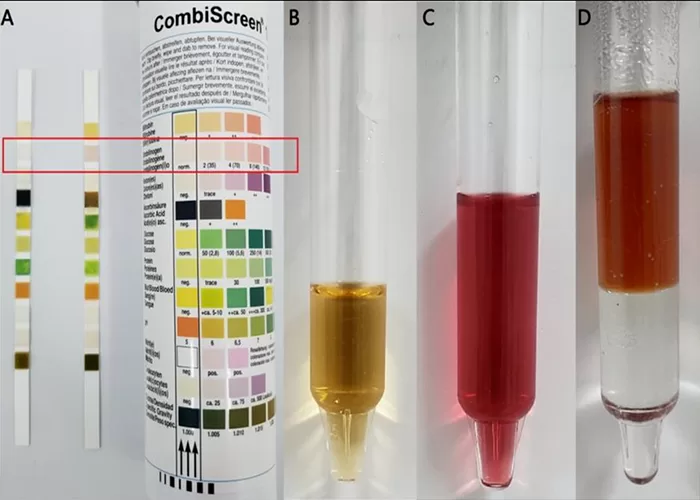
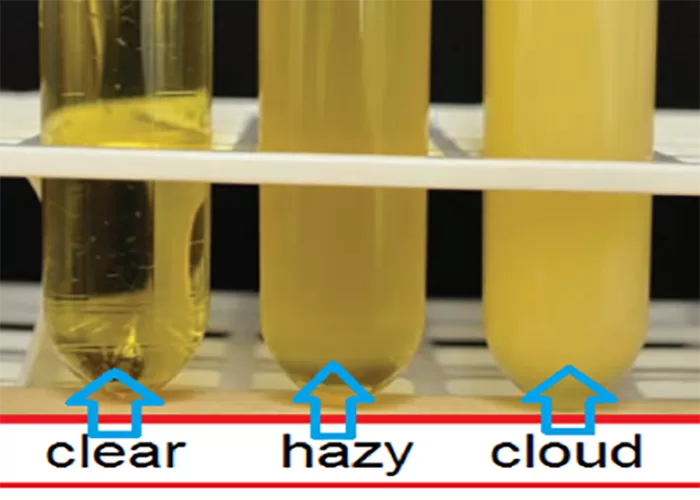
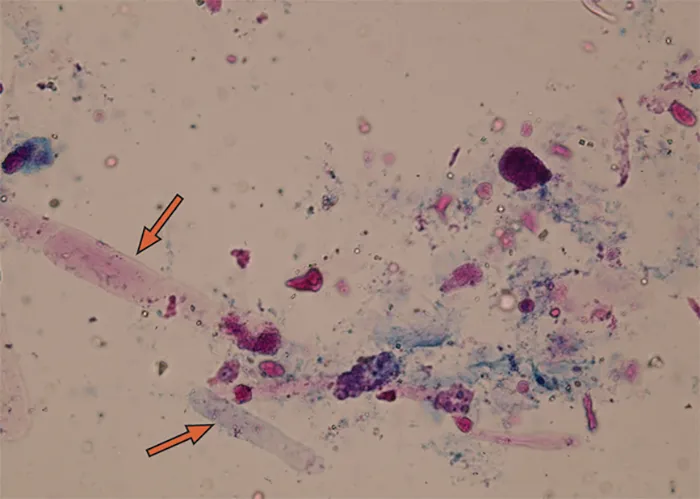
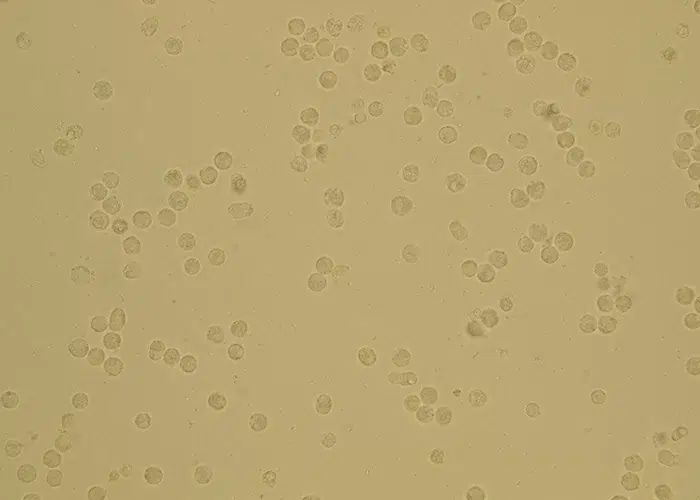
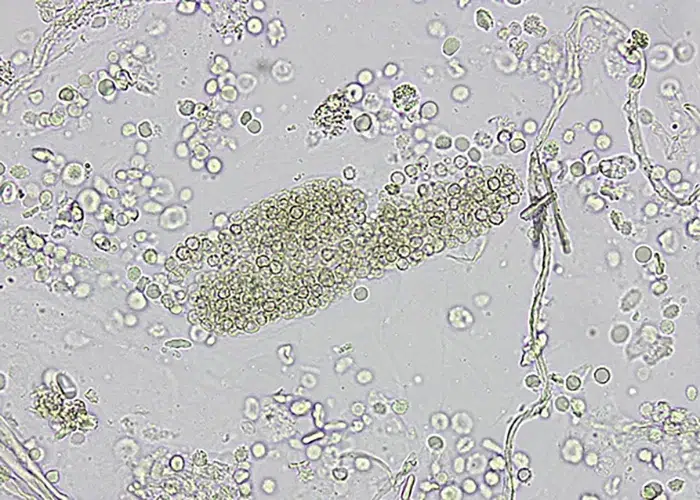
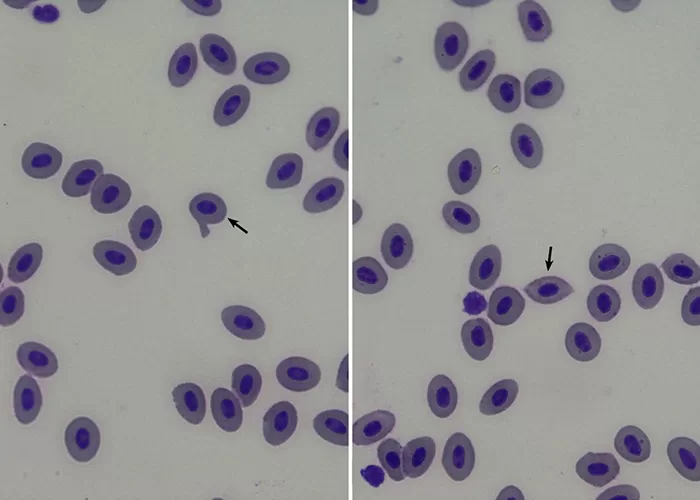
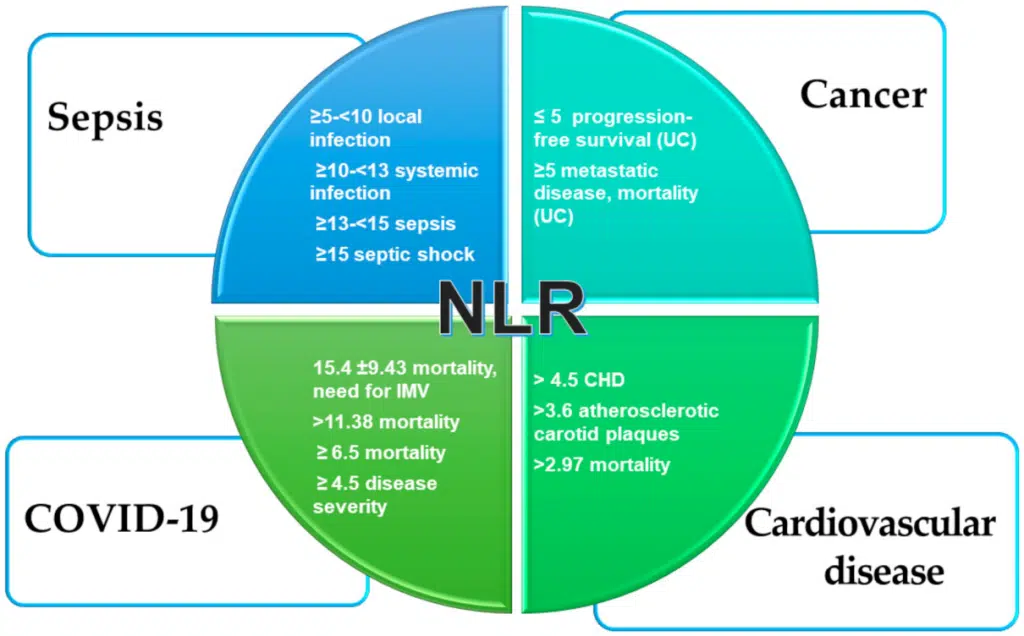
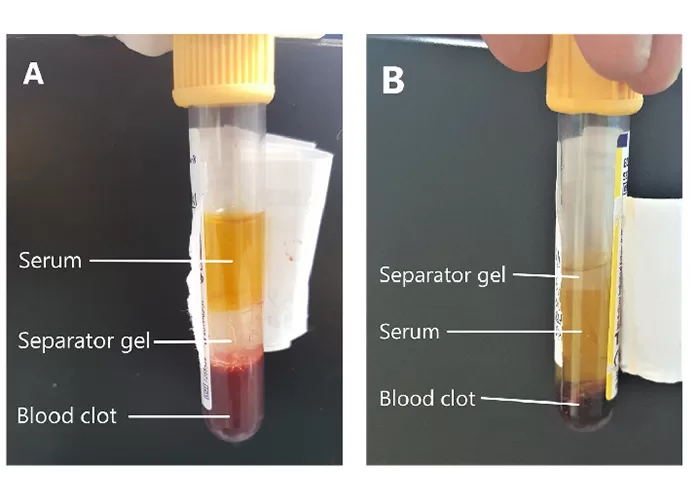
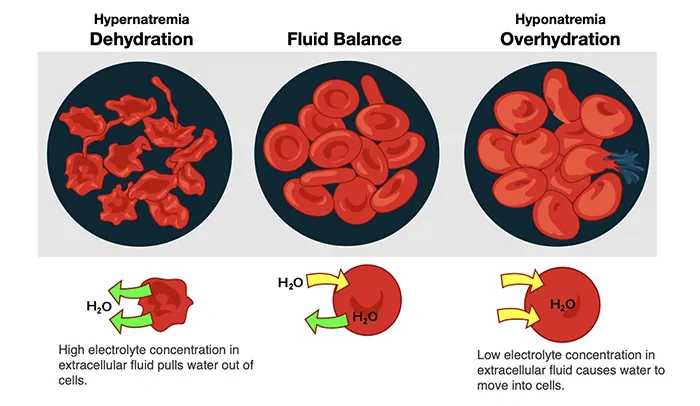
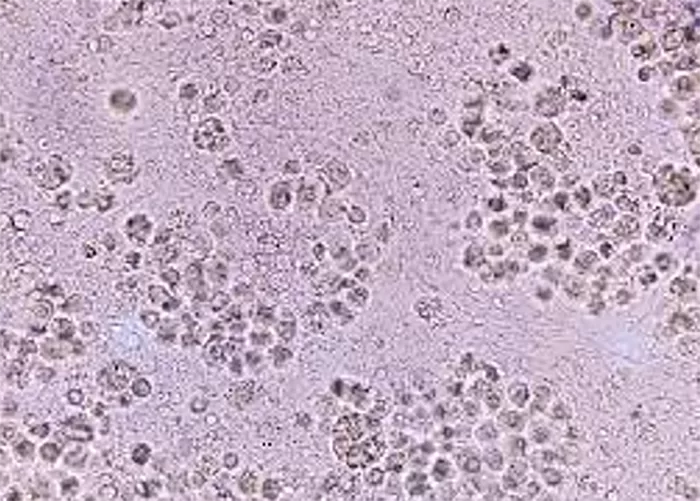
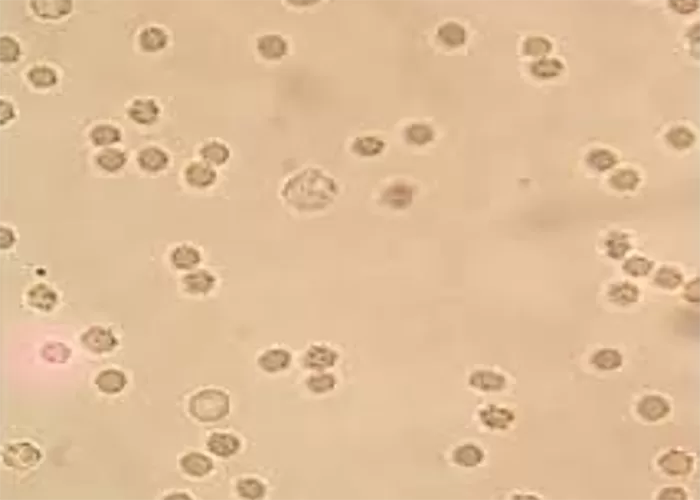
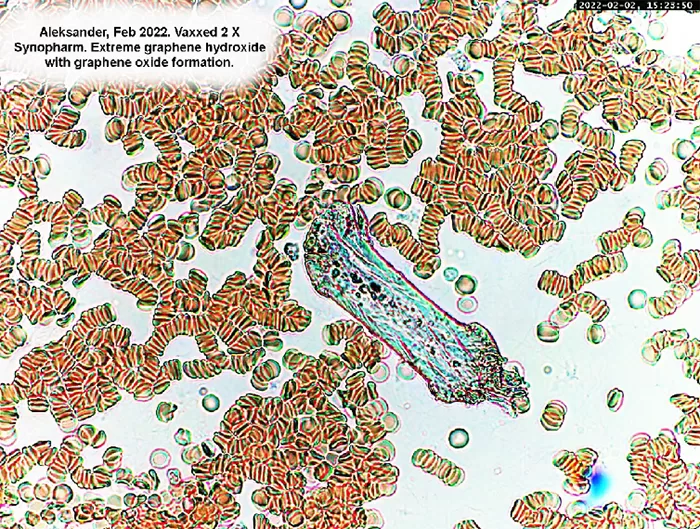
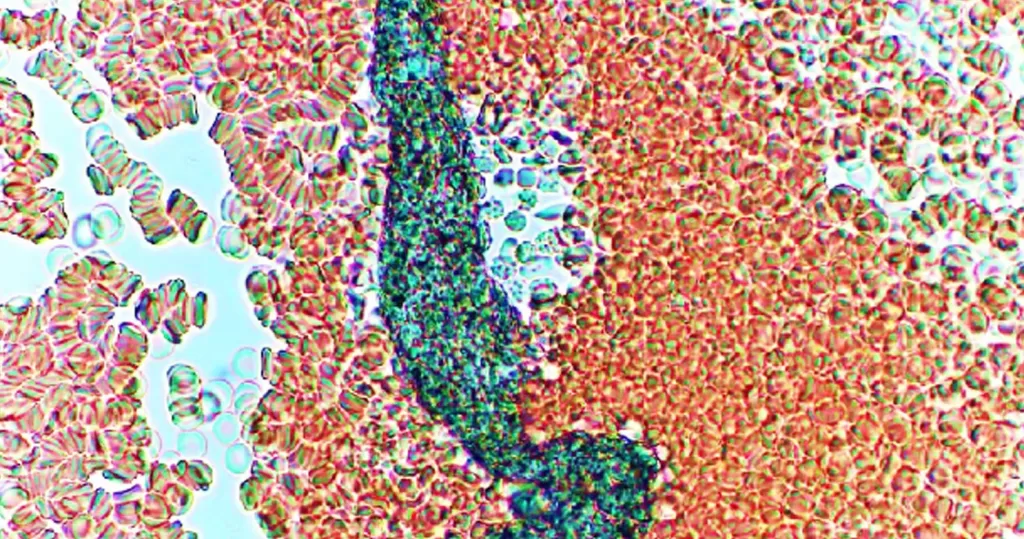
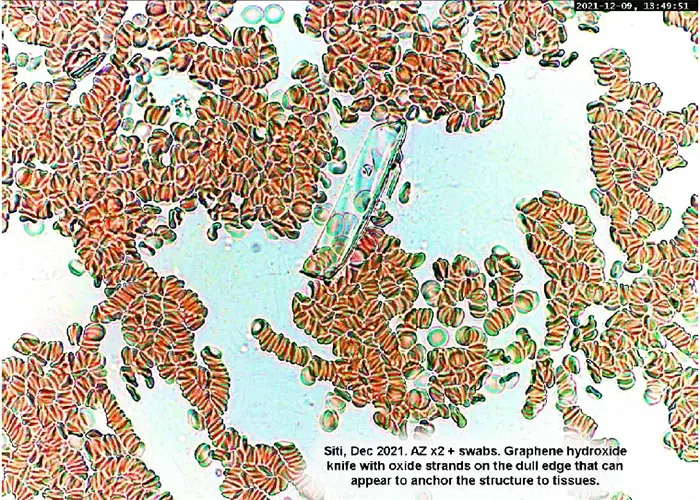
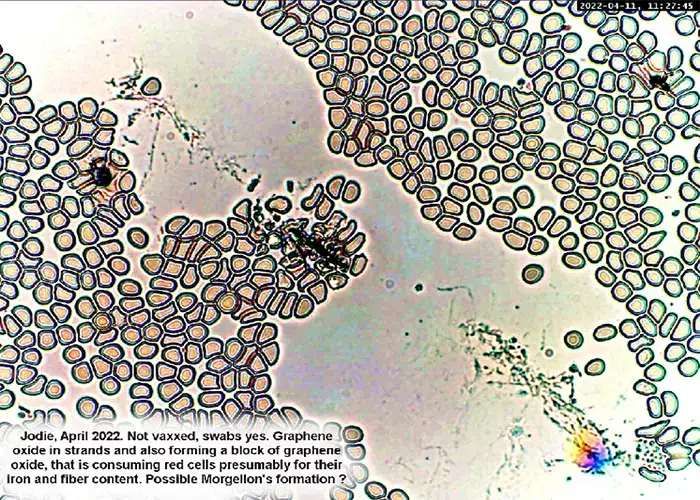
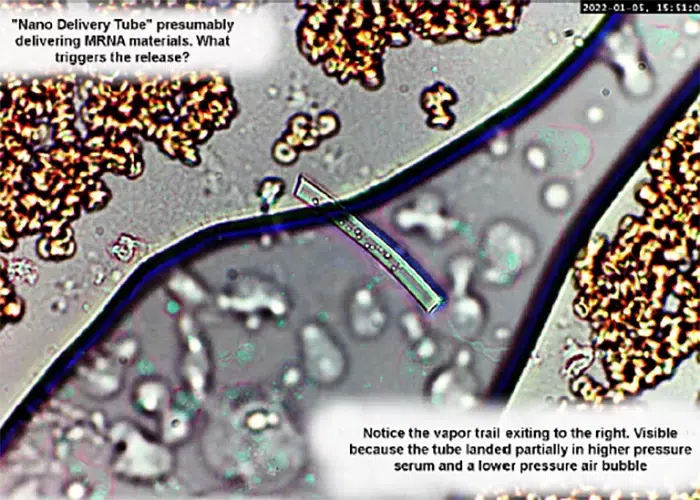
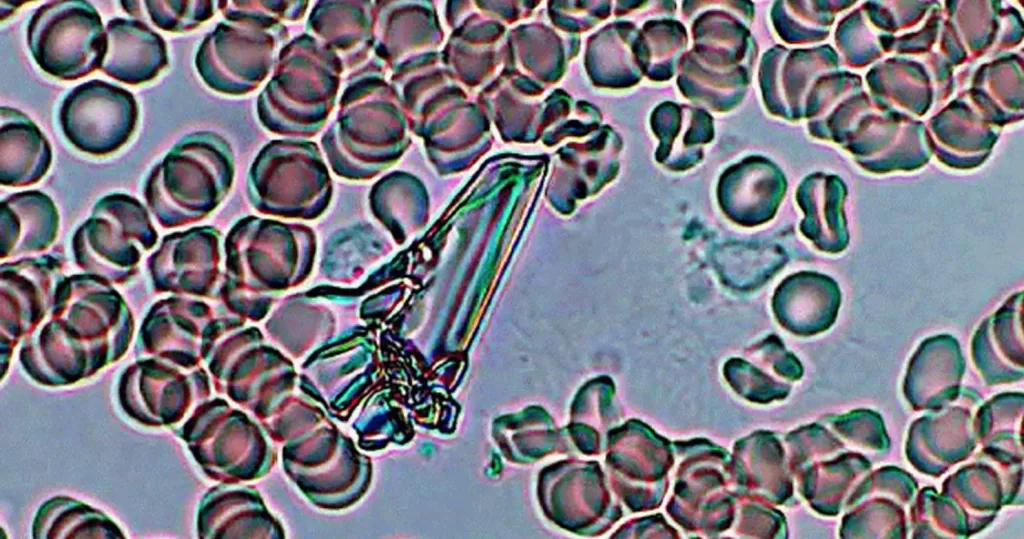
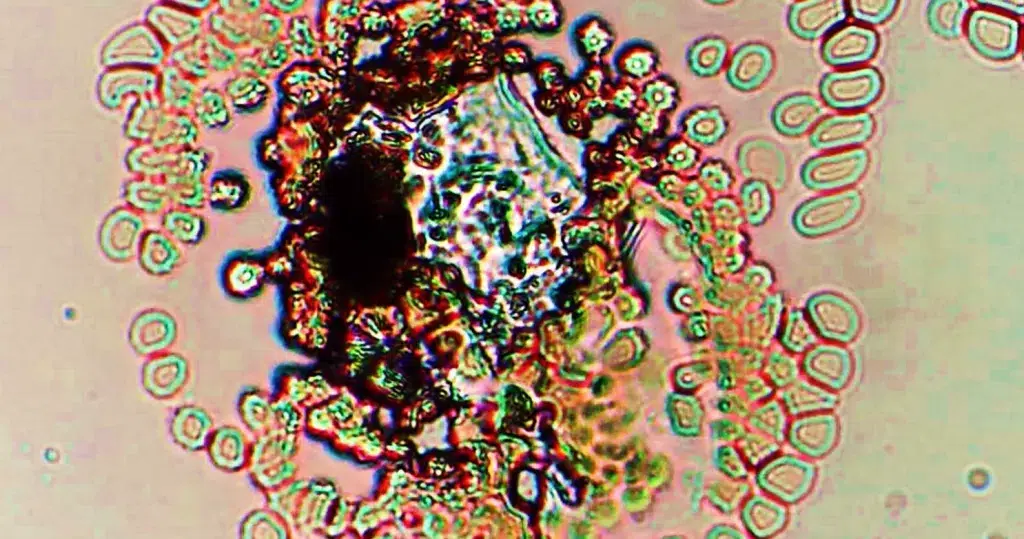
