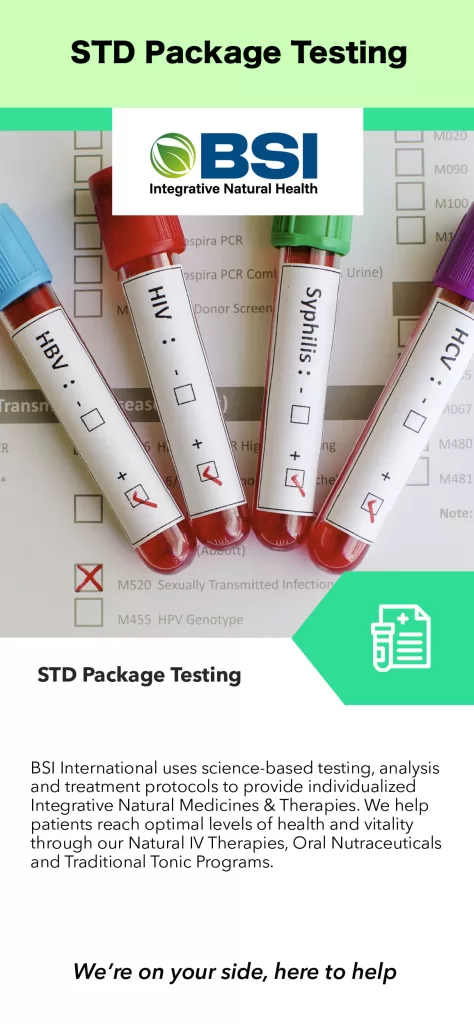
All diseases below tend to be sexually transmitted.
Full Testing Includes:
(All tests are optional – except prescribe by the BSI Practitioner)
Chlamydia trachomatis & Gonorrhea are similar and both extremely common. Almost 75% of female infections and 50% of male infections do not have symptoms.
Syphilis. False positive results may occur due to systemic lupus, leprosy, brucellosis, atypical pneumonia, typhus, yaws, pinta, or pregnancy.
Herpes Simplex Virus I (HSV-1 IgG – IgM) is more commonly associated with the mouth. Specific typing is not usually required for diagnosis or treatment. The herpes simplex virus is transmitted by direct contact with a sore or the body fluid of an infected individual.
Herpes Simplex Virus II (HSV-2 IgG – IgM) is more commonly associated with genital tract and neonatal infections. Specific typing is not usually required for diagnosis or treatment. The herpes simplex virus is transmitted by direct contact with a sore or the body fluid of an infected individual.
Trichomonas. Very common, caused by a protozoan parasite called Trichomonas vaginalis. Although symptoms of the disease vary, most people who have the parasite cannot tell they are infected.
Candida / Candidiasis. The official term for the yeast STD, is caused by a body out of balance, sexual transmission, or transmission through infected touch. In other words, it’s quite easy to get a genital yeast STD. This applies to both men and women.
Fungal / Yeast (unspecified) Diseases, which may include if observed; Chancroid, Donovanosis, Enteritis, Proctocolitis, Meningitis, Shigellosis. These fungal STDs are aquired through vaginal, oral, or anal sex. Even just touching can spread these infections to another person or to another site on one’s own body.
Mobilincus. Mobiluncus is an anaerobic, Gram-variable, curved bacillus, associated with bacterial vaginosis, also found in the bowel. Can be related to the use of the intrauterine contraceptive device (IUD). Mobiluncus tend to symbiotic with Gardnerella vaginalis, and some strains are antibiotic-resistant.
Gardnerella Vaginalis is the most common cause of bacterial vaginitis in the sexually active mature patient. Complaints may include a malodorous, non-irritating discharge, and gray-white secretions.
Staphylococcus (non-beneficial strains). S. aureus, or “staph”, is the same bacteria responsible for TSS, or Toxic Shock Syndrome, which is associated with the use of highly absorbent tampons. Antibiotic-resistant Staph strains are termed as MRSA. MRSA is primarily responsible for causing skin infections, pneumonia, soft tissues infections, and if left untreated can cause sepsis.
Non-beneficial Bacterial Strains. Extracell, Intracell, Intercell. Further identification of bacterial types, identifying if a bacteria is on the outside of a cell (Extracell) the inside of a cell (Intercell), or connecting cells together (Intracell).
Clue Cell. Vaginal epithelial cell, thickly coated with coccobacillary organisms. Clue cells are a hallmark of bacterial vaginosis.
Pregnancy test (Optional and additional fee)
Hepatitis A, B, C, D, E. Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. While we usually think of hepatitis A to E viruses, however anything that causes inflammation or damage to the liver can be considered as a form of hepatitis.
Specimen: Blood, urine, and vaginal swab or penile swab. The patient should not have urinated for at least one hour prior to specimen collection. Female patients should not cleanse the labial area prior to providing the specimen. Women should not be menstruating or recently finished menstruation for this test.
Fasting: No
Results: 2-3 business days
Also suggested:
Contact Us
Tel: +62 812 3838 4040
medical@bsi.international
WA: +62 878 6171 7442

@ 2025 Yayasan Biological Science Innovation. All rights reserved.
You can see how this popup was set up in our step-by-step guide: https://wppopupmaker.com/guides/auto-opening-announcement-popups/
WhatsApp us

The MXD count tracks the actual number of mid-range immune cells (eosinophils, basophils, and monocytes) in your blood. This value can help identify inflammation, allergies, or certain types of infections.

MXD % measures the percentage of mid-range cells, such as eosinophils, basophils, and monocytes, in the blood. These cells are part of your immune system and help fight infections. An abnormal value may indicate allergic reactions or infections.

The lymphocyte count measures the actual number of lymphocytes in your blood. A high or low lymphocyte count can indicate viral infections, immune deficiencies, or chronic conditions like leukemia.

LYM % is the percentage of lymphocytes (another type of white blood cell) in your blood. Lymphocytes play a key role in fighting viral infections and regulating immune responses. Abnormal lymphocyte levels may indicate viral infections or immune system disorders.

The neutrophil count measures the total number of neutrophils in your blood. High or low neutrophil counts can be a sign of infection, bone marrow issues, or immune disorders.

NEUT % refers to the percentage of neutrophils (a type of white blood cell) in your blood. Neutrophils help fight bacterial infections. An increase or decrease in neutrophils can indicate infection, inflammation, or other health conditions.

The WBC count measures the number of white blood cells in your blood. White blood cells help fight infections and protect the body from diseases. An abnormal WBC count could indicate infections, immune disorders, or blood cancers.

Similar to RDW-SD, RDW-CV evaluates the variability in red blood cell sizes, but using a different method. An increased RDW-CV is often associated with nutrient deficiencies or blood disorders.

RDW-SD measures the variation in the size of your red blood cells. High RDW can indicate anemia, iron deficiency, or other blood-related disorders, helping doctors understand the cause of blood cell abnormalities.

PDW assesses the variation in the size of your platelets. High PDW values may suggest certain platelet disorders or bone marrow problems, which affect clotting and bleeding.

MPV measures the average size of your platelets. Larger platelets can indicate an increased platelet production in response to blood loss or disorders like bone marrow conditions.

The PLR ratio compares the number of platelets to lymphocytes in the blood. An increased ratio can be linked to inflammation or certain cancers, helping doctors monitor inflammatory diseases or immune responses.

Platelet count measures the number of platelets in your blood. Platelets help with clotting and stopping bleeding. Abnormal platelet counts can indicate bleeding disorders or risks of excessive clotting.

MCHC is a measure of the concentration of hemoglobin in a given volume of red blood cells. It helps to determine if your red blood cells are normal or if they are more concentrated, as seen in certain conditions like spherocytosis.

MCH measures the average amount of hemoglobin inside each red blood cell. It helps assess the oxygen-carrying capacity of your red blood cells. Abnormal MCH levels can indicate anemia or other blood-related disorders.

MCV refers to the average size of your red blood cells. It is used to help classify the type of anemia. A higher or lower MCV may indicate specific conditions, such as vitamin deficiencies or dehydration.

The reticulocyte count measures the number of immature red blood cells in your blood. This helps doctors assess your bone marrow’s ability to produce new red blood cells, which is important in diagnosing anemia and monitoring blood loss recovery.

The HGB/HCT ratio compares the amount of hemoglobin in the blood (HGB) to the total volume of red blood cells (HCT). It helps in identifying potential issues like anemia or dehydration. A balanced ratio is important for proper oxygen transport in the body.

Hematocrit is the proportion of red blood cells in your blood. It is measured as a percentage of total blood volume. Abnormal levels of hematocrit may indicate dehydration or other medical conditions.

Hemoglobin is the protein inside red blood cells that binds to oxygen and transports it through the body. A low hemoglobin level indicates anemia, which means you don’t have enough healthy red blood cells to carry oxygen throughout your body.
Normal Range: 13.8 to 17.2 grams per deciliter (g/dL) for men, and 12.1 to 15.1 g/dL for women.

Red blood cells are responsible for carrying oxygen from your lungs to the rest of your body and returning carbon dioxide from your body to your lungs to be exhaled. A normal RBC count helps detect various health conditions such as anemia or dehydration.
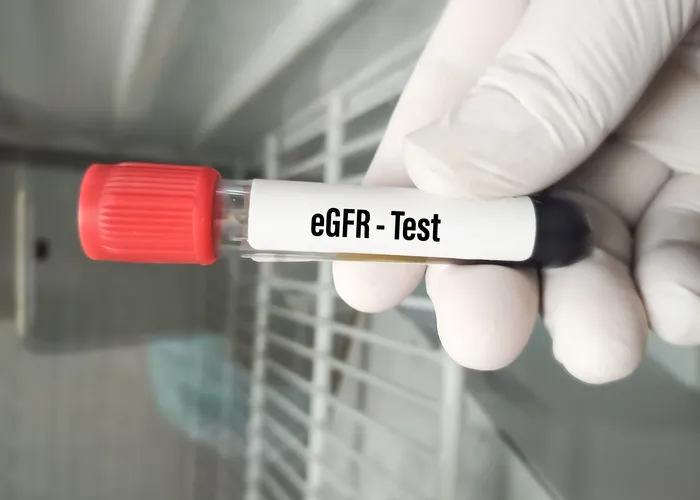
Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate (eGFR) is a test used to assess how well your kidneys are functioning. It is a calculation based on your serum creatinine level, age, sex, and sometimes race. The result gives an estimate of how much blood your kidneys filter per minute, which is a measure of kidney function.
The eGFR is important because it helps identify kidney damage or disease early, even before symptoms appear. A normal eGFR is typically 90 mL/min/1.73 m² or higher, but this can vary based on individual factors like age and sex.
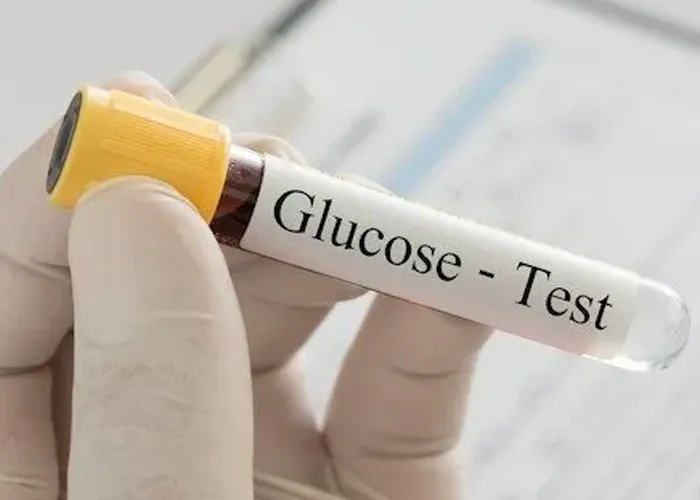
A non-fasting glucose test measures the level of glucose (sugar) in your blood after eating. This test differs from a fasting glucose test, which measures blood glucose after an overnight fast. Understanding non-fasting glucose levels helps identify potential issues with blood sugar regulation, such as hypoglycemia (low blood glucose) or hyperglycemia (high blood glucose), and determine if medical attention is needed.

