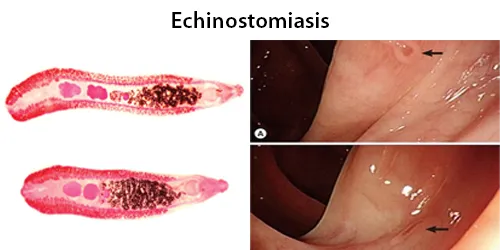
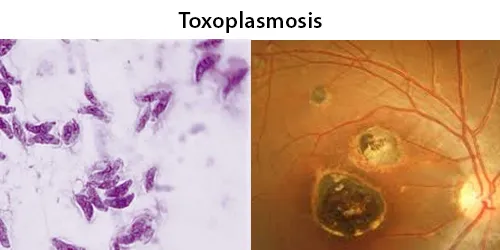
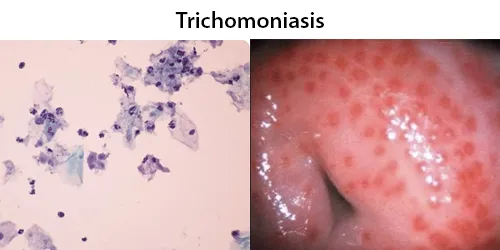
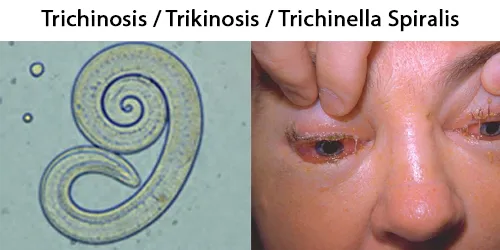
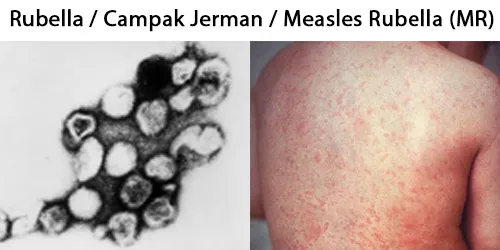
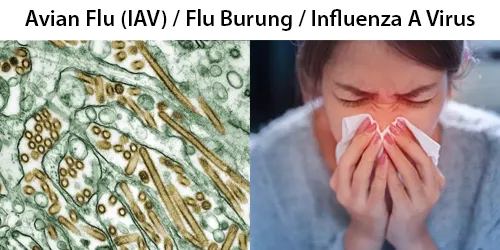
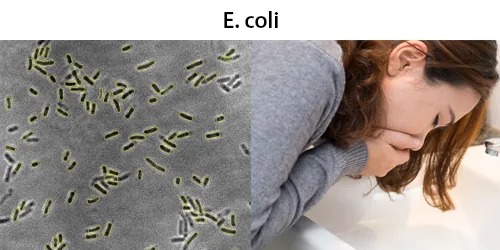
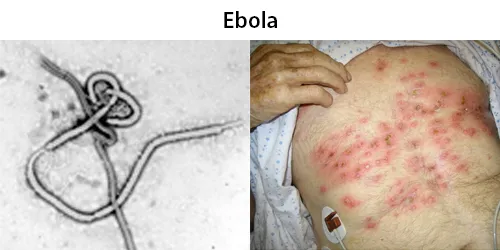
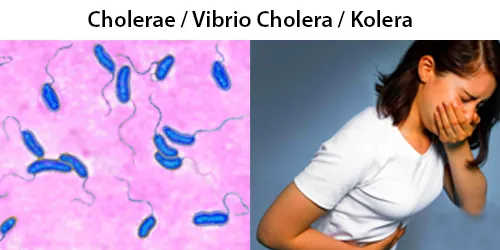
Urine Specific Gravity
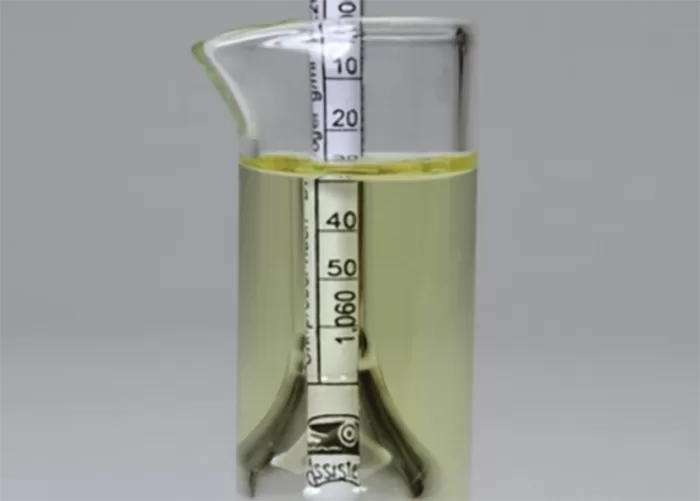
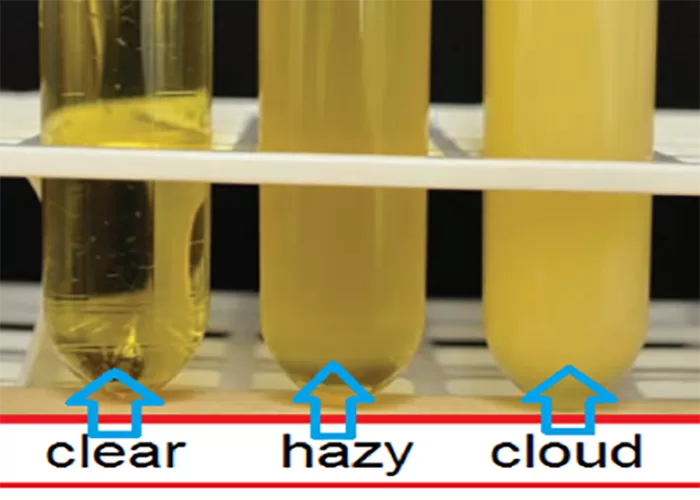
Urine specific gravity is a measure of the concentration of particles in urine, reflecting the kidney’s ability to balance water and waste. It is typically measured on a scale ranging from 1.000 (completely dilute) to 1.030 (highly concentrated).
- Normal range: A specific gravity between 1.005 and 1.030 is generally considered normal, indicating that the kidneys are effectively regulating hydration and waste elimination.
- Low specific gravity (closer to 1.000): This may suggest that the urine is very diluted, which can occur due to excessive fluid intake or conditions affecting kidney function.
- High specific gravity (closer to 1.030): This indicates concentrated urine, often a sign of dehydration, where the body retains water. It can also be influenced by certain medical conditions such as kidney disease or diabetes.