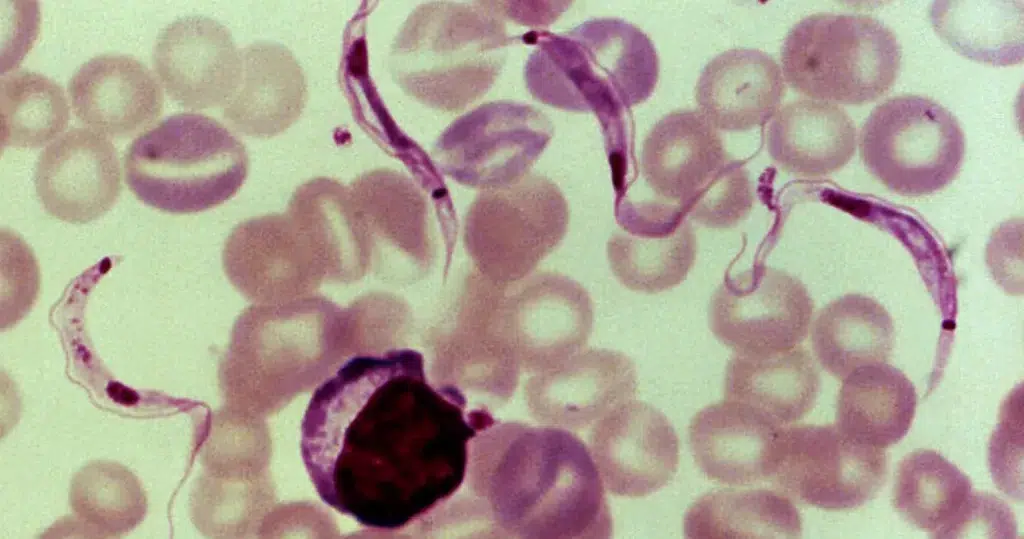
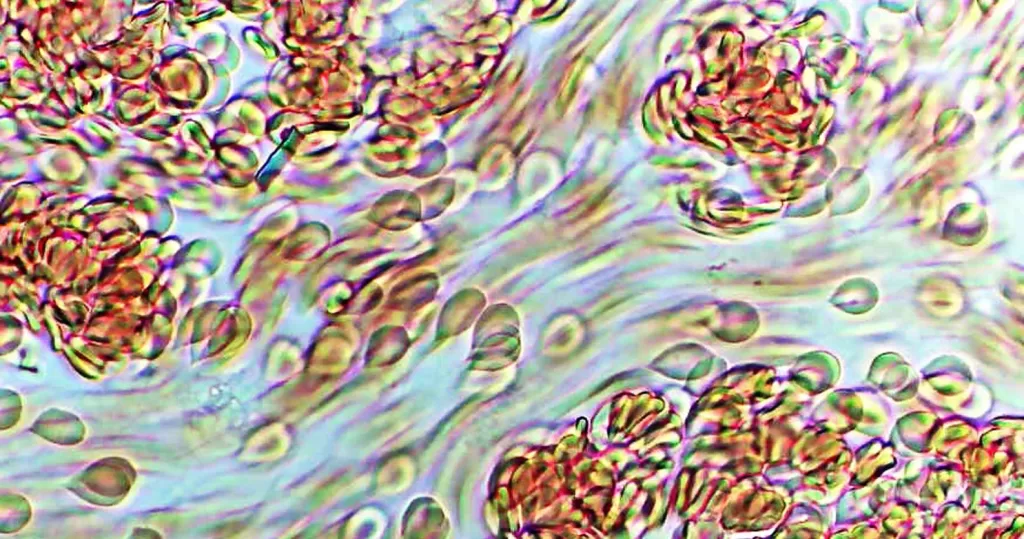
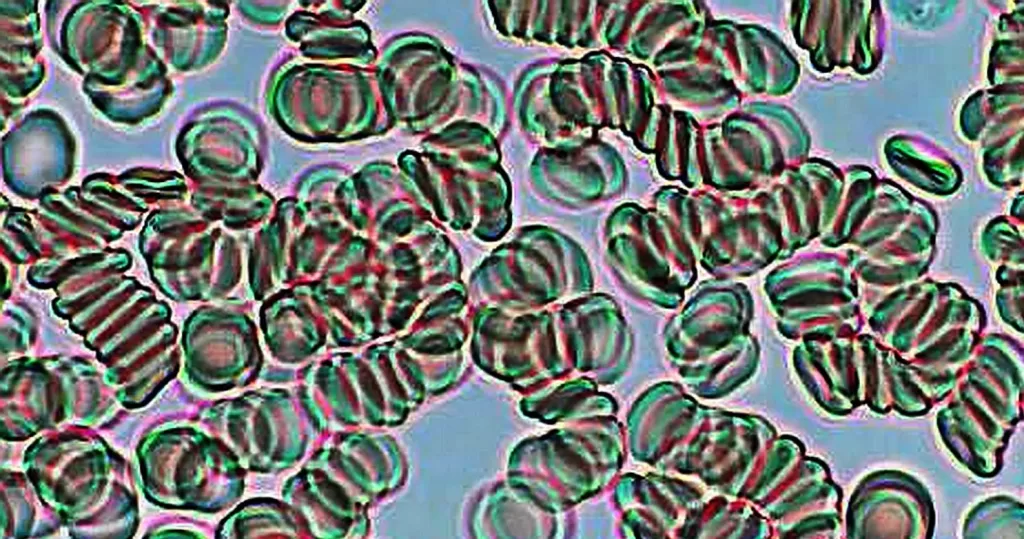
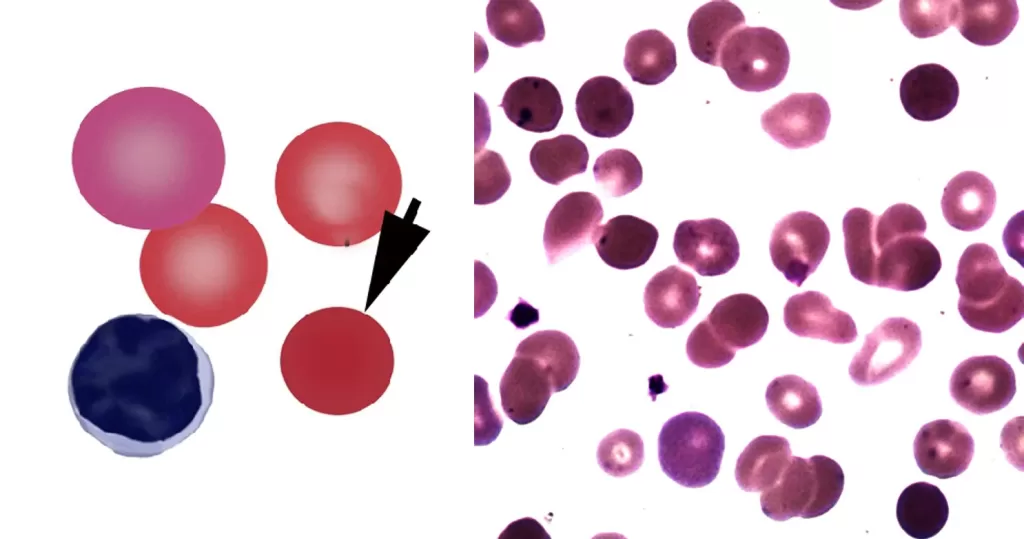
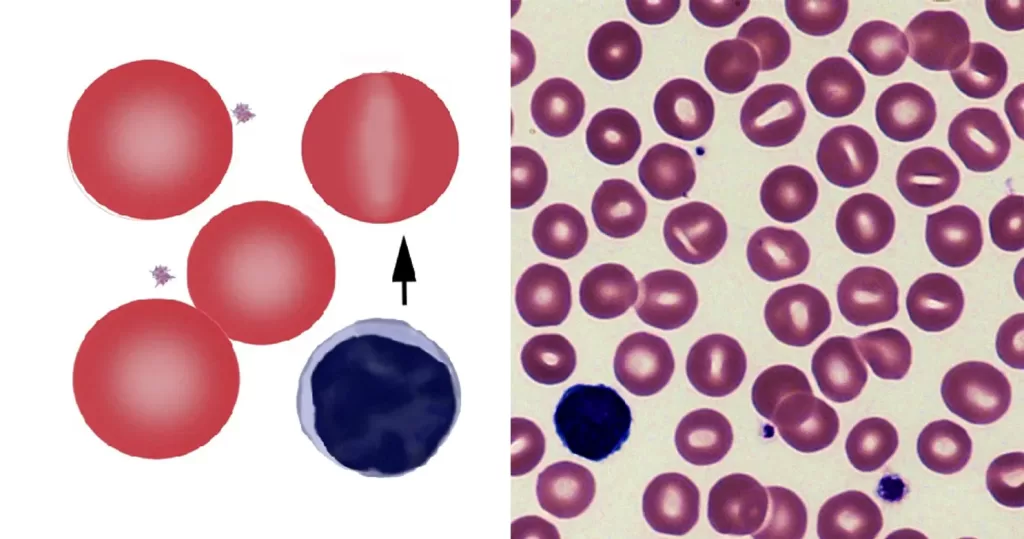
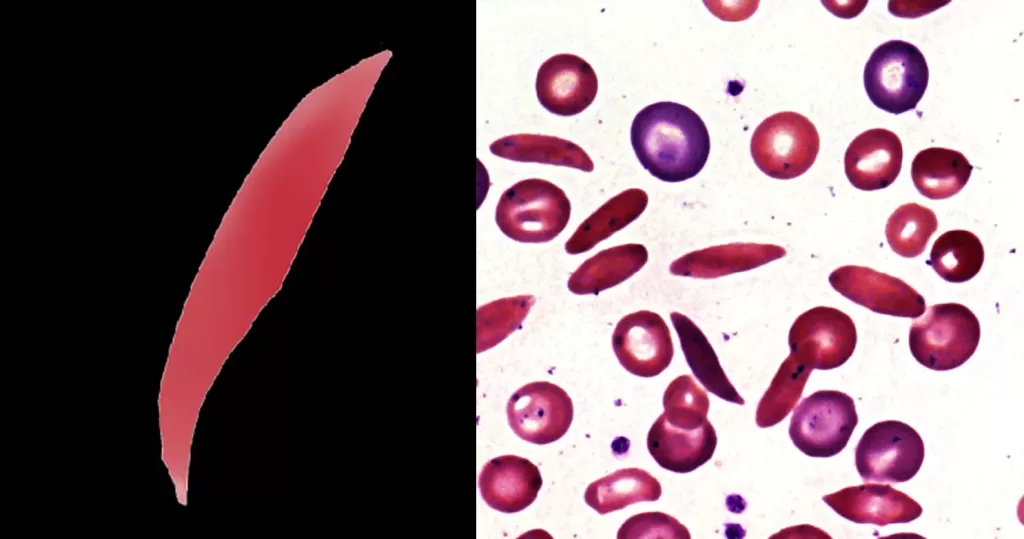
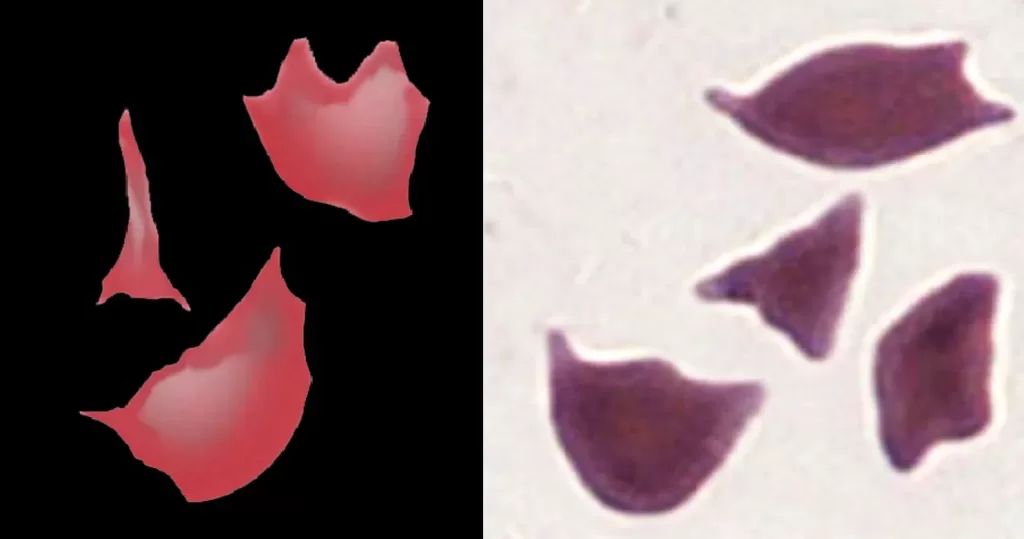
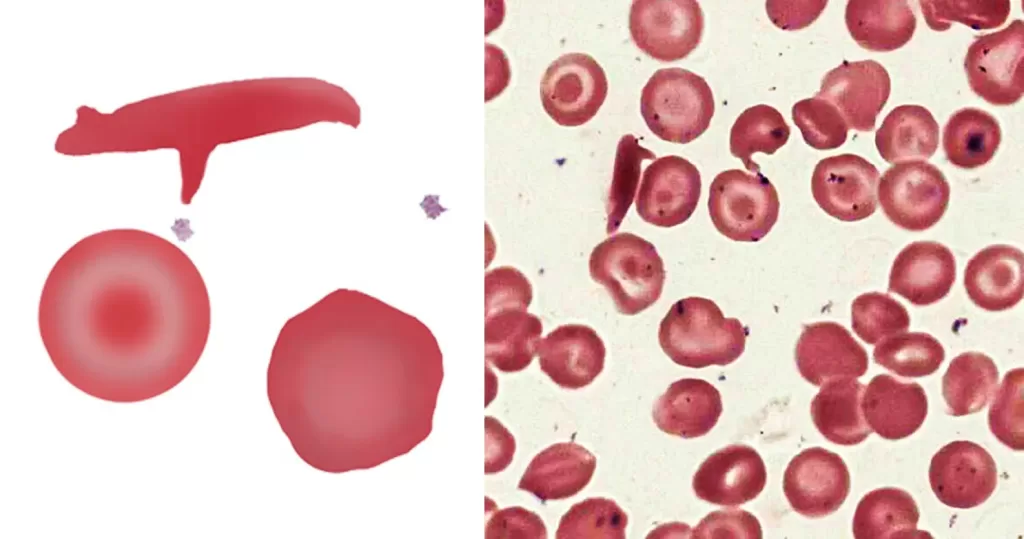
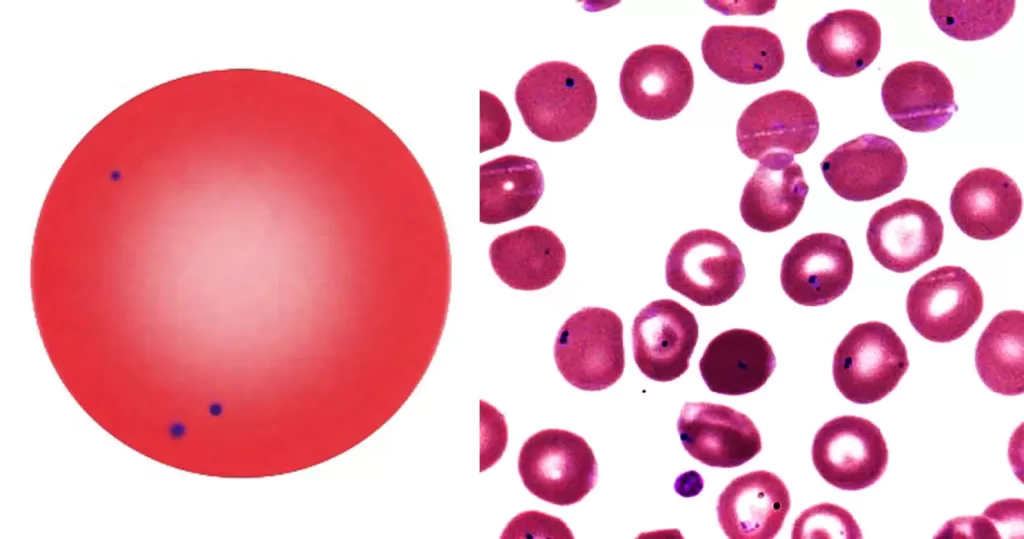
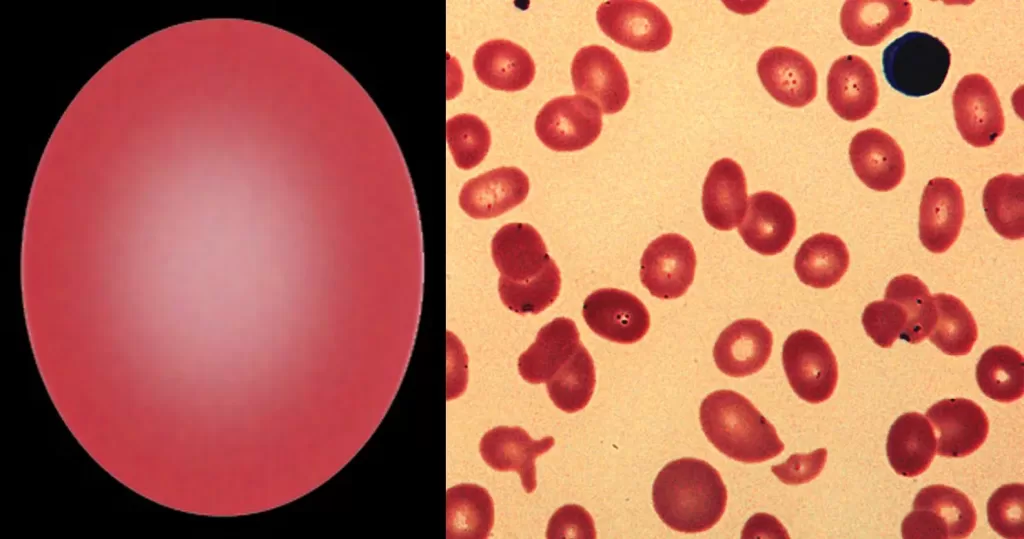
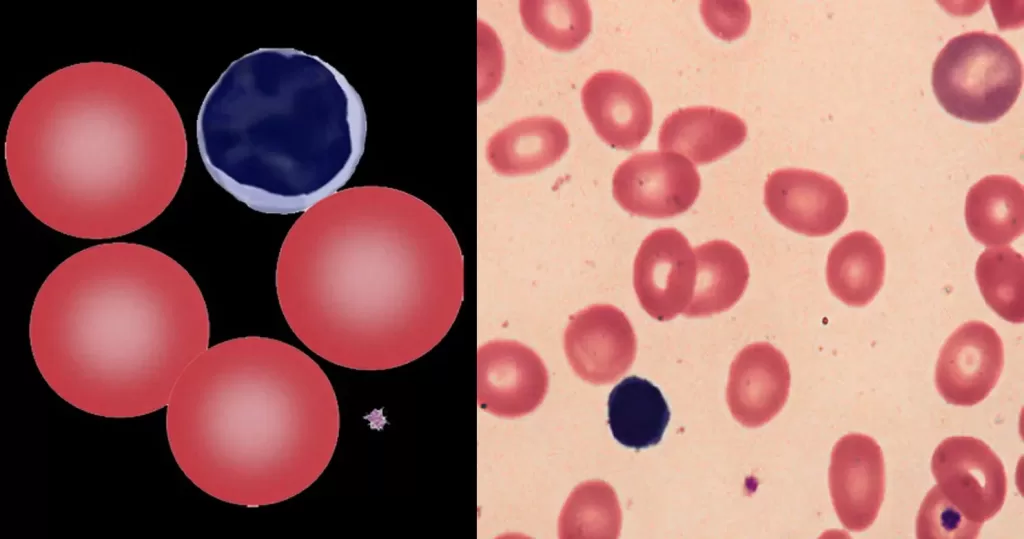
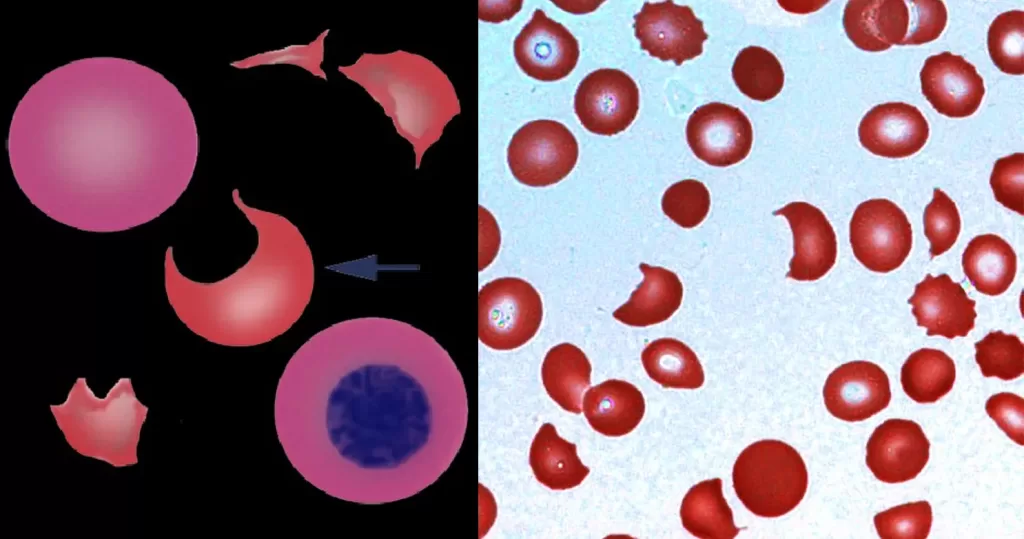
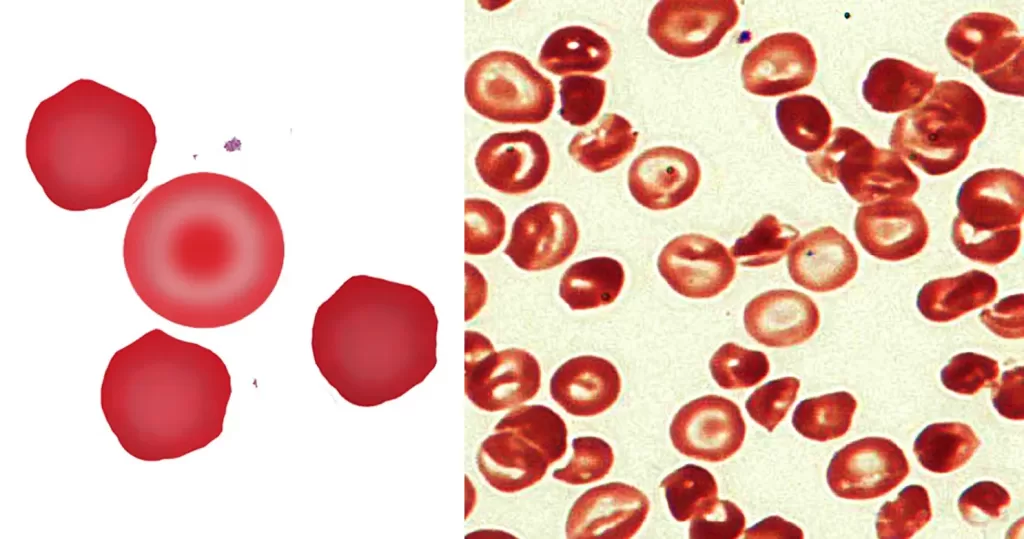
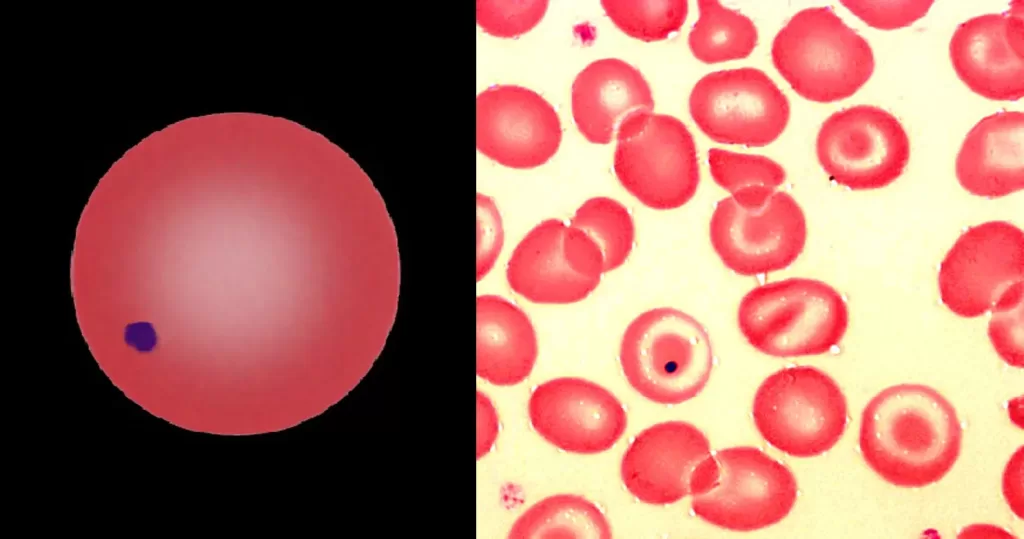
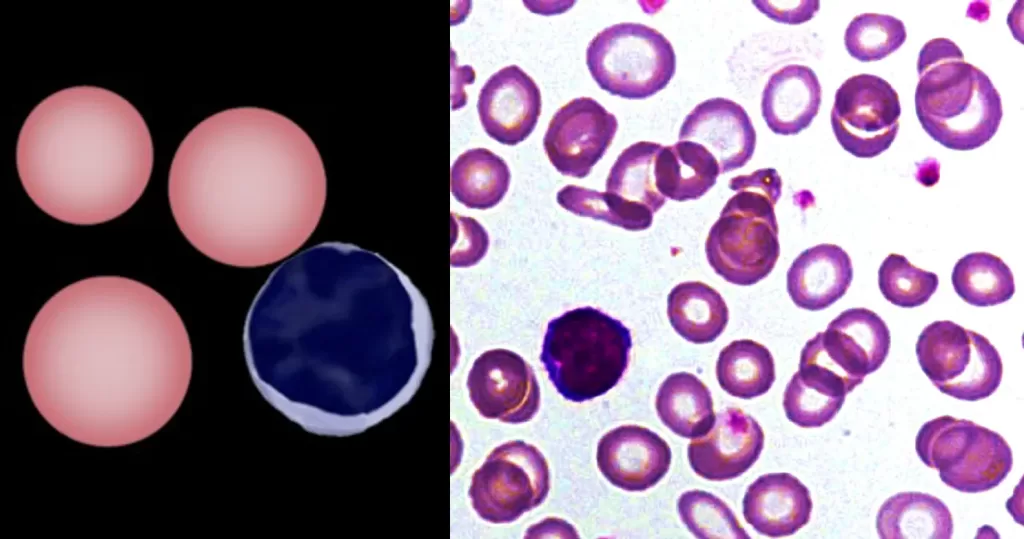
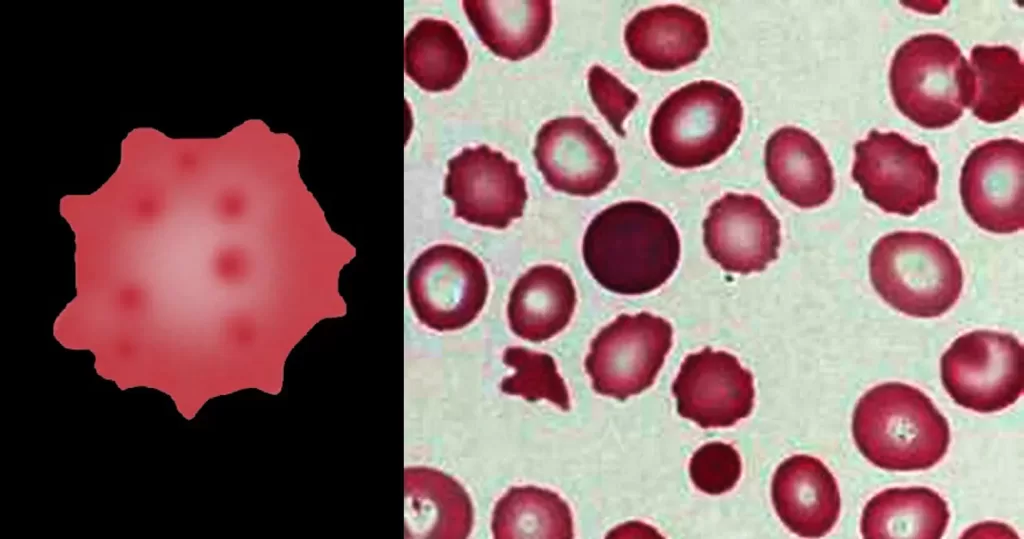
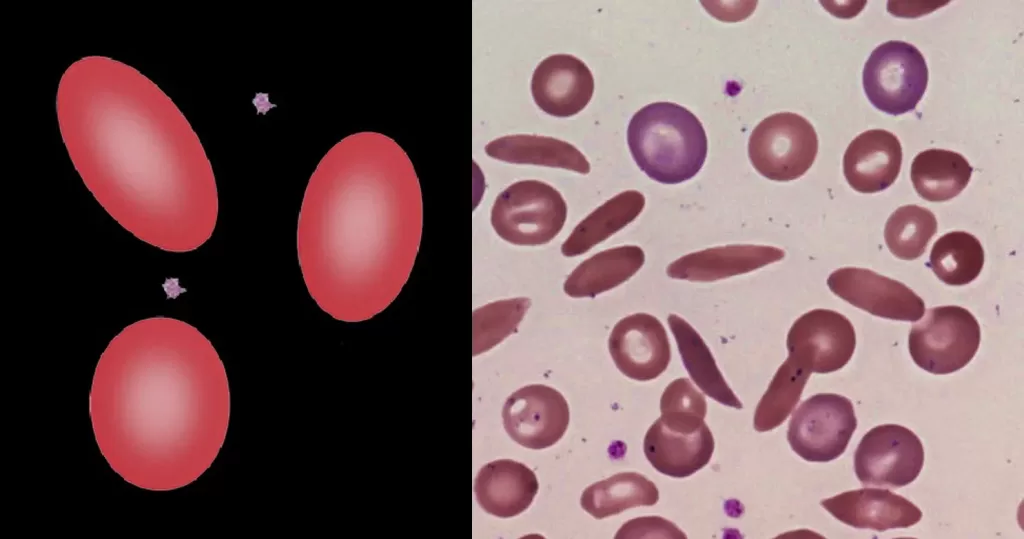
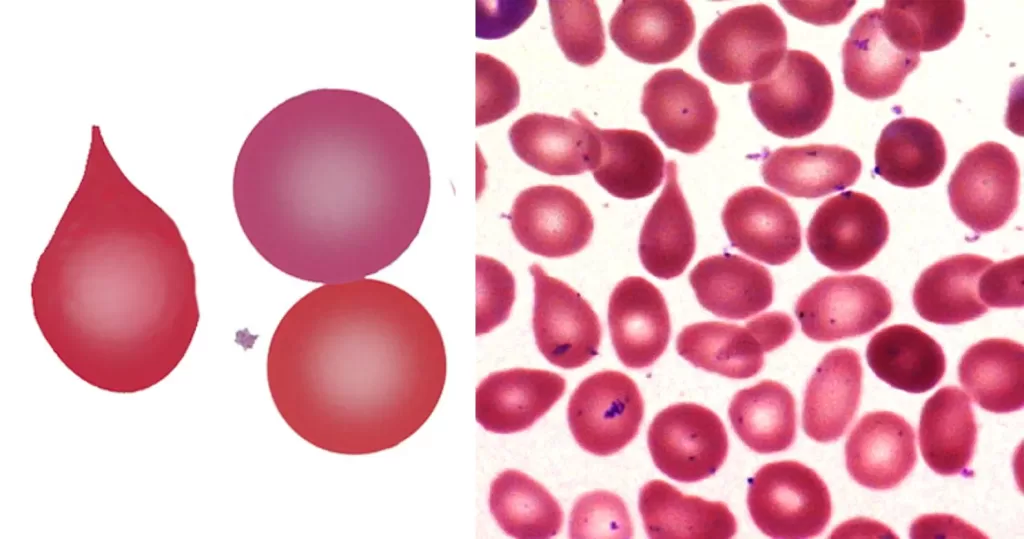