Uric acid is a waste product produced from the breakdown of nucleic acids in the body. It is normally found in the blood and urine. High levels of uric acid are commonly associated with gout, a condition characterized by painful, swollen joints due to the buildup of uric acid crystals. Elevated uric acid levels can also occur as a side effect of treatments like chemotherapy or radiation therapy. Additionally, an excessive buildup of uric acid can lead to the formation of uric acid kidney stones, which are hard deposits that can cause pain, urinary obstruction, and other health problems if they move or become lodged in the urinary tract.

The BUN/Creatinine ratio is a blood test that compares the levels of blood urea nitrogen (BUN) to creatinine in the blood. It is used as a screening tool to help detect kidney disease and other health issues. The normal BUN/creatinine ratio typically ranges from 10:1 to 20:1. This ratio is a better indicator of kidney function than BUN or creatinine levels alone. A high ratio can suggest conditions like congestive heart failure, gastrointestinal bleeding, or dehydration, while a low ratio may indicate malnutrition or liver disease.
The BUN/Creatinine ratio calculator helps assess kidney function by comparing the levels of BUN and creatinine in the blood. Through this method, doctors can determine how efficiently your kidneys are filtering waste products from the blood and identify any underlying abnormalities.

Creatinine is a waste product produced from the normal breakdown of muscle tissue and the digestion of protein in food. It is filtered out of the blood by the kidneys and excreted in urine. While small amounts of creatinine are always present in the blood, high levels can indicate a potential kidney problem. The serum creatinine test measures the amount of creatinine in the blood to assess how well the kidneys are functioning. This test is commonly used to check kidney health, monitor chronic kidney disease, and track kidney function changes over time. It is often part of routine health checks or used when kidney issues are suspected.
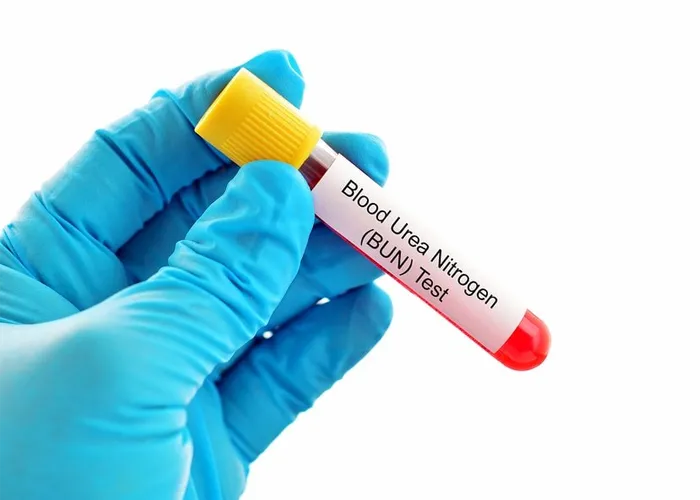
Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) is a test that measures the amount of urea nitrogen in your blood. Urea nitrogen is a waste product formed when the liver breaks down protein. It travels through the bloodstream, is filtered by the kidneys, and is excreted in urine. If the liver or kidneys aren’t functioning properly, urea nitrogen may build up in the blood. BUN levels are used to assess kidney function and can help diagnose kidney disorders or monitor treatment effectiveness for kidney disease.

Albumin is the most abundant protein in the blood. It is produced by the liver and plays a crucial role in maintaining proper fluid balance in the body by helping to “pull” excess fluid from tissues back into the bloodstream. Albumin also transports substances like hormones, medications, and enzymes throughout the body. Low albumin levels can indicate liver or kidney problems, as the kidneys may allow albumin to leak into the urine when they are not functioning properly. A blood test can measure the amount of albumin to help diagnose and monitor liver and kidney conditions.
Total bilirubin is the sum of two forms of bilirubin in the blood: direct (conjugated) bilirubin and indirect (unconjugated) bilirubin. Indirect bilirubin is transported to the liver, where it is converted into direct bilirubin by binding with glucuronic acid. The direct bilirubin is then excreted in bile. Elevated total bilirubin levels can indicate various health issues, such as liver disease, bile duct obstruction, or conditions like neonatal jaundice.
Direct bilirubin, also known as conjugated bilirubin, is a form of bilirubin that has been processed in the liver and attached to glucuronic acid. This makes it water-soluble, allowing it to be excreted in bile. Elevated levels of direct bilirubin can indicate various health conditions related to liver or bile duct problems. Diseases causing high bilirubin levels are classified into three categories: pre-hepatic (due to conditions like hemolytic anemia, affecting indirect bilirubin), hepatic (liver-related issues), and post-hepatic (due to blockages like gallstones or tumors in the bile ducts, leading to high direct bilirubin).
The SGOT (Serum Glutamic Oxaloacetic Transaminase) to SGPT (Serum Glutamic-Pyruvic Transaminase) ratio is a valuable metric used in medicine to assess liver health and identify potential liver issues. These enzymes, primarily found in liver cells, help in various metabolic processes. Monitoring their ratio can provide valuable insights into the functioning of this vital organ.