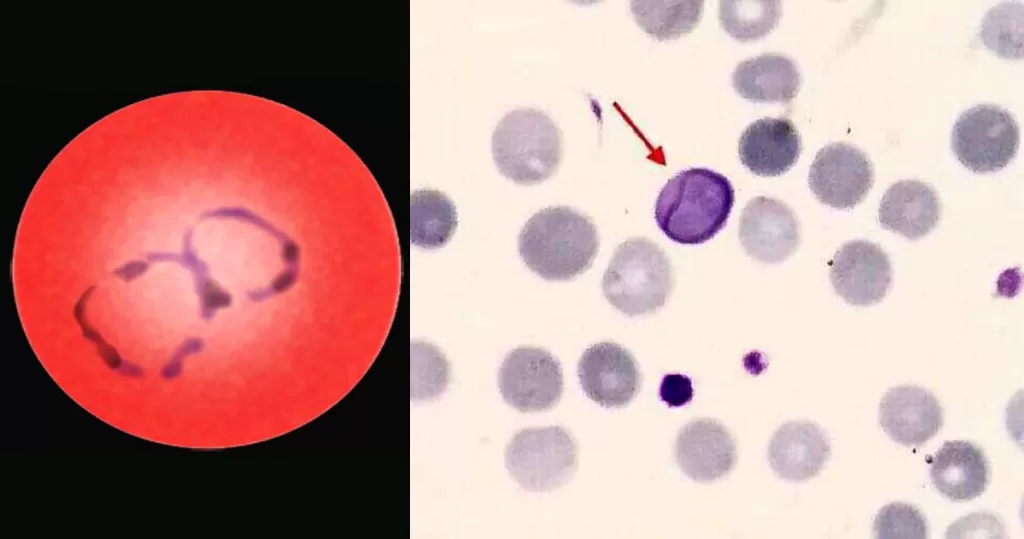
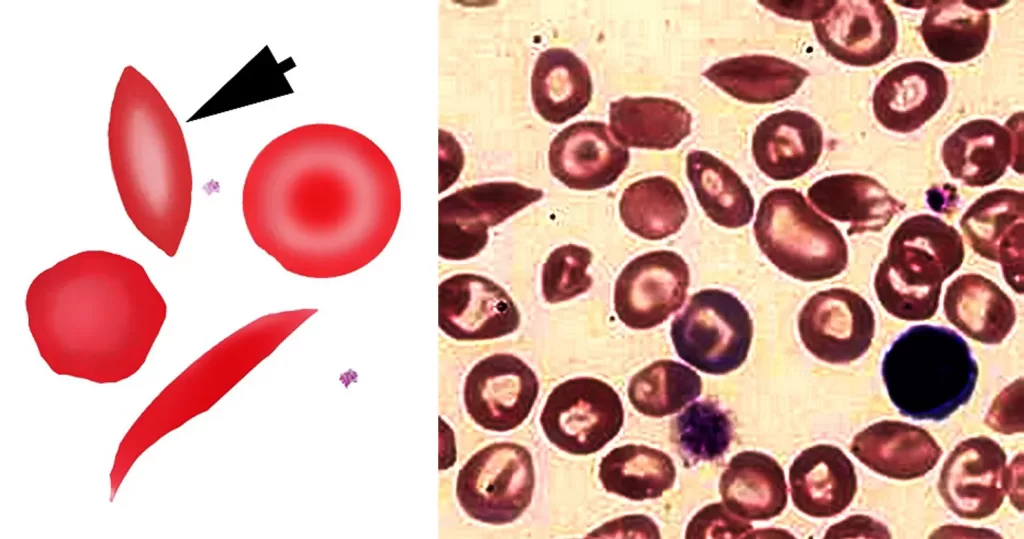
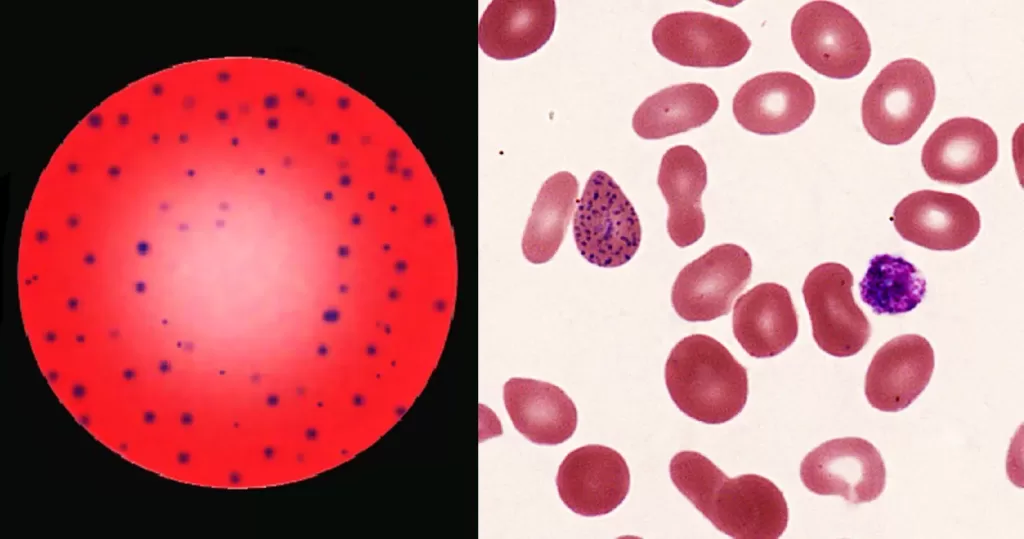
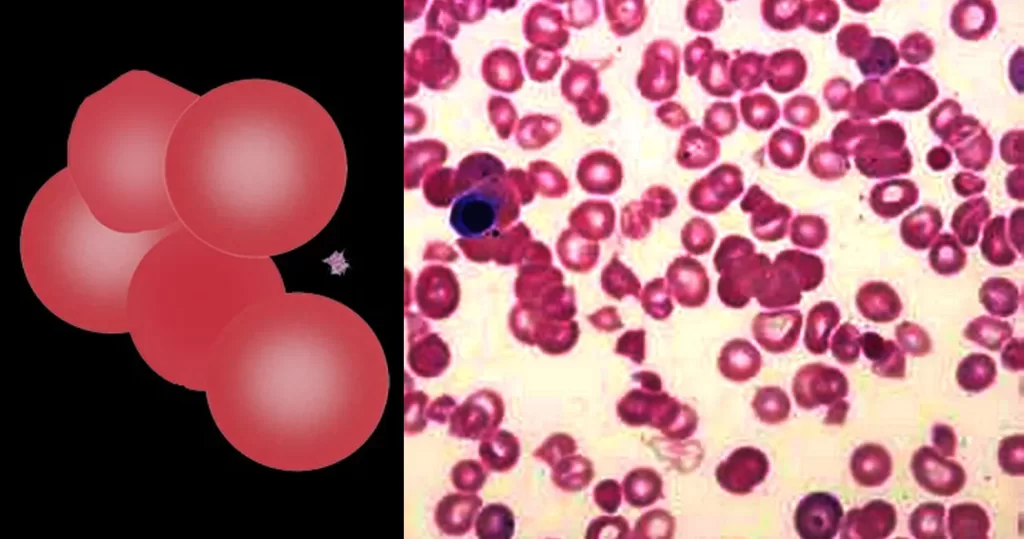
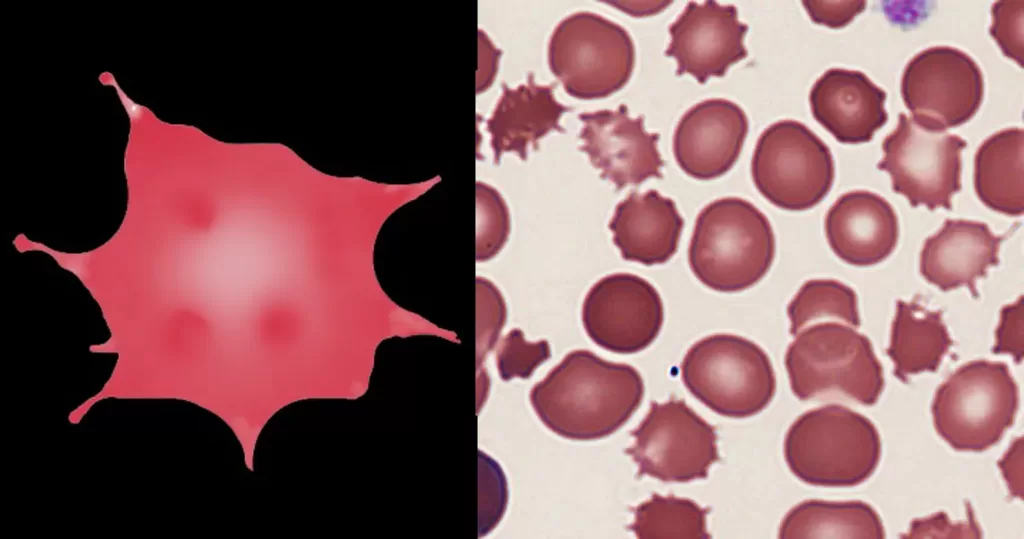
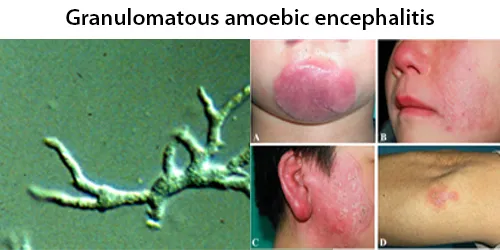
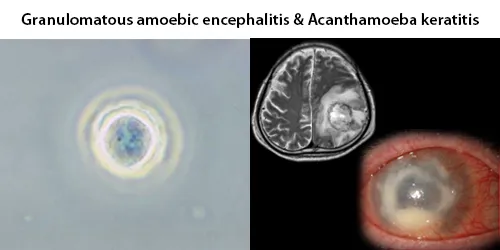
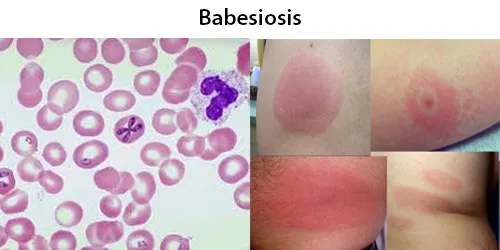
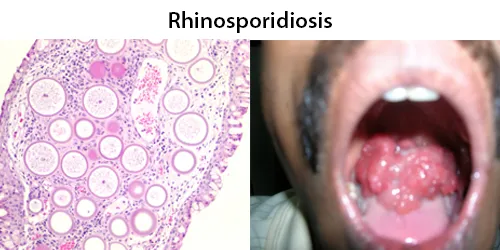
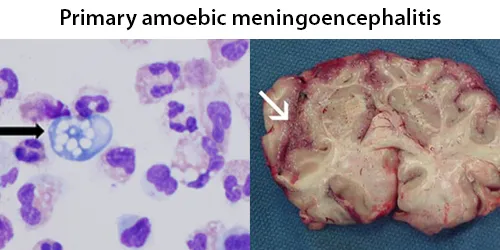
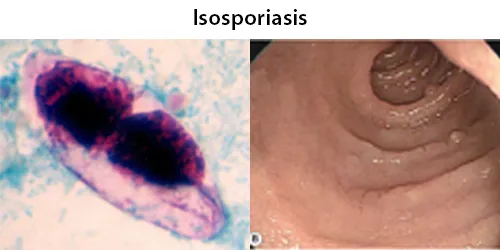
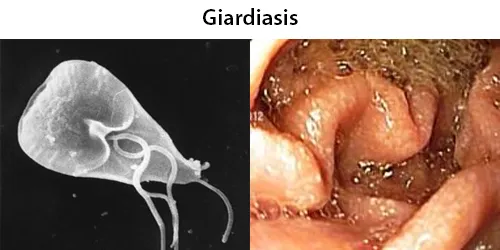
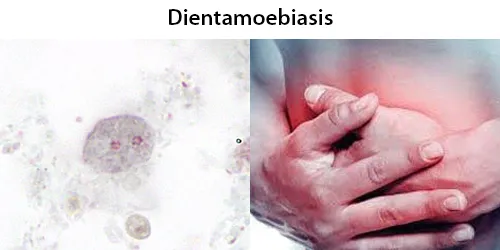
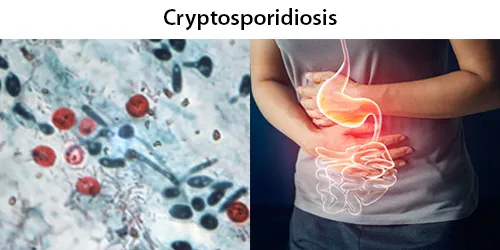
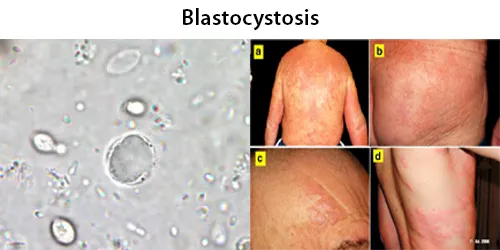
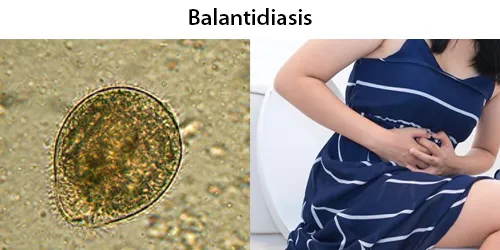
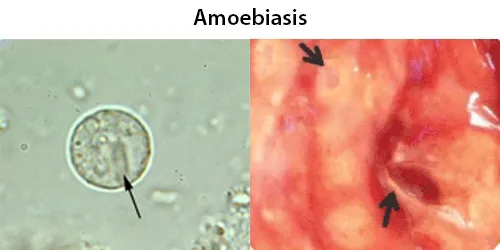
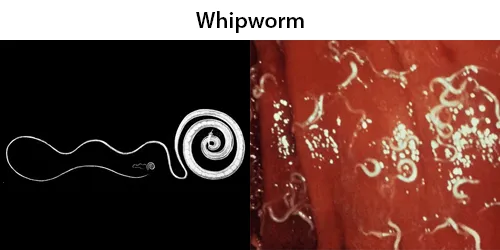
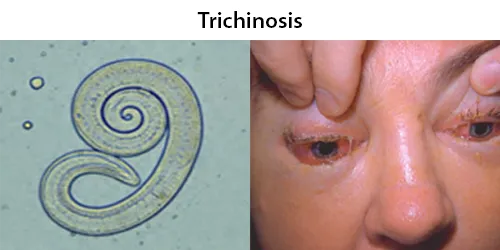
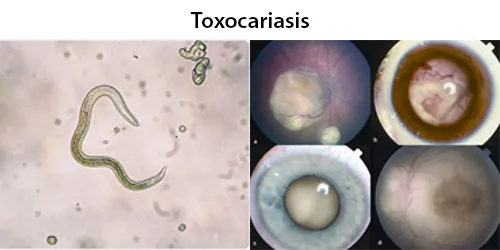
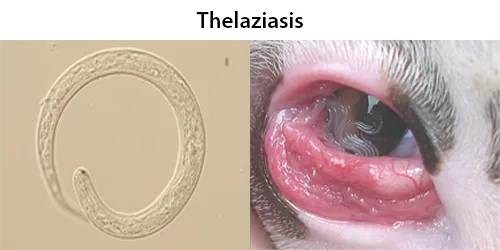
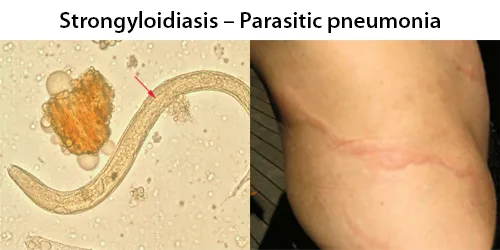
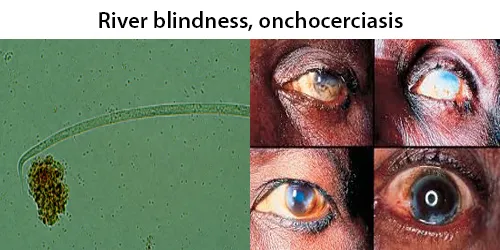
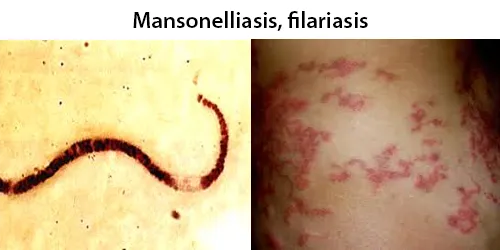
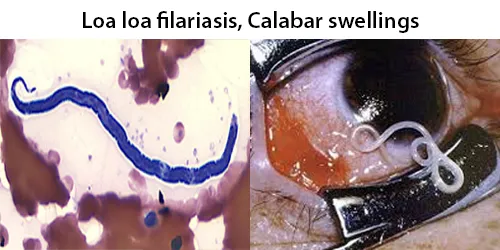
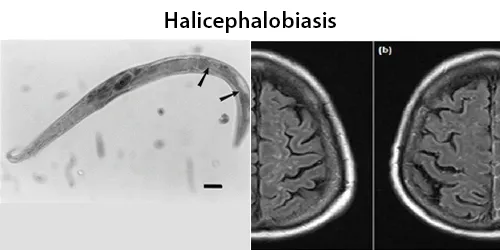
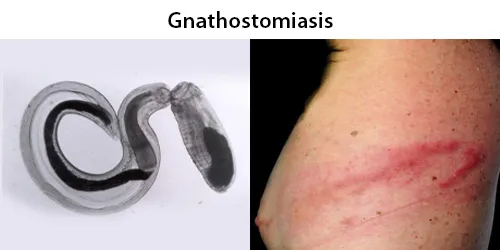
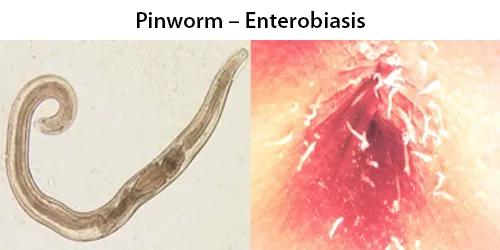
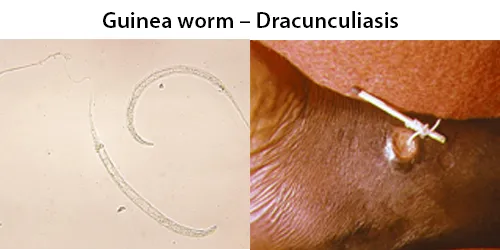
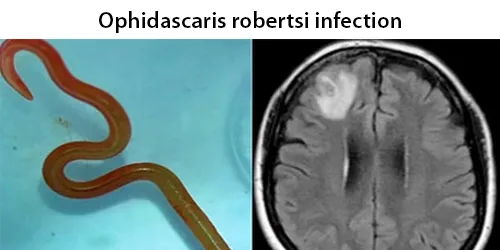
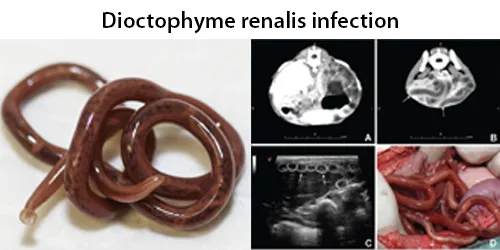
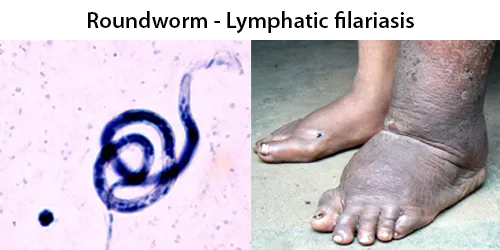
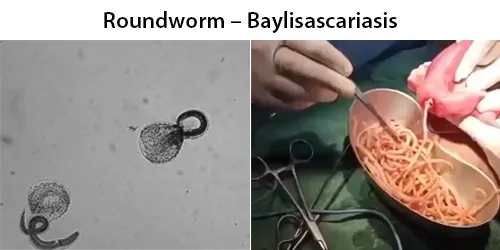
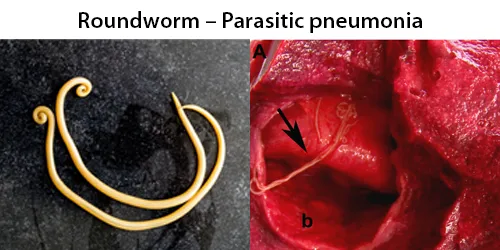
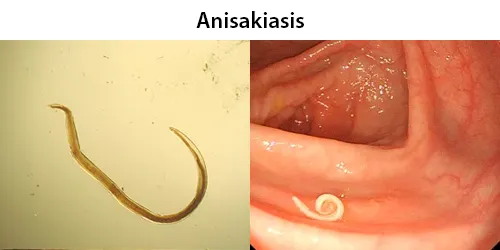
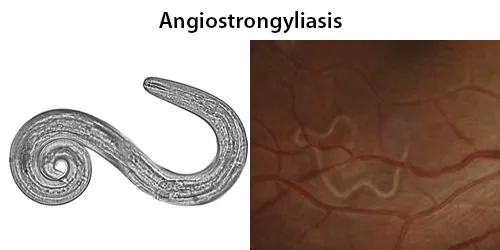