Serum glutamic pyruvic transaminase, an enzyme that is normally present in liver and heart cells. SGPT is released into blood when the liver or heart are damaged. The blood SGPT levels are thus elevated with liver damage (for example, from viral hepatitis) or with an insult to the heart (for example, from a heart attack). Some medications can also raise SGPT levels. Also called alanine aminotransferase (ALT).
Serum glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase (SGOT or AST) is an enzyme found in the liver, heart, and other tissues. A high level of SGOT released into the blood may be a sign of liver or heart damage, cancer, or other diseases. Also called aspartate transaminase and serum glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase.
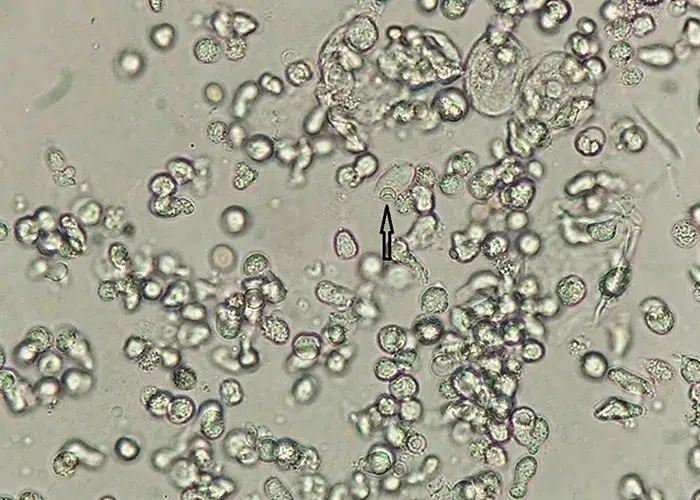
Trichomonas is a genus of anaerobic excavate parasites, and is estimated to be the most prevalent non-viral STI worldwide. Infection rates in men and women are similar but women are usually symptomatic, while infections in men are usually asymptomatic. Transmission usually occurs via direct, skin-to-skin contact with an infected individual, most often through vaginal intercourse. 160 million cases of infection are acquired annually worldwide.
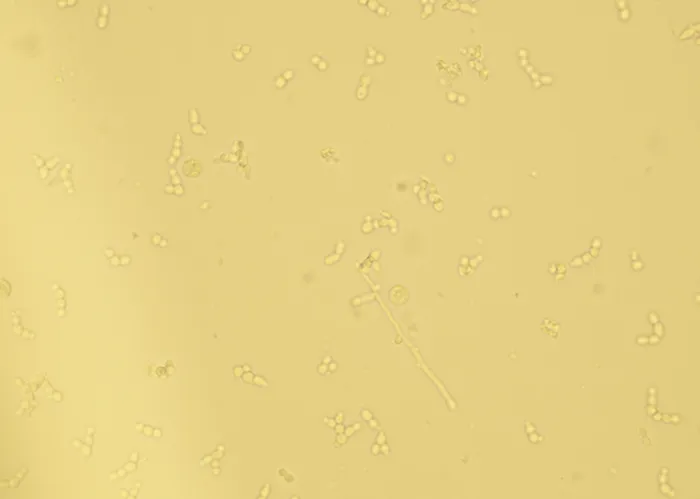
Sometimes found in urine particularly in cases of fungal infections.
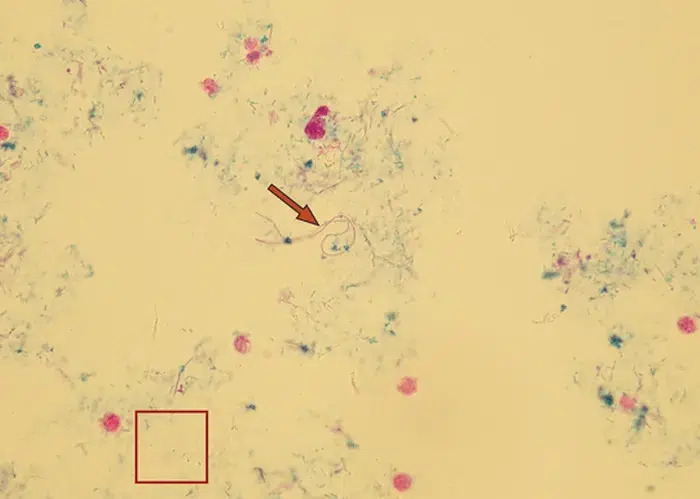
Their presence typically signals a urinary tract infection (UTI)
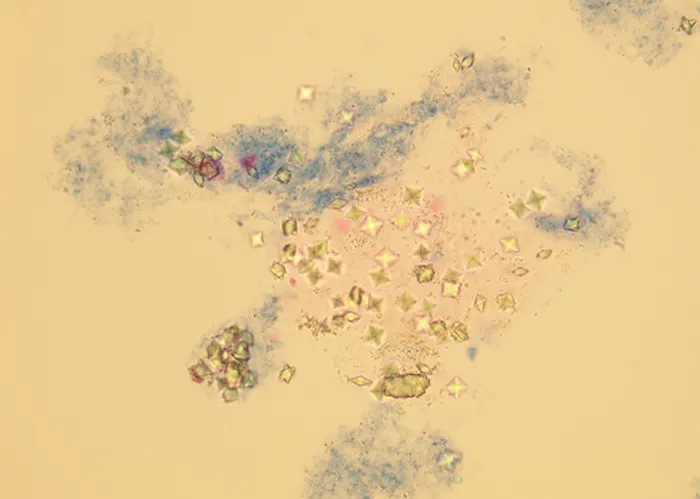
Certain types of crystals can form in the urine and may be a sign of kidney stones or metabolic disorders.
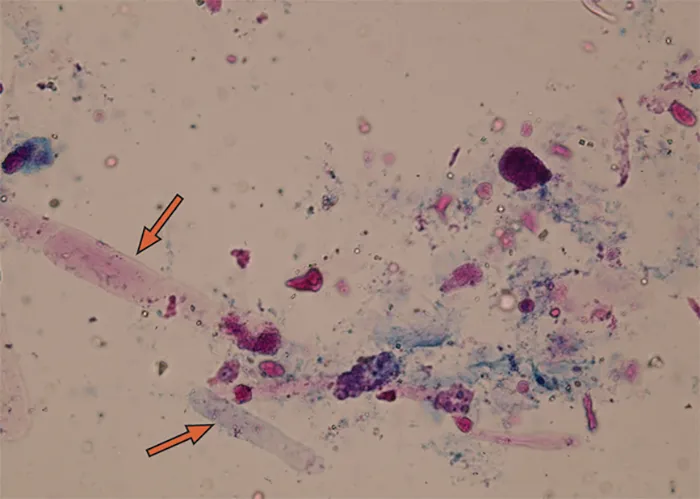
These are tube-shaped structures formed in the kidneys, and their presence can indicate kidney disease.
High numbers suggest infection or inflammation in the urinary system.
Their presence could indicate bleeding in the urinary tract or kidneys.
“Odd biologicals” is a term used in live blood analysis to refer to unusual or atypical structures observed in the blood that do not belong to the typical range of red blood cells, white blood cells, or platelets. For example, the presence of abnormal cell shapes or unexplained inclusions in the blood could point to issues with cell regeneration, genetic mutations, or other underlying conditions. “Odd biologicals” could also refer to artifacts introduced by external factors such as improper blood collection techniques or contamination during sample preparation.
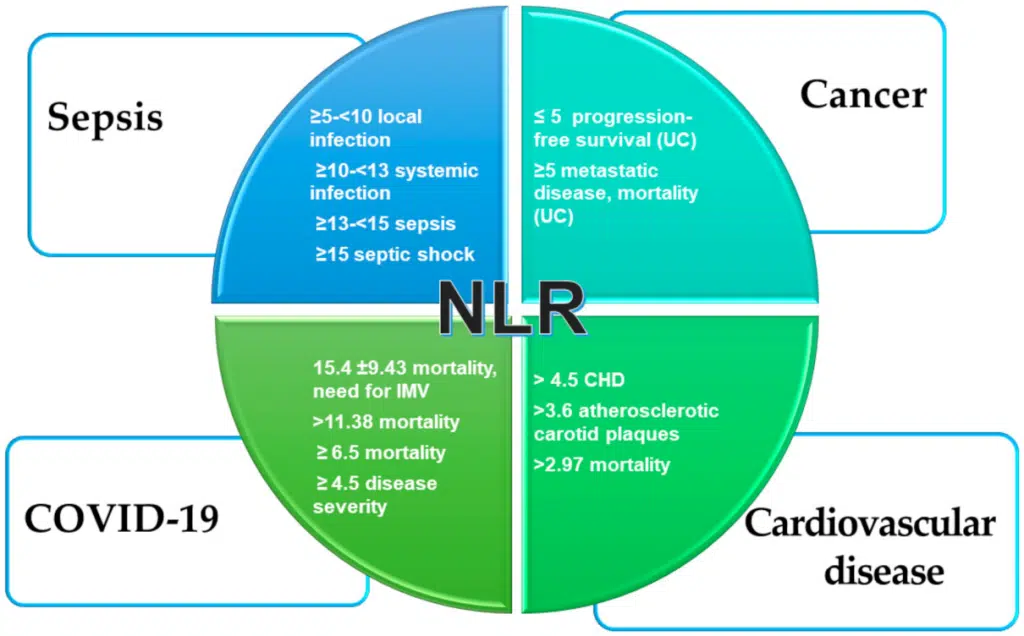
The Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR) is a significant biomarker used in live blood analysis to assess the balance between neutrophils and lymphocytes, two critical types of white blood cells involved in the body’s immune response. Neutrophils are the first responders to infection or injury, playing a key role in the inflammatory response, while lymphocytes are responsible for adaptive immunity, including the recognition of pathogens and immune memory.
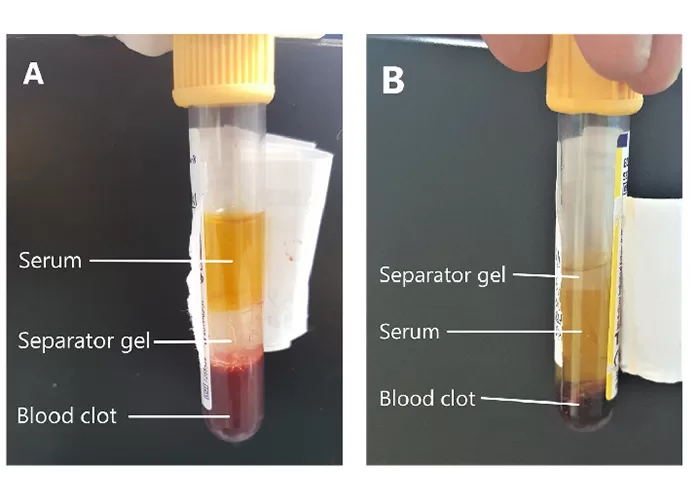
In live blood analysis, serum refers to the liquid portion of the blood that remains after the blood cells have been separated through clotting. It is a key focus in non-magnified blood observations because it provides valuable information about the biochemical state of the body. The serum contains proteins such as albumin and globulins, electrolytes like sodium and potassium, as well as metabolic waste products and hormones. Observing the serum in its natural state can help identify imbalances, nutrient deficiencies, or the presence of inflammatory markers.
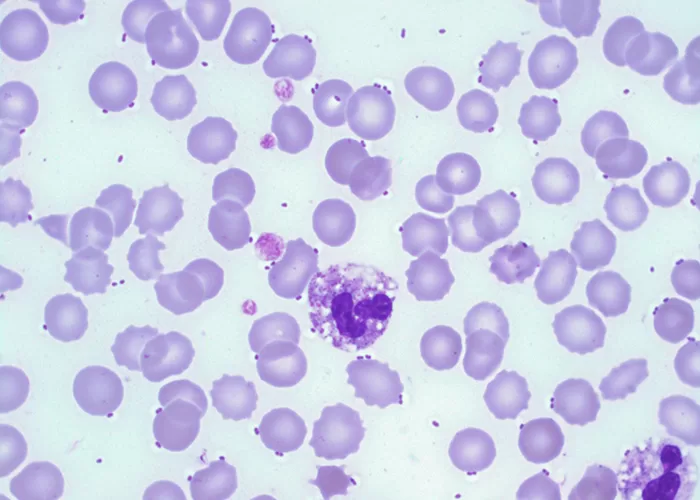
In live blood analysis, the presence of both fungal elements and bacteria in the blood can be observed as an indicator of infection or imbalance in the body’s microbiome. Fungus, such as Candida species, may appear as distinct forms like yeasts or hyphal structures, while bacteria can show up as clusters or individual organisms depending on the type. The simultaneous presence of both fungi and bacteria in blood can point to a compromised immune system or an overgrowth of microorganisms, often due to poor gut health, stress, or antibiotic use. Fungal and bacterial overgrowths are often linked to systemic infections, chronic illnesses, or imbalances like leaky gut syndrome.
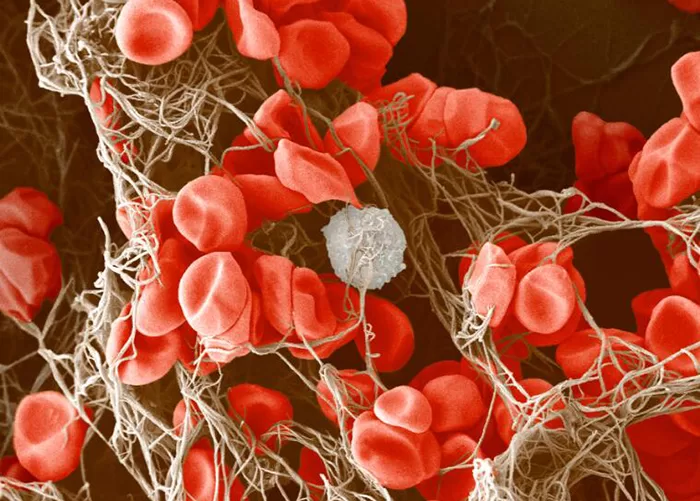
Clotting in live blood analysis refers to the formation of fibrin strands or blood clots, which occur when blood cells aggregate in an attempt to seal an injury or stop bleeding. Non-magnified blood observations can help identify clotting tendencies by looking for signs such as abnormal clumping of blood cells or the presence of fibrin strands in the serum. These clots may be indicative of underlying health issues like an inflammatory response, oxidative stress, or even blood coagulation disorders, including conditions such as thrombophilia or hypercoagulability. In some cases, excessive clotting can lead to poor circulation, increasing the risk of thrombosis, heart attack, or stroke.
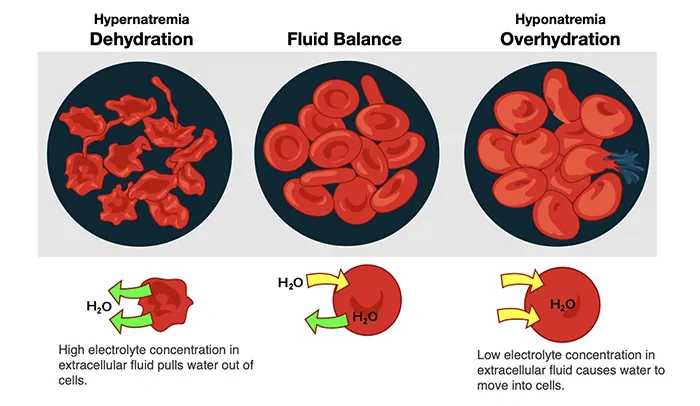
Dehydration in live blood analysis is observed when the blood appears more concentrated than normal. In a non-magnified view, this can be seen as thicker plasma with blood cells that are more tightly packed together, often leading to a reduction in the volume of plasma compared to the cellular components. Dehydration can have serious implications for blood flow, as it reduces the blood’s ability to carry oxygen and nutrients to the cells. As the plasma becomes more viscous due to insufficient fluid, it can lead to sluggish circulation, increased stress on the heart, and reduced efficiency in waste elimination.
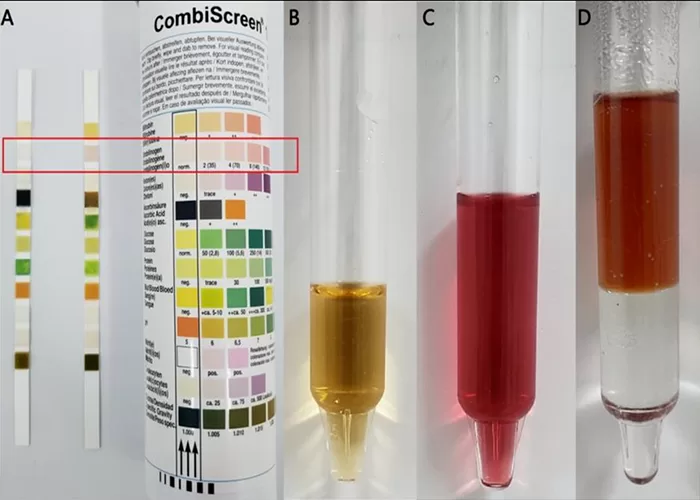

Urobilinogen is a substance formed in the intestines from the breakdown of bilirubin, which is produced when the liver processes red blood cells. It is normally present in small amounts in urine. Higher or lower levels of urobilinogen in the urine may indicate liver disease, hemolysis, or other health conditions. Testing for urobilinogen can help assess liver function and overall health.
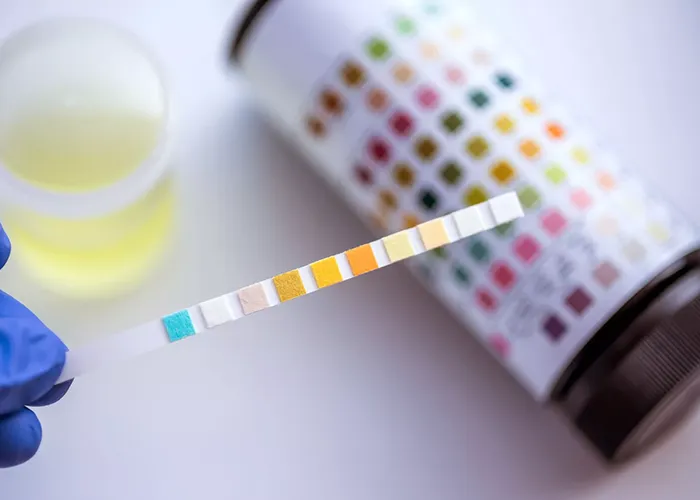
Ketones in urine refer to the presence of ketone bodies, which are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy instead of carbohydrates. This usually happens when there is a lack of glucose, such as during fasting, a low-carbohydrate diet, or uncontrolled diabetes. The presence of ketones in urine can be detected through a test and may indicate conditions like diabetes, starvation, or a low-carb diet. High levels of ketones can be a sign of a medical issue and may require attention.
Nitrites in urine refer to the presence of nitrite compounds, which are typically produced when bacteria in the urinary tract convert nitrates into nitrites. The presence of nitrites in urine often indicates a urinary tract infection (UTI), as certain bacteria that cause these infections can trigger this process. Detecting nitrites in urine through a test can help diagnose a UTI.