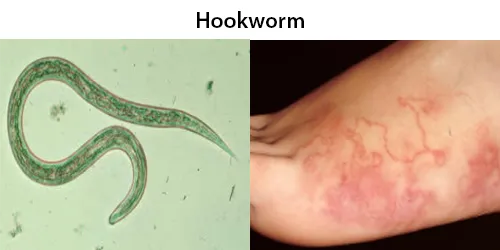
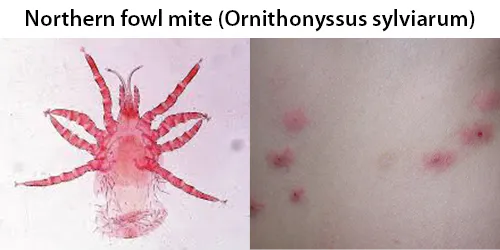
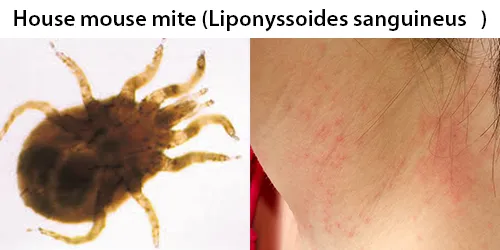
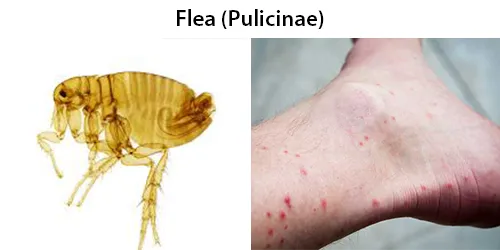
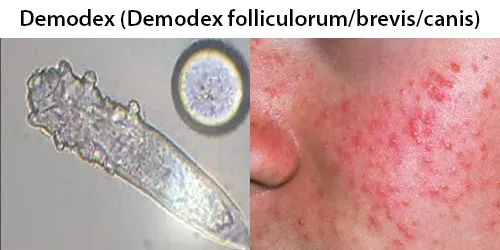
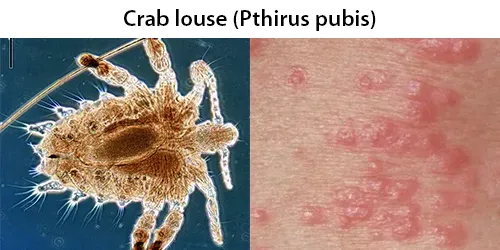
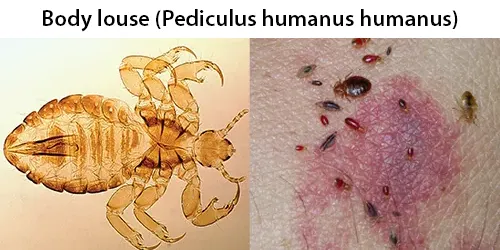
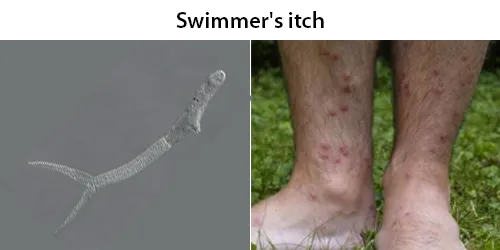
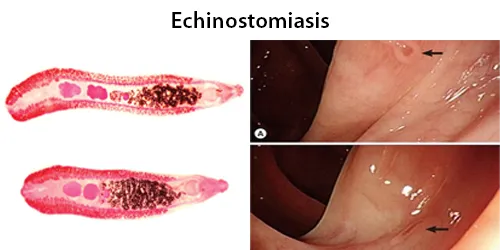
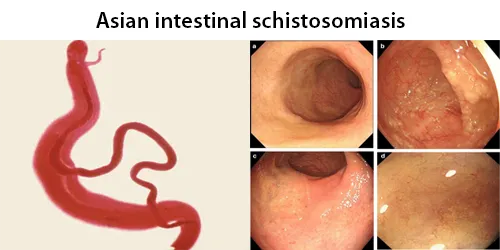
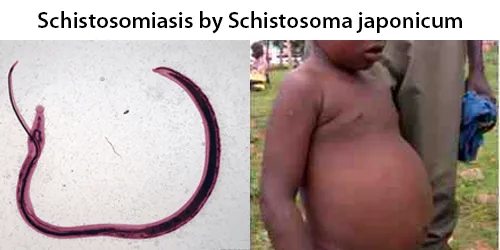
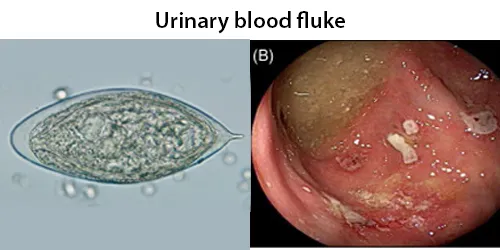
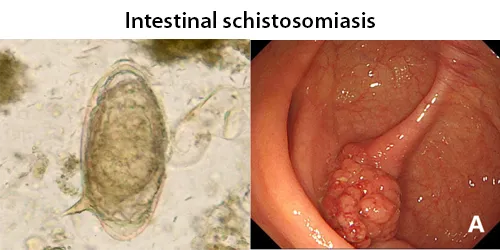
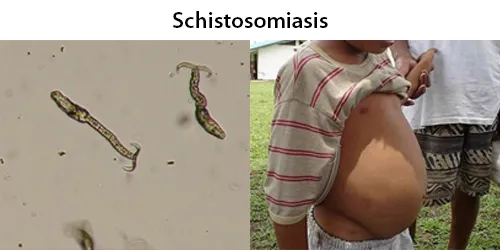
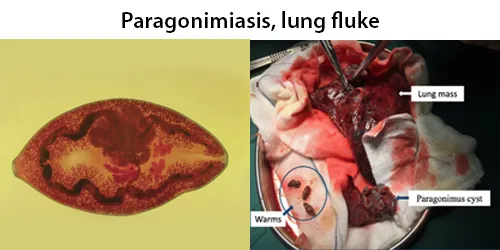
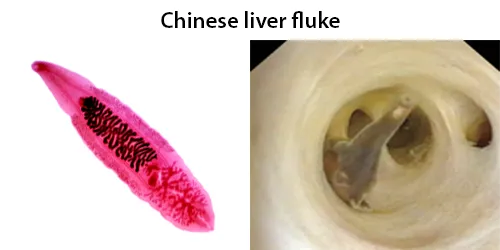
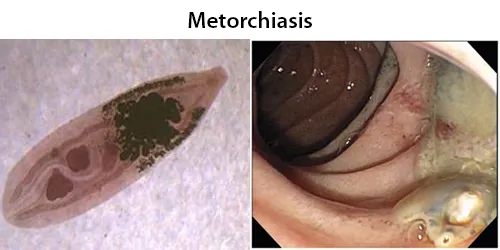
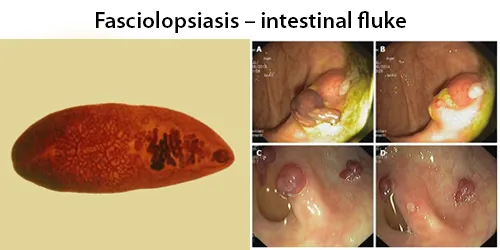
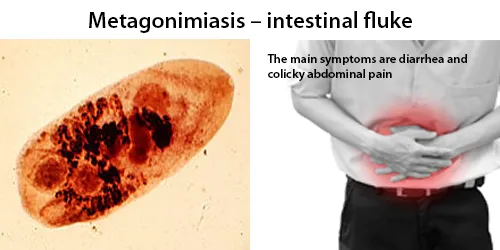
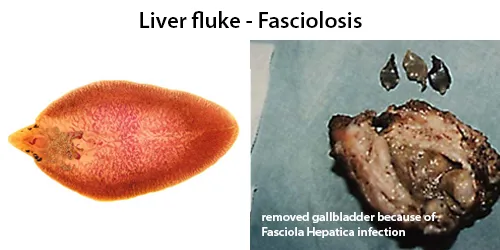
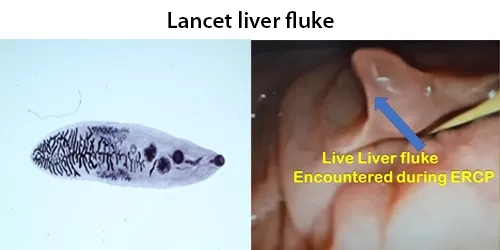
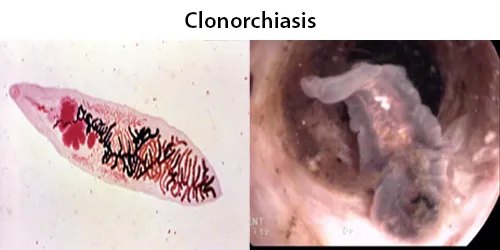
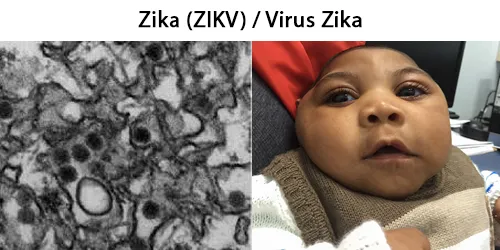
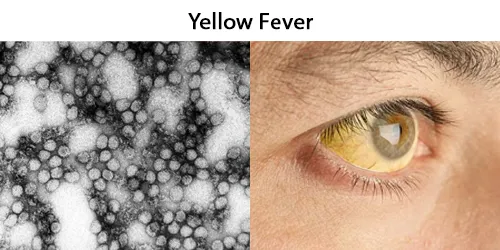
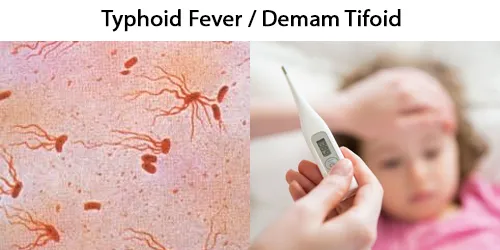
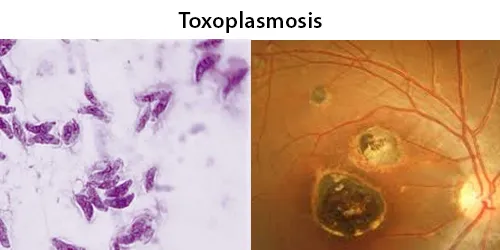
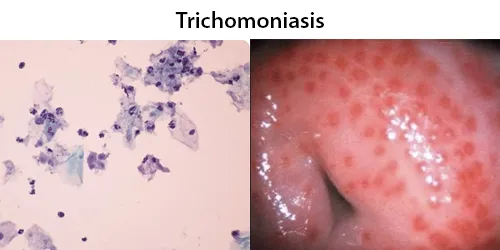
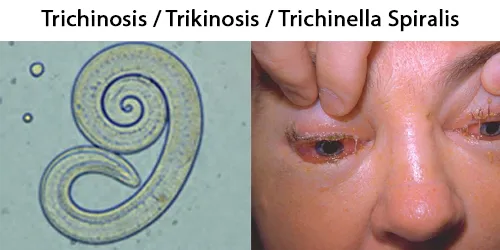
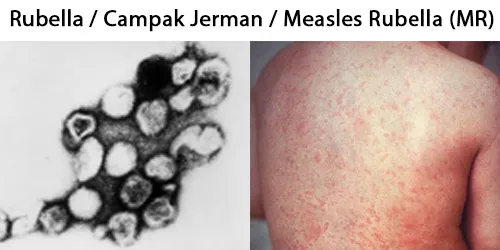
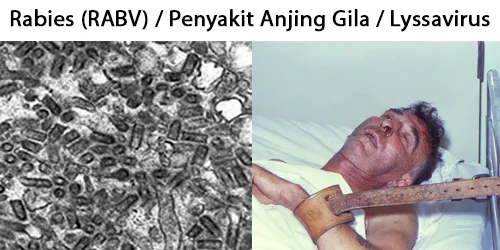
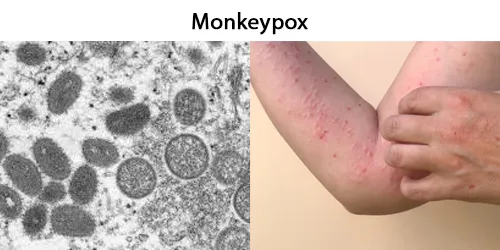
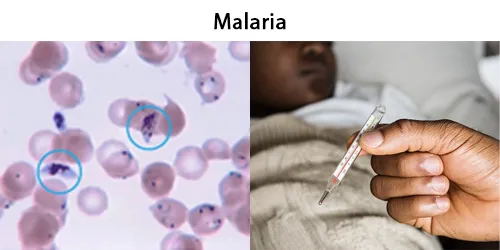
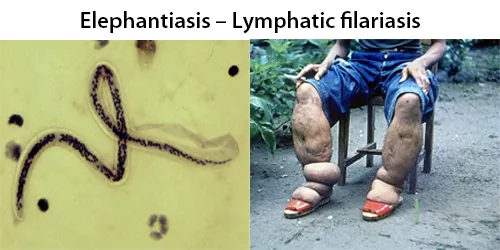
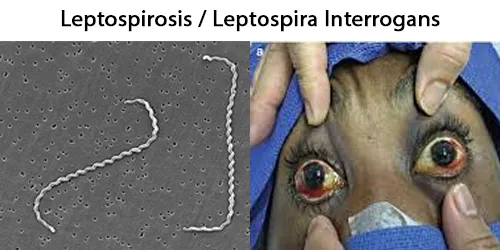
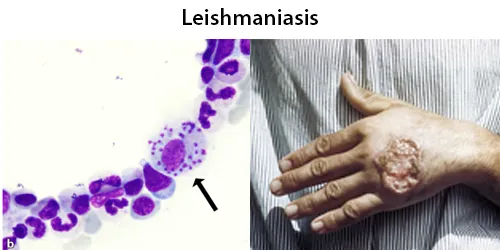