Bilirubin in urine refers to the presence of bilirubin, a substance produced when the liver breaks down old red blood cells. Normally, bilirubin is processed by the liver and removed through the bile, not found in urine. Its presence in urine can indicate liver problems, such as liver disease or bile duct obstruction. Testing for bilirubin in urine helps assess liver function and identify potential health issues.
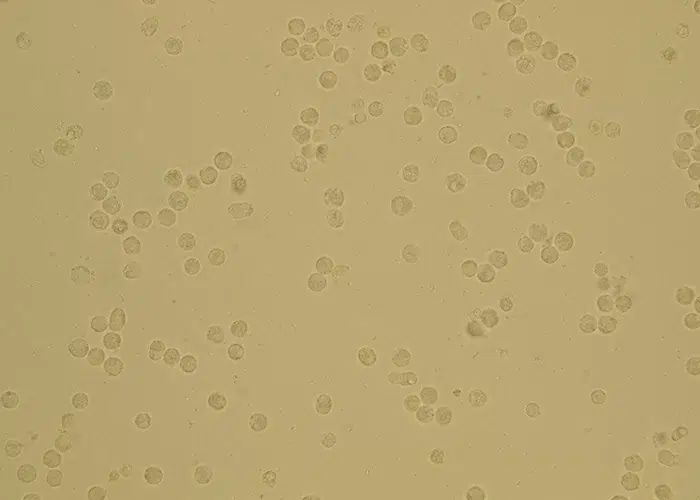
Leukocytes (White Blood Cells) in urine refer to the presence of white blood cells in the urine, which can indicate an infection or inflammation in the urinary tract. Normally, white blood cells are part of the immune system and help fight infections. Their presence in urine is often a sign of conditions such as urinary tract infections (UTIs) or kidney disease. A urine test can detect leukocytes and help diagnose underlying health issues.
Erythrocytes (Red Blood Cells) in urine refer to the presence of red blood cells in the urine, which is not normal. Their presence can indicate various health conditions, such as urinary tract infections, kidney stones, or injury to the urinary tract. A urine test can detect red blood cells, and their presence may require further investigation to determine the underlying cause.

Glucose in urine, also known as glycosuria, refers to the presence of glucose (sugar) in the urine. Under normal conditions, the kidneys filter glucose from the blood and reabsorb it, preventing its loss in urine. However, when blood glucose levels are too high, the kidneys may not be able to reabsorb all of the glucose, resulting in its appearance in the urine.
Finding glucose in urine is often a sign of high blood sugar levels, which could indicate an underlying condition such as diabetes. If glucose is detected in urine, further medical evaluation is recommended to determine the cause and manage any potential health issues. Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels is important for maintaining overall health.
The presence of protein in urine, known as proteinuria, can be an indicator of various health conditions. Under normal circumstances, urine contains little to no protein because the kidneys filter out waste and retain essential substances like proteins.
Healthy urine should have very low or no protein. If protein is detected, it may suggest kidney problems and should be evaluated by a healthcare provider. Regular monitoring can help identify potential health issues early.
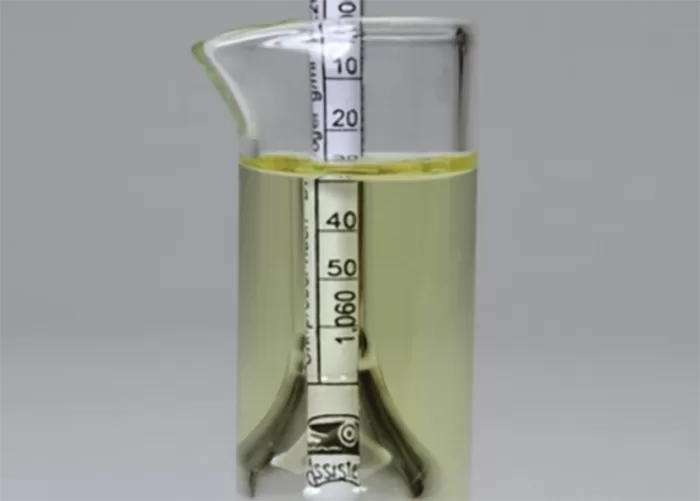

Urine specific gravity is a measure of the concentration of particles in urine, reflecting the kidney’s ability to balance water and waste. It is typically measured on a scale ranging from 1.000 (completely dilute) to 1.030 (highly concentrated).
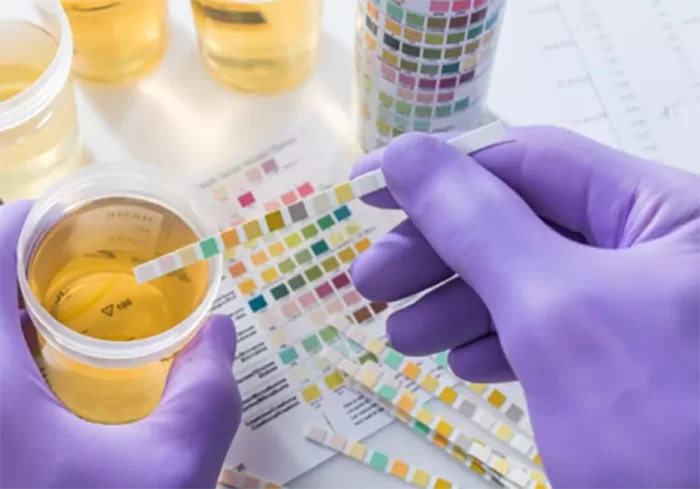

Urine pH refers to how acidic or alkaline (basic) your urine is. It is measured on a scale from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral.
Acidic urine: A pH below 7. This can happen if you eat a lot of protein or drink acidic drinks like coffee. It may also occur if your body is dehydrated or fighting an infection.
Alkaline urine: A pH above 7. This can occur if you eat a lot of fruits and vegetables, or if your body is responding to certain conditions like kidney disease or urinary tract infections.
Normal urine pH typically ranges from 4.5 to 8. A balanced pH helps your body get rid of waste properly.
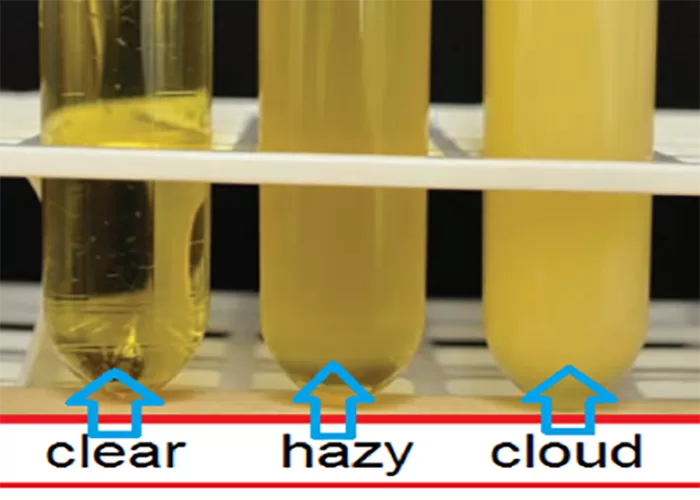

Urine clarity refers to how clear or cloudy your urine looks. Clear urine is usually a sign of good hydration, meaning you’re drinking enough water. Cloudy urine might indicate that something is wrong, like an infection, dehydration, or even the presence of excess minerals or mucus.
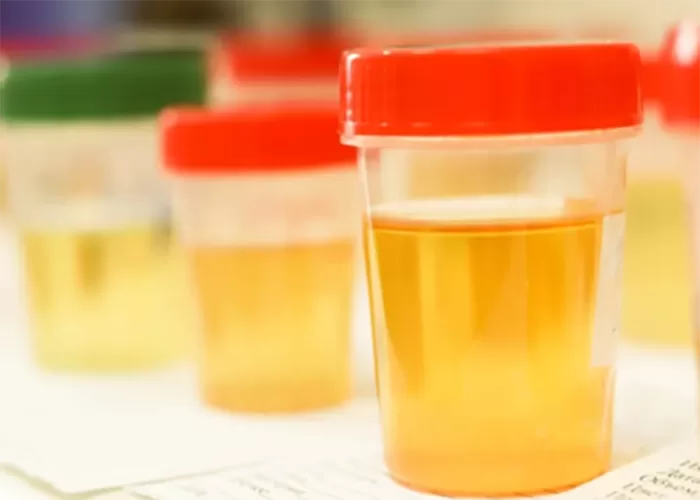

Urine color can give clues about your health and hydration. Here’s a simpler breakdown:
Clear to Light Yellow: Healthy and well-hydrated.
Dark Yellow: Slight dehydration; drink more water.
Brown or Tea-Colored: Could mean dehydration or liver problems; consult a doctor.
Red or Pink: Could be blood in urine (infection, stones) or from foods like beets.
Orange: May be from dehydration, certain medications, or foods like carrots.
Cloudy: Could be a sign of infection or dehydration.
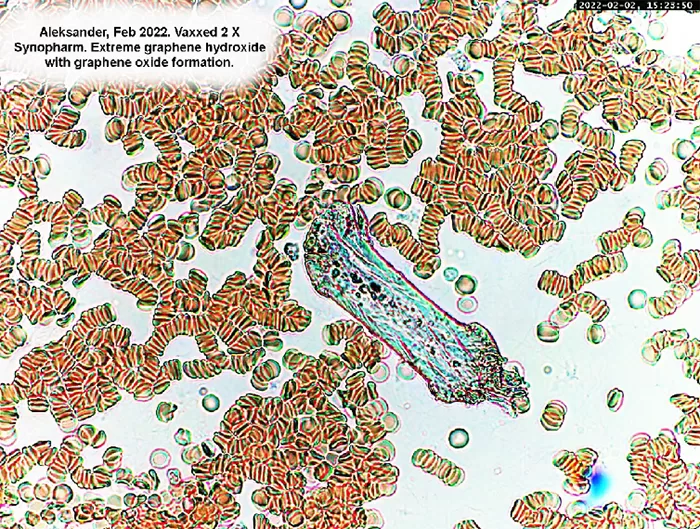
The characteristic common to all graphene structures observed in blood is that they consume red cells, perhaps for their iron content, and in production of hybrid structures of various types and purpose.
These can be the beginnings of red cell clots or amyloid clots. We have proven that EDTA chelation therapy breaks up these clots and helps remove them from the body.
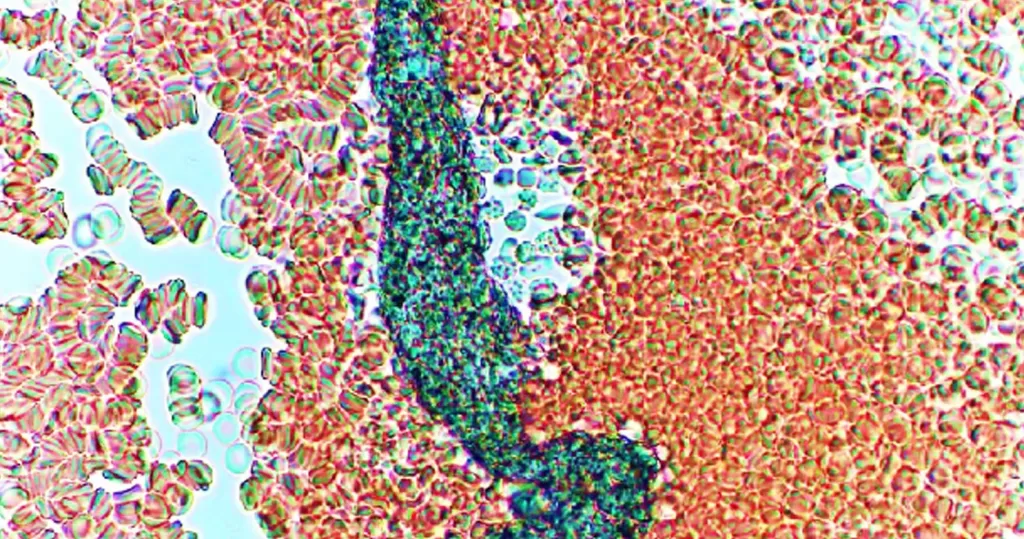
Exceptionally large hybrid graphene worm, being futilely attacked by lymphocytes.
None of these structures have ever been observed by us before April of 2021. In some cases they appear to be hybrids of graphene, in other cases strictly biological, perhaps from sources that have hybridized them.