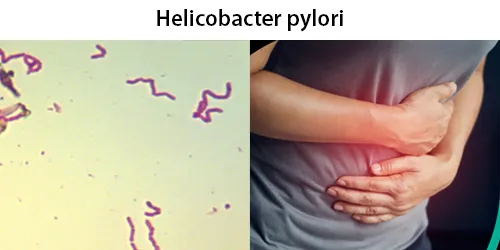
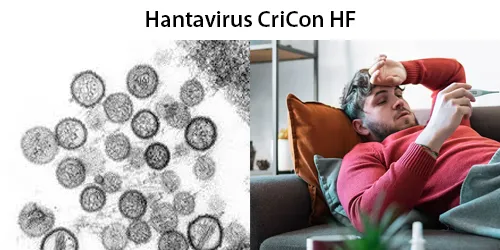
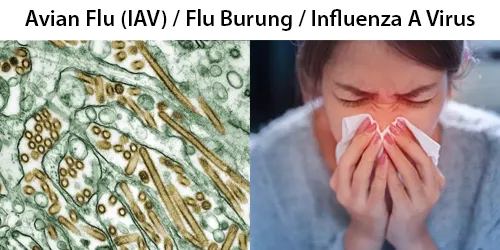
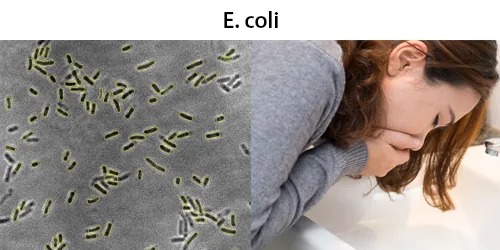
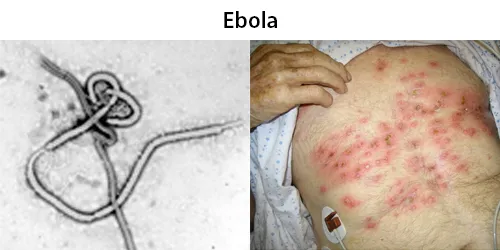
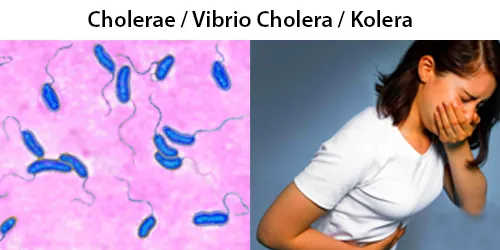
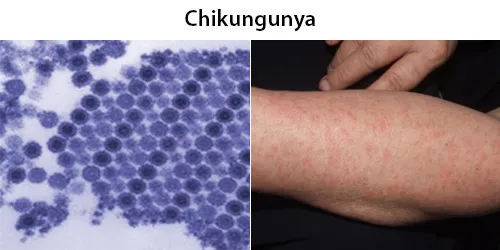
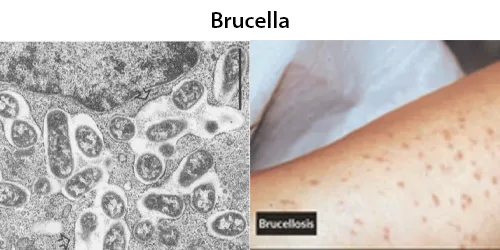
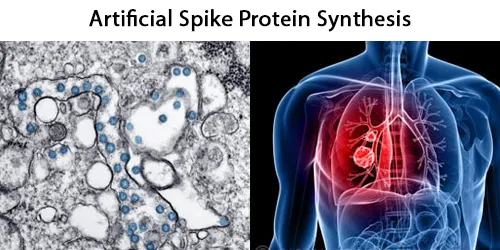
Clotting
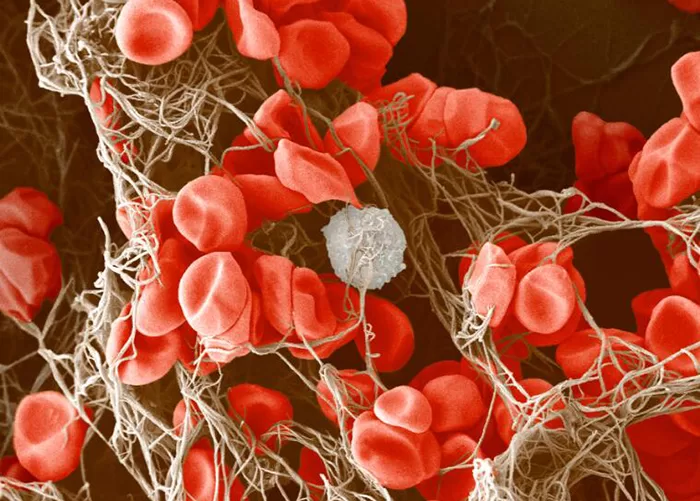
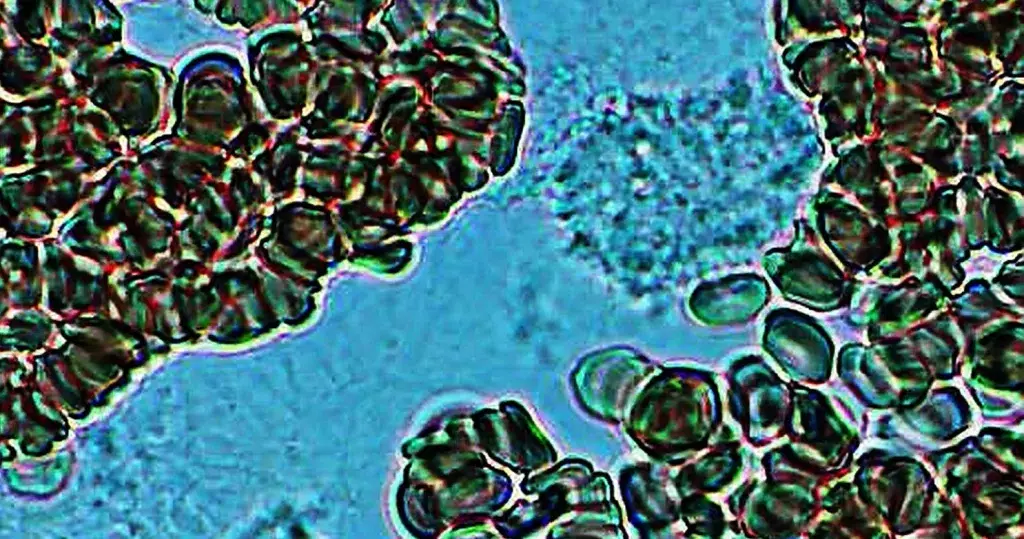
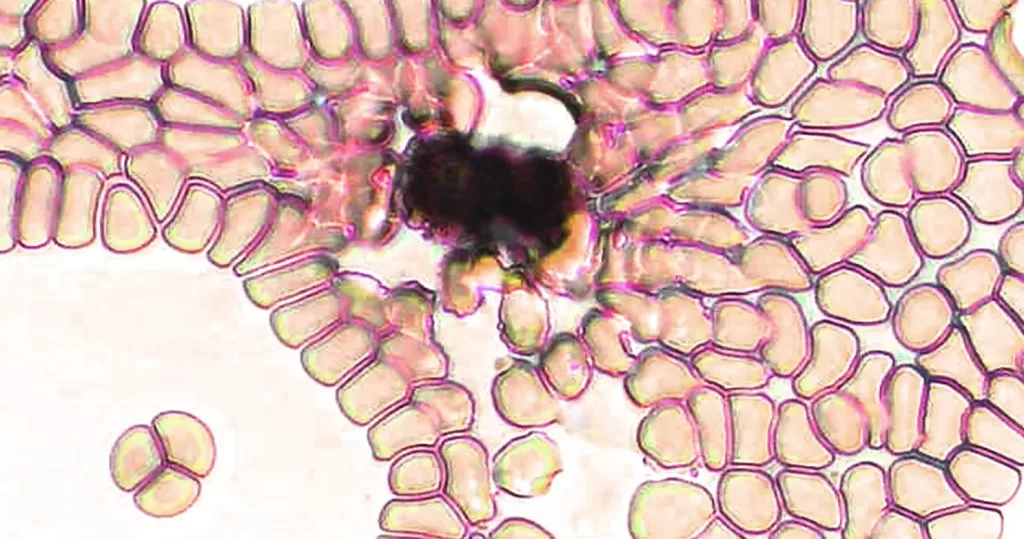
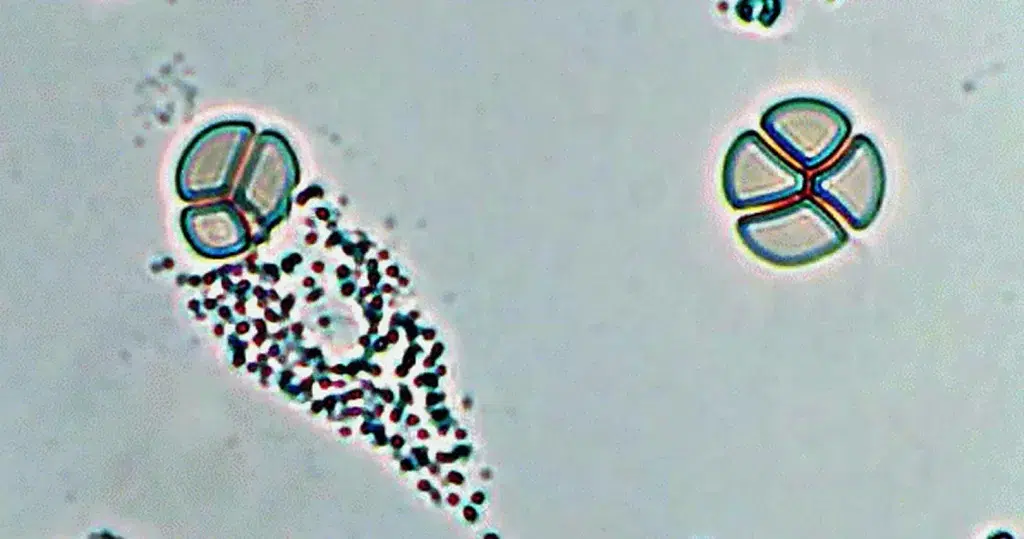
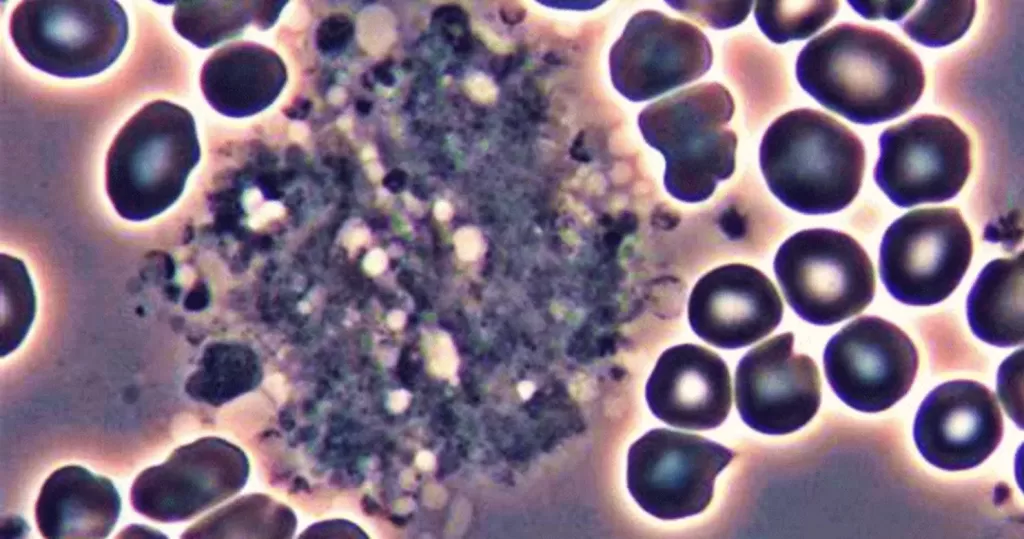
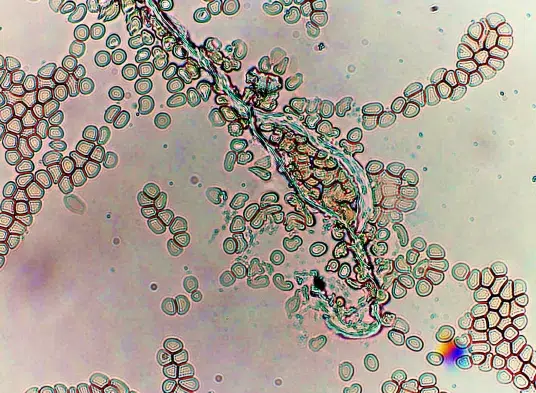
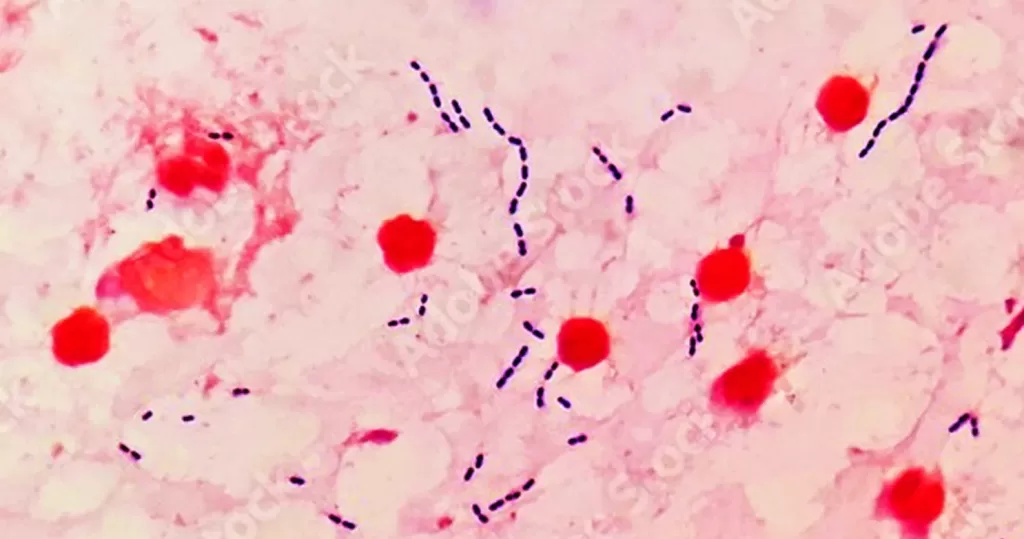
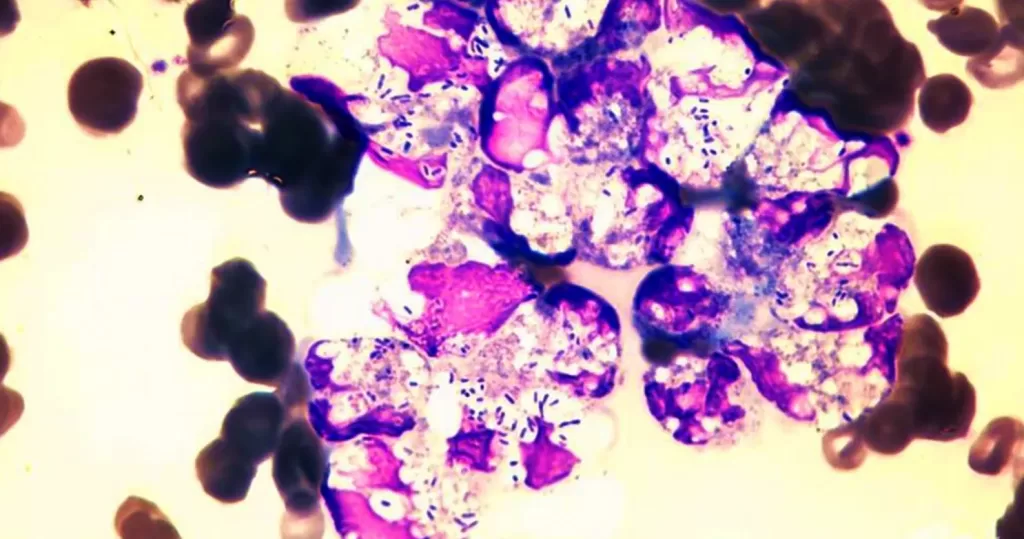
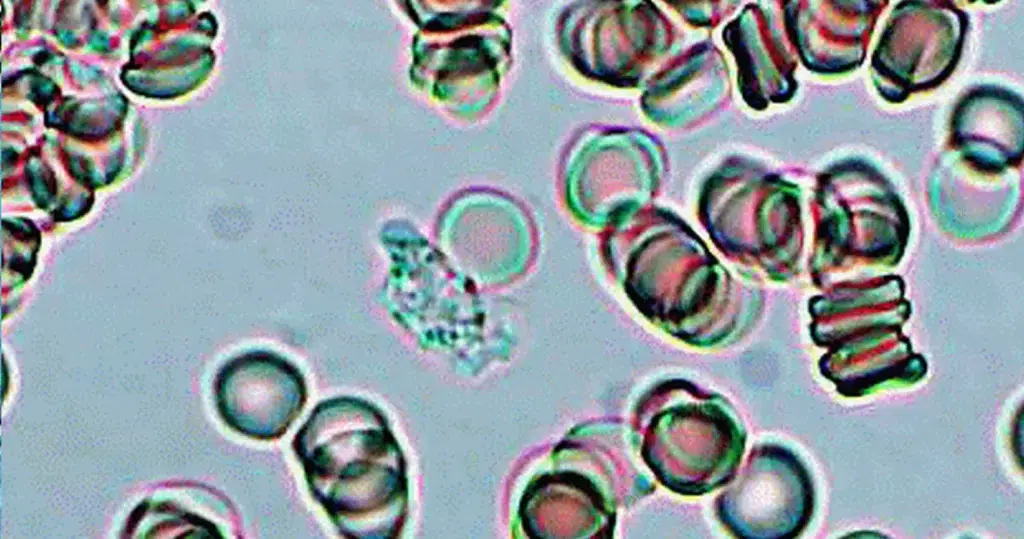