Graphene hydrogel or nano gel is a water-based three dimensional (3D) graphene hybrid that readily absorbs water and swells to large volumes. Graphene hydrogel nanoparticles are outstanding drug delivery systems, owing to their unique properties that combine the characteristics of high water content with a very small (nano) size. They combine well with drugs, and most importantly carry lipid nanoparticles in even distribution, while enhancing the action of LNP targeting ligands.
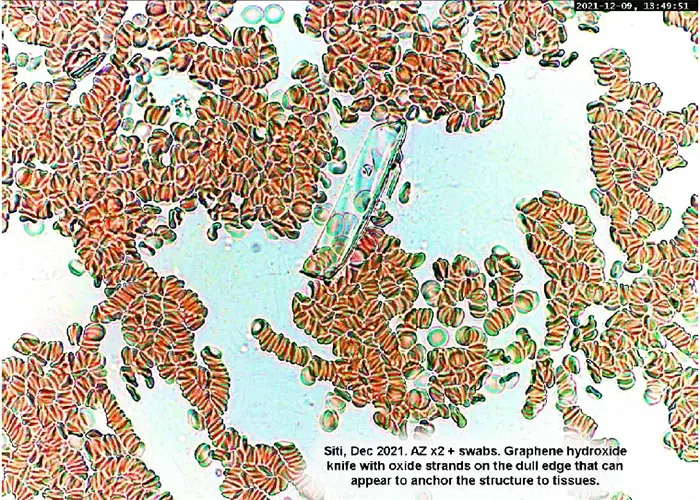
Dr. Andreas Noack is a German expert in graphene nano structures. He describes these nanoscale structures as “tiny razor blades”. Only one atom layer thick, they are relatively wide and long. Fortunately we have observed their consumption by white blood cells, known as lymphocytes, in people with intact immune systems, these structure do deteriorate over time in a healthy, immunities-intact body.
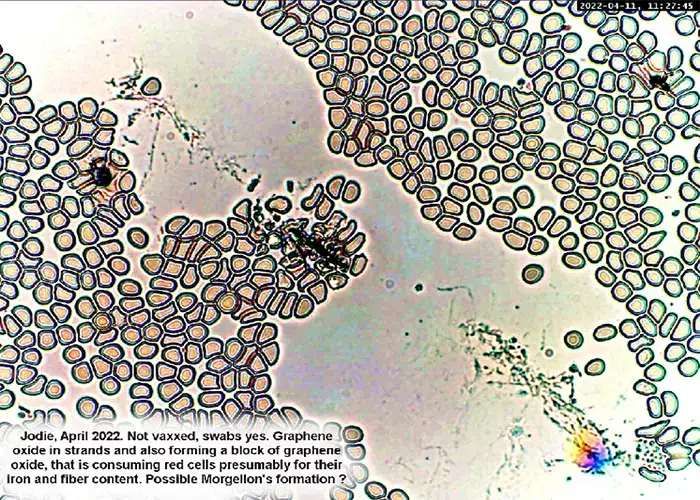
Graphene Oxide is a two-dimensional (2D) material composed of carbon atoms. Its bi-dimensional nature causes unique interactions with blood proteins and biological membranes that can lead to unusual effects like blood clotting and immune cell activation, when combined with mRNA, lipid nanoparticles, and more.
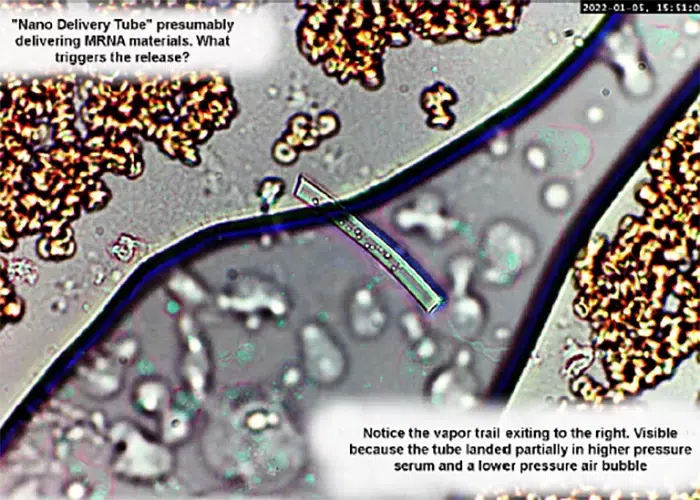
‘Nano Delivery Tube’ presumably delivering mRNA materials.
Notice the vapor trail exiting to the right. Visible because the tube landed partially in higher pressure serum and a lower pressure air bubble.
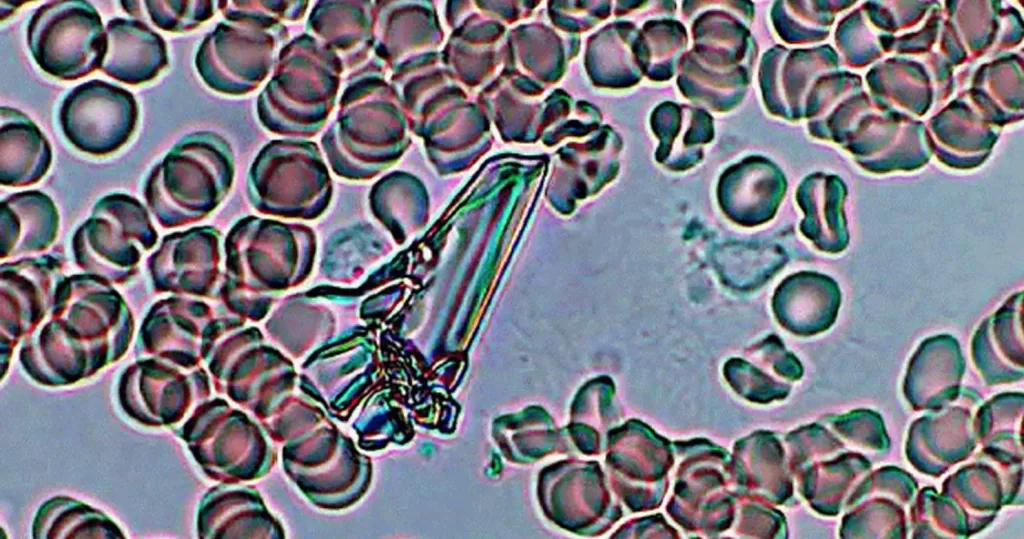
Glass fragment, from the edge of a slide, not from the patient.
Note that the fragment diffracts light, is crystalline in structure. And is it
not affecting, nor harming the surrounding cells.
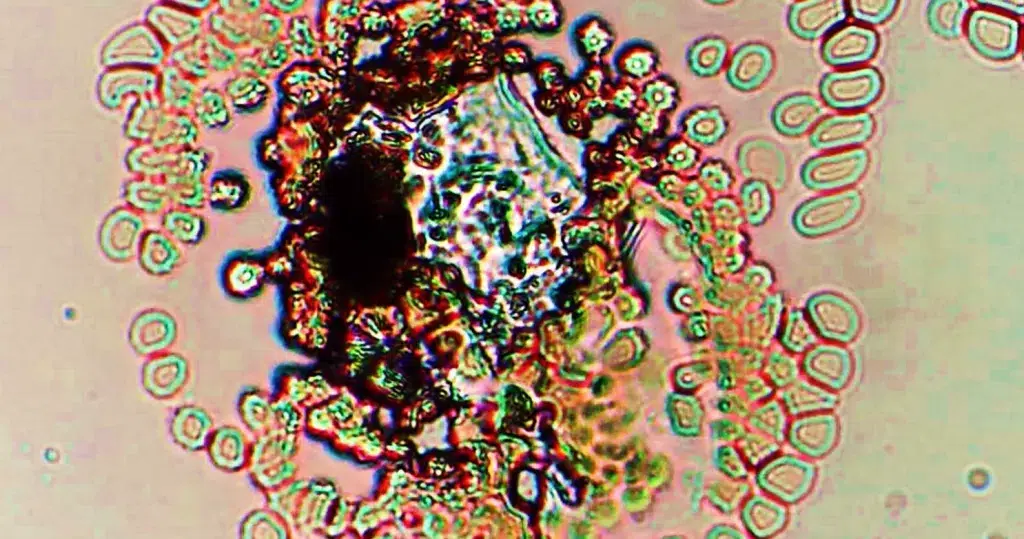
Highly toxic double crystaline structures.
On the left is carbon or other dark element, perhaps lead.
On the right is a lighter element, such as aluminum or something more toxic. Could also be related to graphene hydroxide with graphene oxide.
The orbiting Burr cells also indicate high toxicity. The surrounding red cells are all highly affected.
Mottled serum on the lower right can indicate acidity.
This can indicate a loosened fragment of a cancer elsewhere in the body.
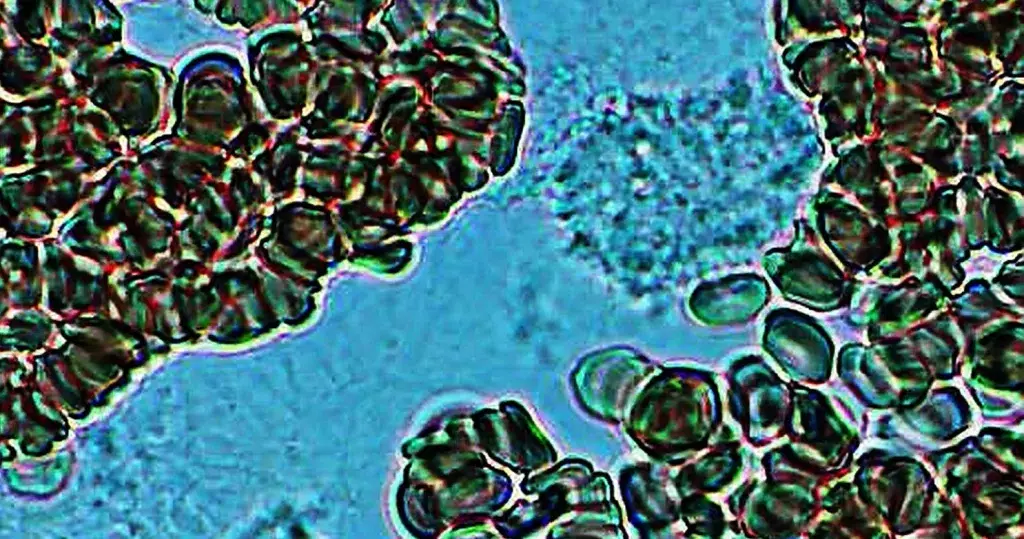
Triglycerides. Note the barbs or macrophylla emanating from the edges – which makes it stick to other cells or vessel walls.
Easily mistaken for fungus or bacteria. Sticking to red cells, but not consuming them. Fungus or bacteria would probably consume adjacent red cells, causing a bleached or depleted appearance.
Also note heavy fibrin activity, indicating dehydration, and possible crystals formation.
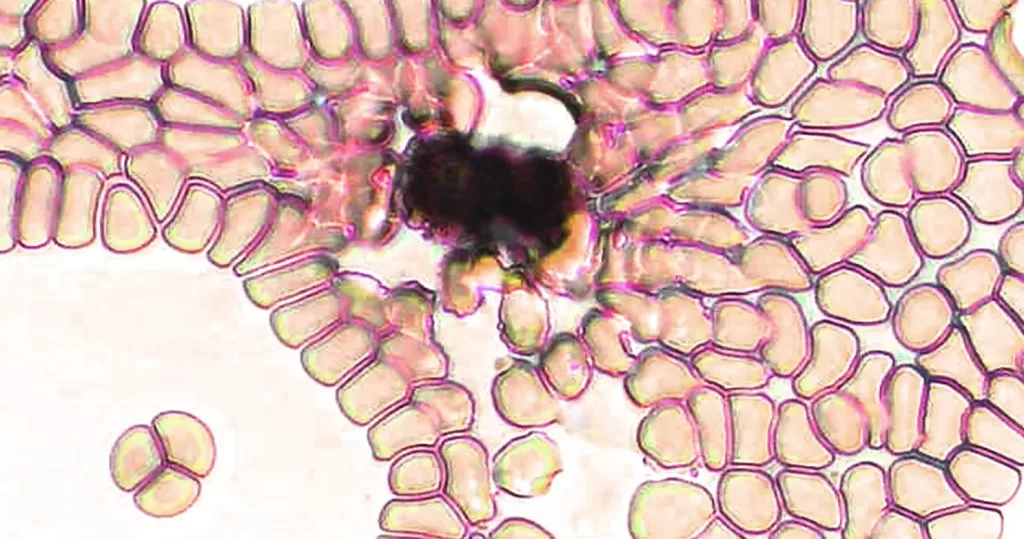
Low to moderate toxicity crystal, probably carbon – the most common of blood solids contaminants. Unstained sample.