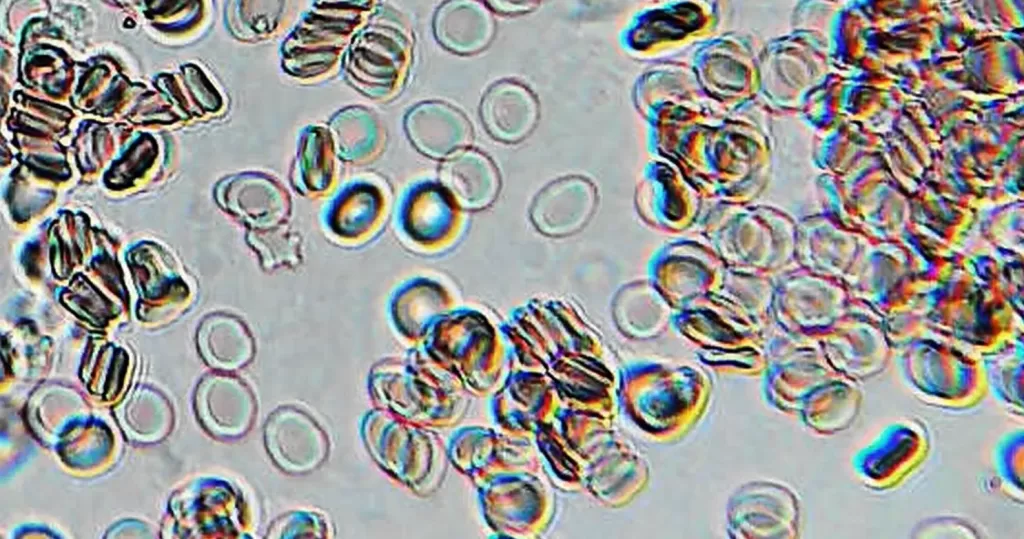
Clotting in live blood analysis refers to the formation of fibrin strands or blood clots, which occur when blood cells aggregate in an attempt to seal an injury or stop bleeding. Non-magnified blood observations can help identify clotting tendencies by looking for signs such as abnormal clumping of blood cells or the presence of fibrin strands in the serum. These clots may be indicative of underlying health issues like an inflammatory response, oxidative stress, or even blood coagulation disorders, including conditions such as thrombophilia or hypercoagulability. In some cases, excessive clotting can lead to poor circulation, increasing the risk of thrombosis, heart attack, or stroke.