Notice that it is affected surrounding red cells, there appears to be an exchange of elements between them.
This was probably inhaled by the patient, which is of course immediately transferred to blood.
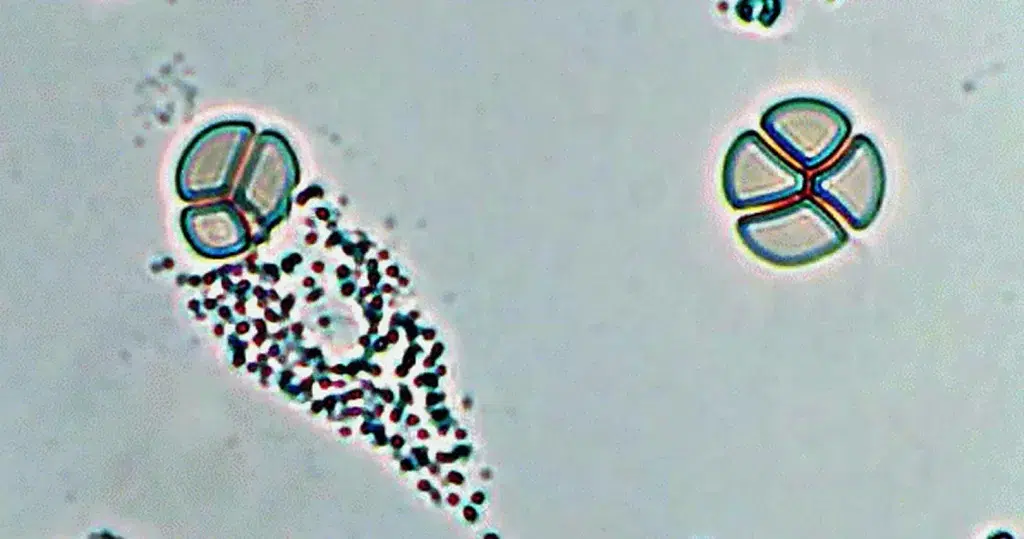
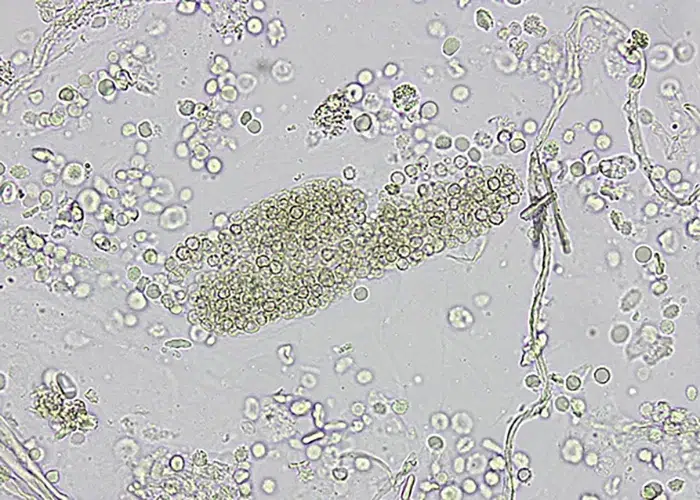
Candida albicans. Notice the formation is similar to a bunch of grapes. Larger white cells are can be seen attacking the edge of the infestation. This person has healthier immune function than the one pictures above.
Must be differentiated from similar looking bacteria
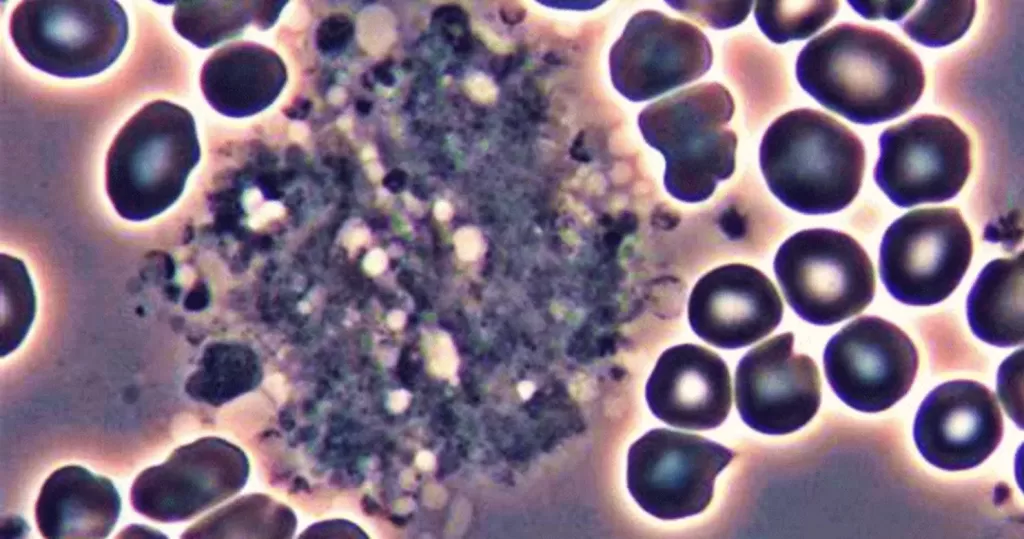
Stained, non-differentiated fungal colony, that is consuming surrounding cells.
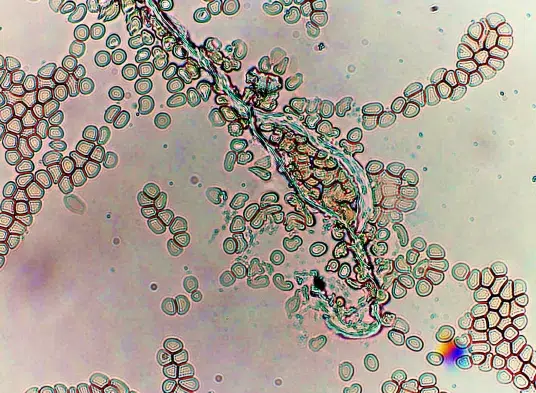
String bacteria, that could easily be mistaken for a parasitic worm. Bacteria usually shows green in color. Can be compared to mucous strings from lungs.
Atmospheric carbon crystal, not from blood.
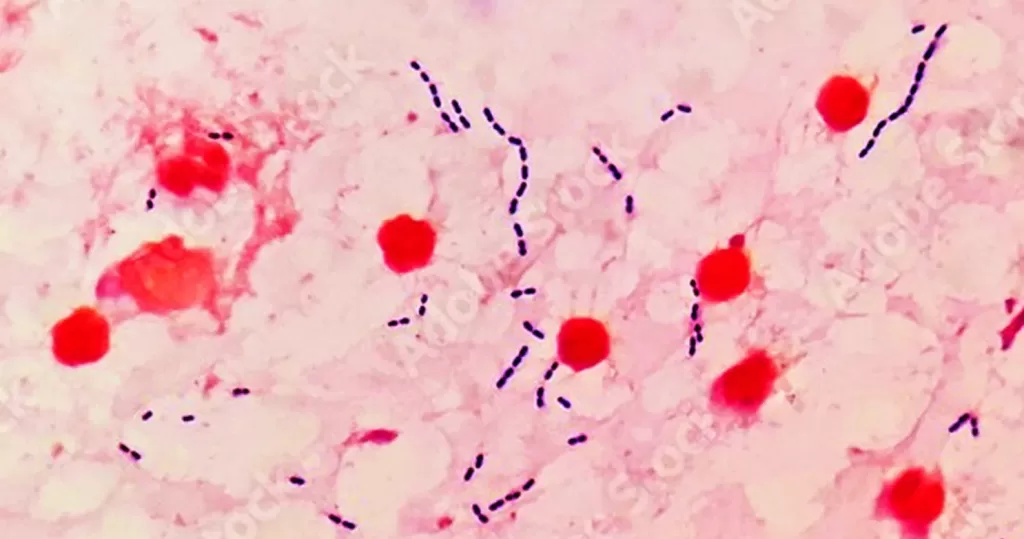
It’s important to remember that bacteria are always present in all areas of the body, and vital to proper function. Bacterium will mutate from so-called good concentrations or balance, to more aggressive concentrations when the body needs to fight off pathogens. Good bacteria can become bad or offensive. Bad bacteria can become benevolent, as the body creates the right balance to custom heal a particular pathogen imbalance.
Bacteria surround and consume pathogens. Along with fever, they can bake-out invading disease.
Gram positive, differentiated bacteria strings.
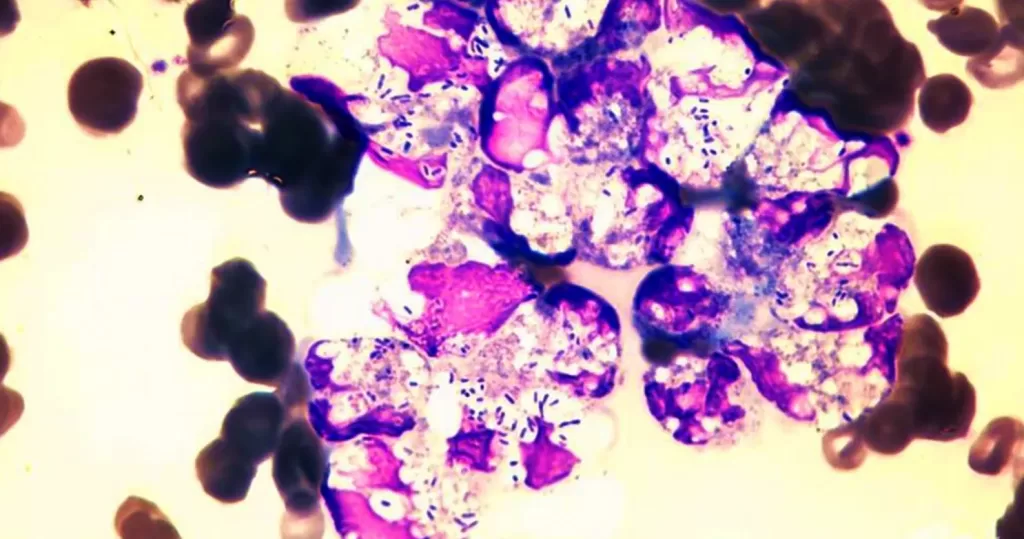
It’s important to remember that bacteria are always present in all areas of the body, and vital to proper function. Bacterium will mutate from so-called good concentrations or balance, to more aggressive concentrations when the body needs to fight off pathogens. Good bacteria can become bad or offensive. Bad bacteria can become benevolent, as the body creates the right balance to custom heal a particular pathogen imbalance.
Bacteria surround and consume pathogens. Along with fever, they can bake-out invading disease.
Non-differentiated, Gram positive intracellular bacteria.
Ameba in motion, moves very slowly, jellylike. No stain.
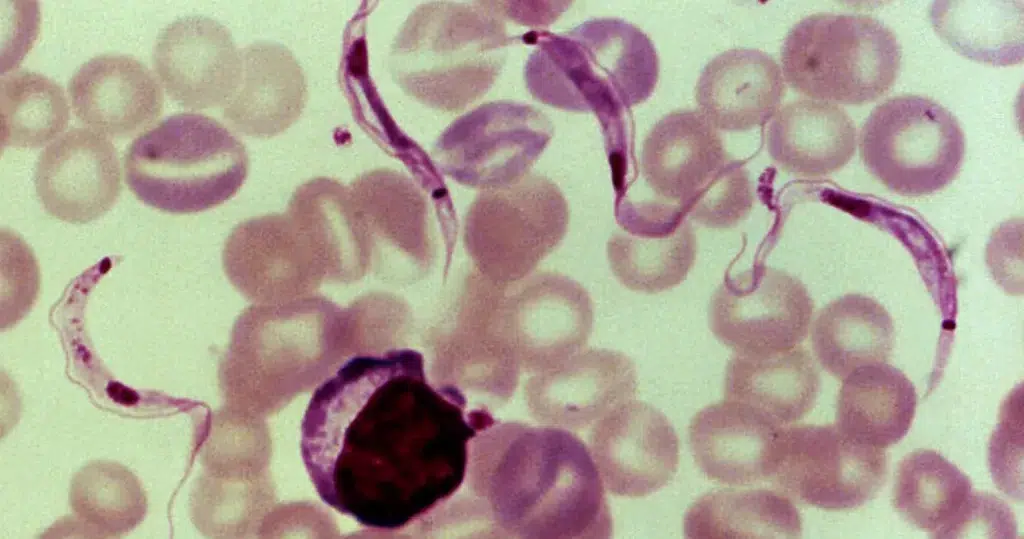
In the event parasites are detected, or eosinophils are low or high, suggest to
the patient to take the Deep Dive Service. Symptoms of parasitic infections depend on where in your body you’re infected. Some common symptoms include:
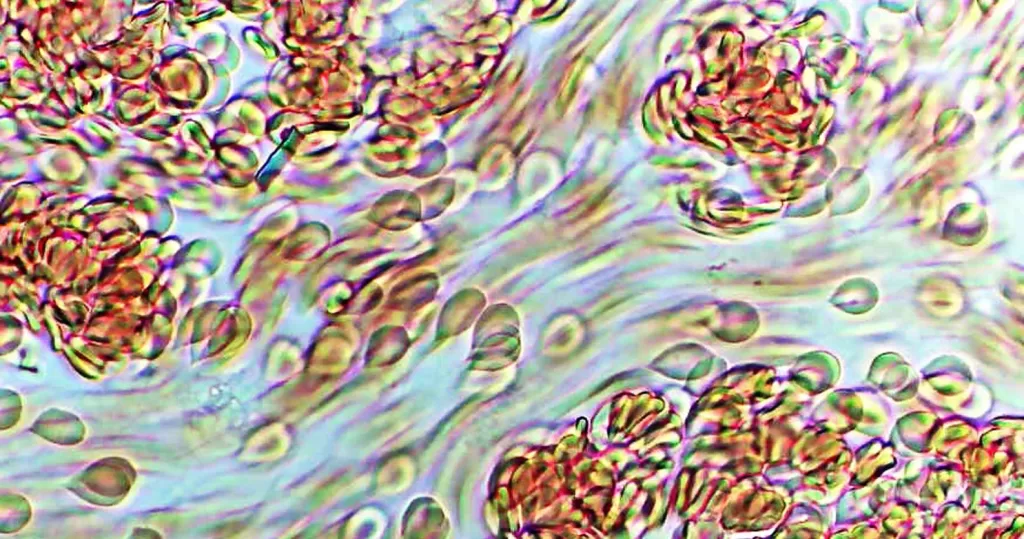
Excellent Vital Force.
Notice the tiny graphene hydroxide fragment. Also notice the non-ds-ifferentiated Roulleux, generally not seen where there is high vital force movement. Ignore teardrop-shaped cells when blood is moving fast.
Blue light filter
Moderate fibrin activity. Almost no crystals formation occurring.
Crystals tend to be formed from fibrin. Also can indicate high dehydration,
acidity.
Indicating hibernation of red cells.
Healthy, recoverable, Roulleux red cell formations. Cells are hibernating. Always locate and photograph the best quality sample for this analysis.
Stem cells will appear like red cells, but do not clot and display a large white center.
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) emanate from bone marrow and can produce all the cells that function in the blood. Stem cells also can become brain cells, heart muscle cells, bone cells or other cell types.
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) circulate under steady state conditions in peripheral blood to
i) to maintain a stem cell pool in remote bone marrow locations in the body and
ii) to “patrol” peripheral tissues and organs and, when needed, to respond to organ injuries and infections. The number of these cells increases in stress situations related to infections, inflammation, organ injury as well as after strenuous exercise.
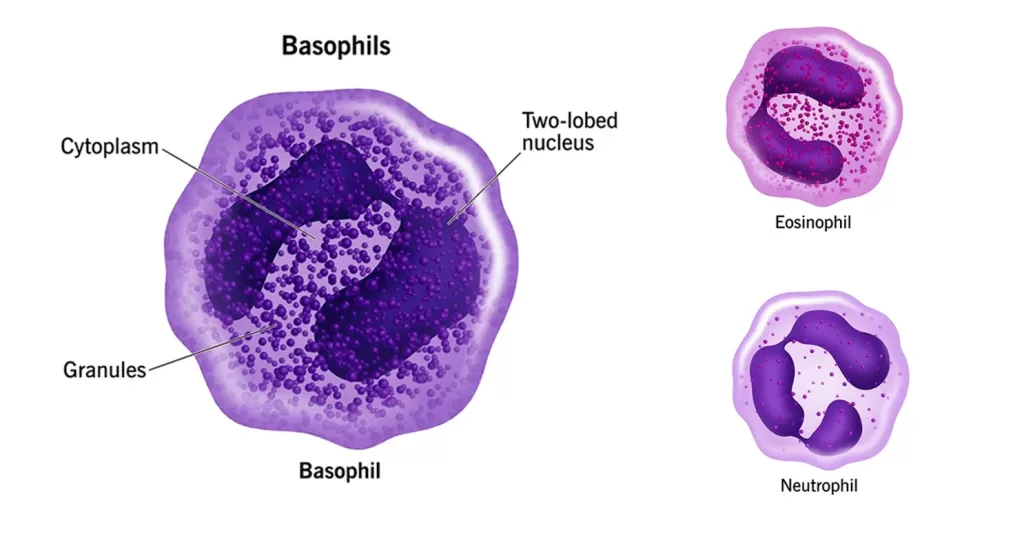
Basophils release enzymes to improve blood flow and prevent blood clots. Basophils function to defend your body against:
Basophil cells are unique in that they don’t recognize pathogens they’ve already been exposed to. Instead, they attack any organism they see that is unfamiliar to your body. Basophils destroy foreign organisms by surrounding and ingesting them (phagocytosis).
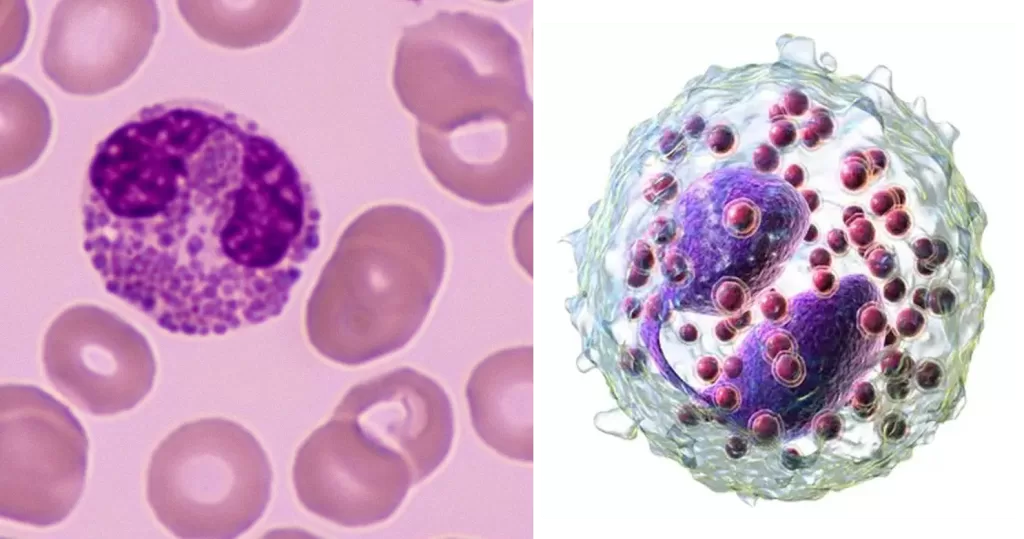
Normally transparent, it is this affinity that causes them to appear brick-red after staining. Eosinophils are responsible for combating multicellular parasites and certain infections in vertebrates. Along with mast cells and basophils, they also control mechanisms associated with allergy and asthma.
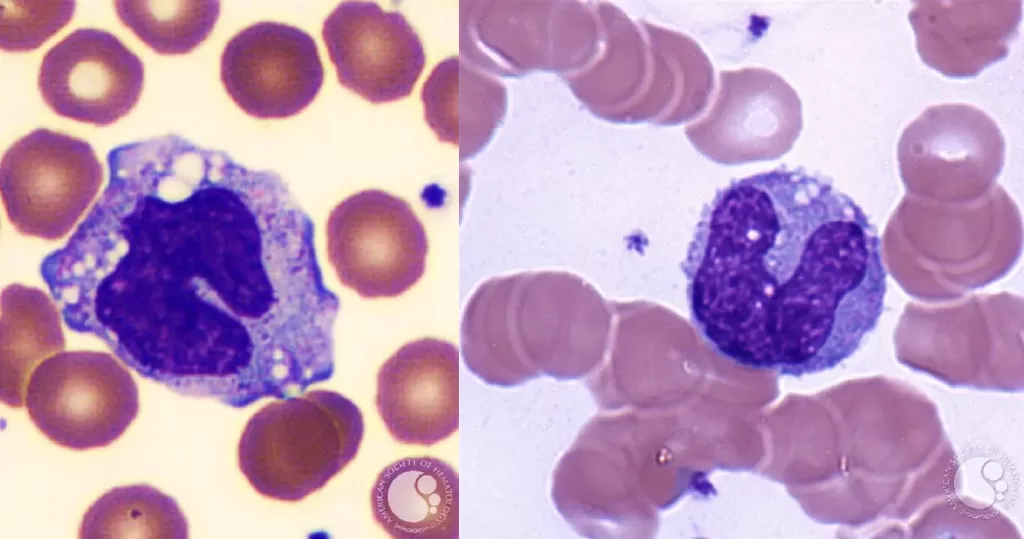
mechanically active cells and migrate from blood to an inflammatory site to perform their functions. In general, monocytes and their macrophage and dendritic cell progeny serve three main functions in the immune system. These are phagocytosis, antigen presentation, and cytokine production. Phagocytosis is the process of uptake of microbes and particles followed by digestion and destruction of this material. Monocytes can perform phagocytosis using intermediary proteins such as antibodies or complement that coat the pathogen, as well as by binding to the microbe directly via pattern recognition receptors that recognize pathogens. Monocytes are also capable of killing infected host cells via antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Vacuolization may be present in a cell that has recently phagocytized foreign matter.
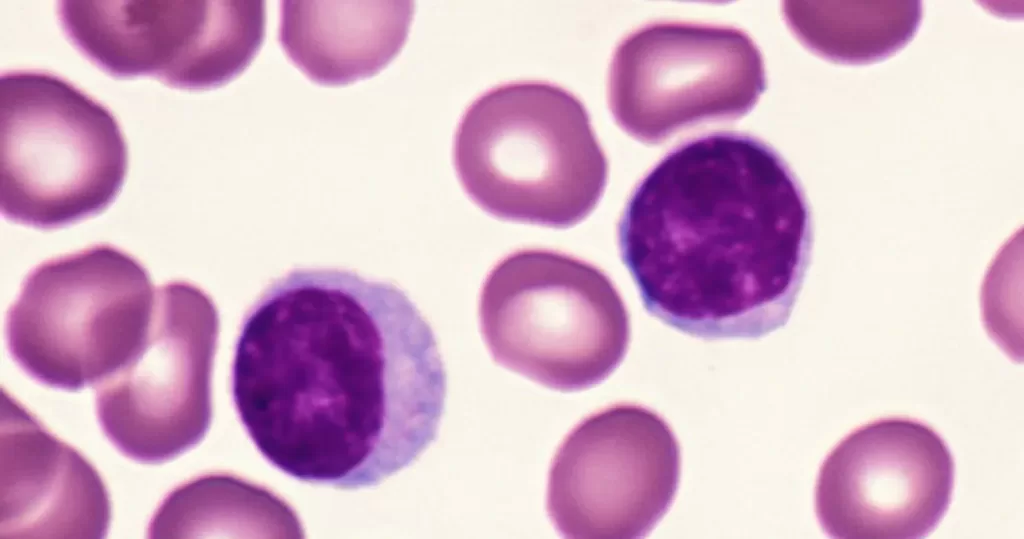
Lymphocytes help fight disease and infection. They are primarily involved in recognizing and responding to foreign substances, such as viruses and bacteria, with two main types: T cells, which destroy infected cells, and B cells, which produce antibodies to target pathogens.
Healthy, non-active lymphocytes. An indication of no significant infection or intoxication.
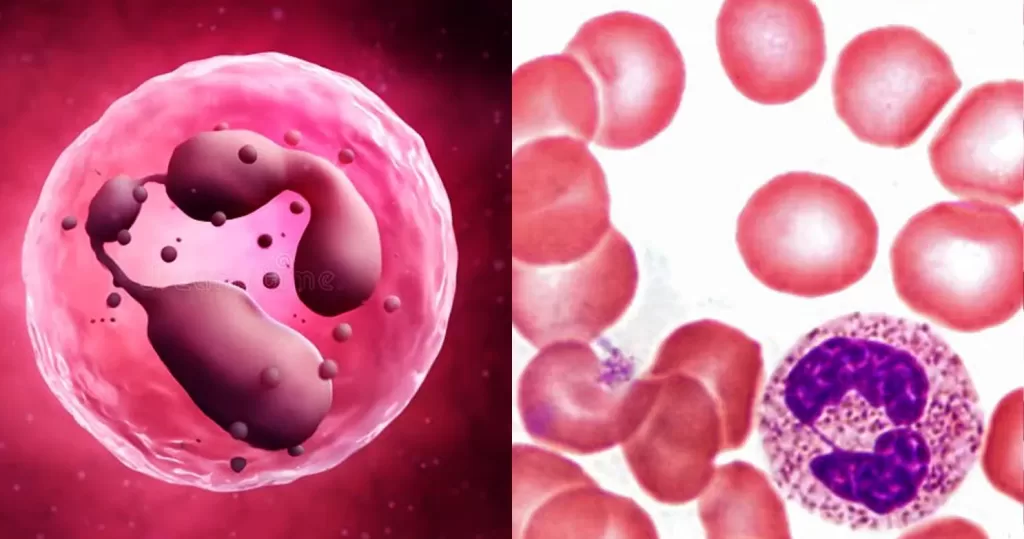
Neutrophils help heal damaged tissues and resolve infections. Neutrophil blood levels increase naturally in response to infections, injuries, and other types of stress. They may decrease in response to severe or chronic infections, drug treatments, and genetic conditions.
Neutrophils block, disable, digest, or ward off invading particles and microorganisms. They also communicate with other cells to help them repair cells and mount a proper immune response. The body produces neutrophils in the bone marrow, and they account for 55–70 percent of all white blood cells in the bloodstream.
A fecal occult blood test is a screening that looks for hidden (occult) blood in stool (poop). The test can identify tiny traces of blood that you can’t see on your own. It helps healthcare providers diagnose several health conditions.
What does a fecal occult blood test show?
Blood in the stool means there’s bleeding happening somewhere in your digestive tract. This type of bleeding isn’t normal and is usually a sign of a health condition, such as:
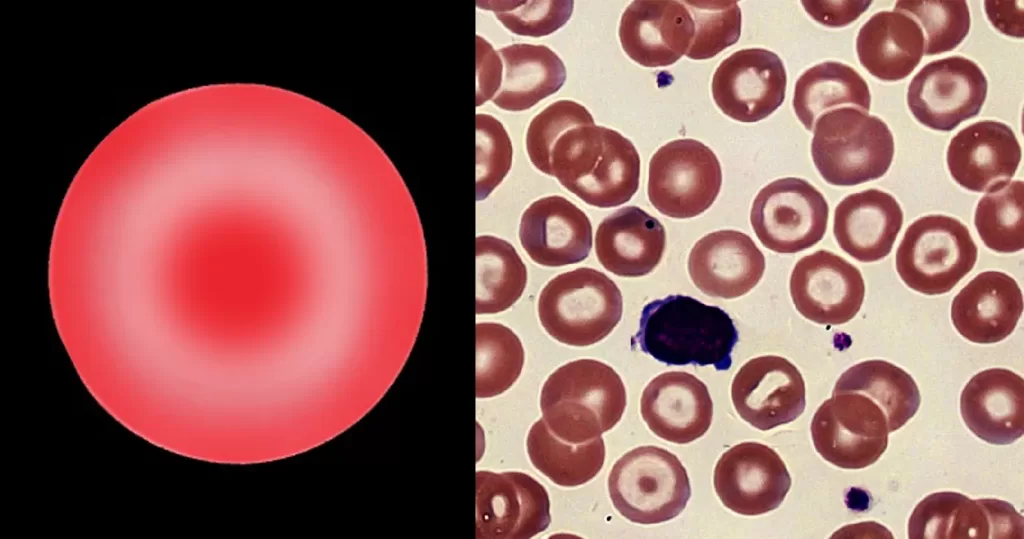
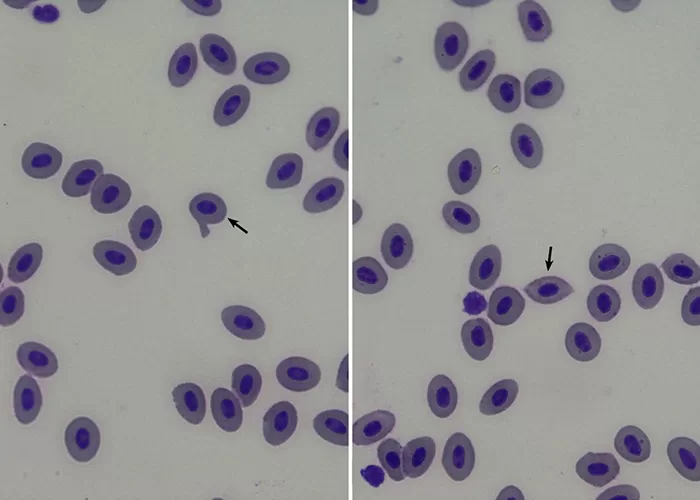
The area of pallor contains a central accumulation of hemoglobin giving the appearance of a “target”. Look for macrocytosis that may imply liver disease; or if MCV is normal or low consider a hemoglobinopathy (HbC, D or E).
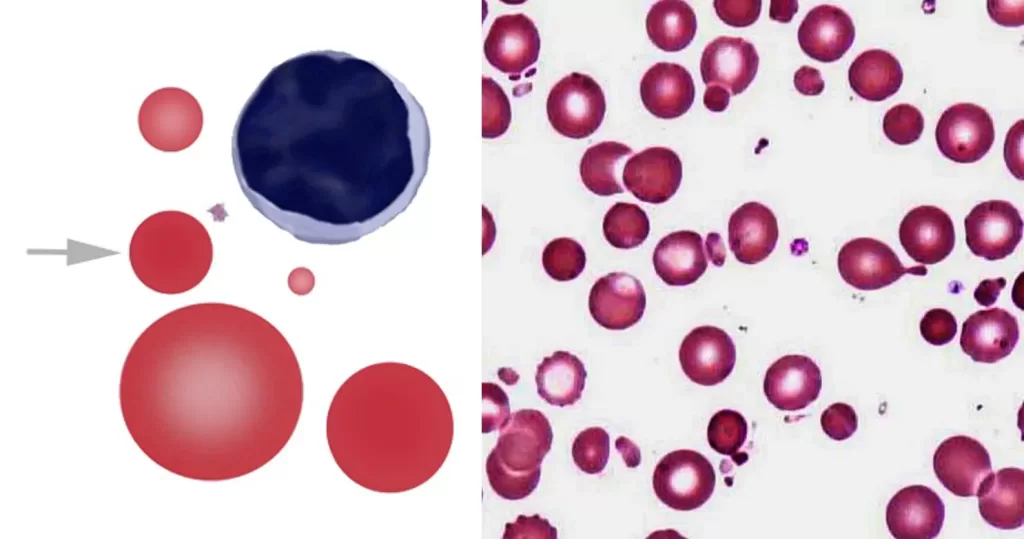
Severe membrane defects (e.g. hereditary pyropoikilocytosis). Toxin induced membrane damage: particularly Clostridium perfringens. Infrequent microspherocytes may appear as part of a spectrum of cells in many conditions with erythrocyte damage (e.g. fragmentation) or fragile production (e.g. megaloblastic states).
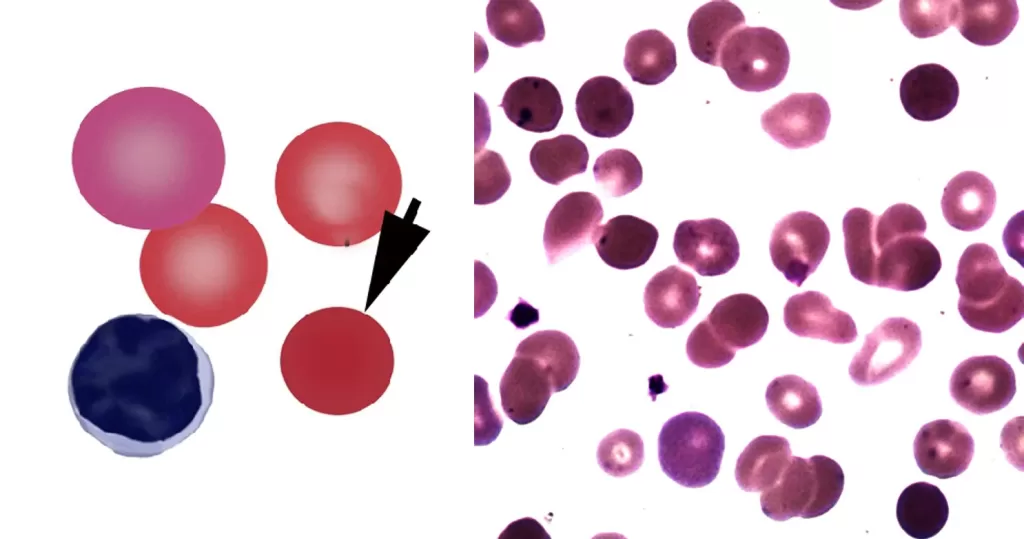
Spherocytes are found in all hemolytic anemias to some degree. Hereditary spherocytosis and autoimmune hemolytic anemia are characterized by having only spherocytes. Where spherocytes are very frequent autoimmune hemolysis or hereditary spherocytosis should be considered.
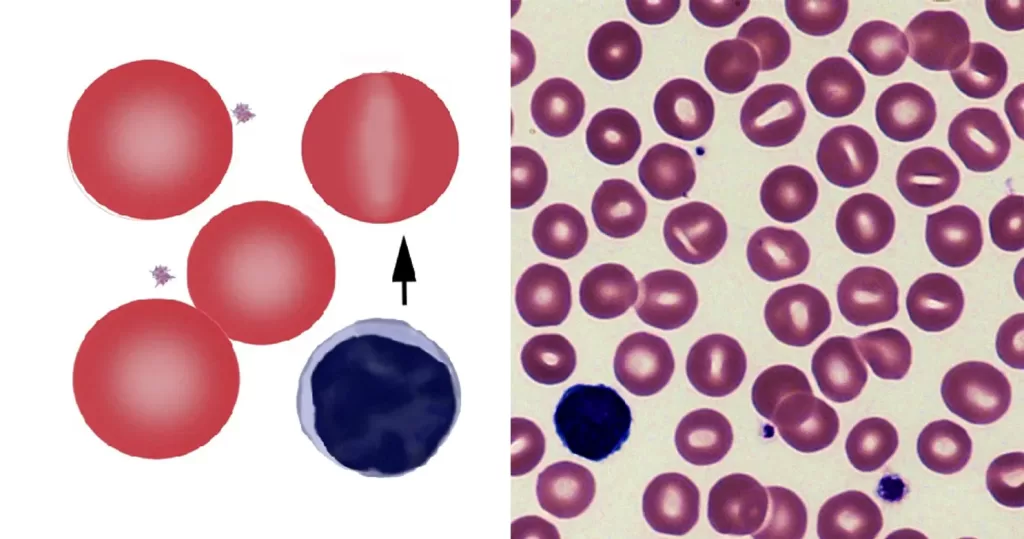
First exclude artefact (slow slide drying), then consider the number of these cells – occasional stomatocytes may arise in many conditions. However, when present in significant number stomatocytes may indicate significant acquired or inherited disease signifying one of a range of conditions (including liver disease, alcohol, or electrolyte imbalance). However, also consider a range of inherited conditions (see table) or look for the characteristic very large and oval-shaped often with a Y-shaped stoma that are seen in South East Asian Ovalocytosis.
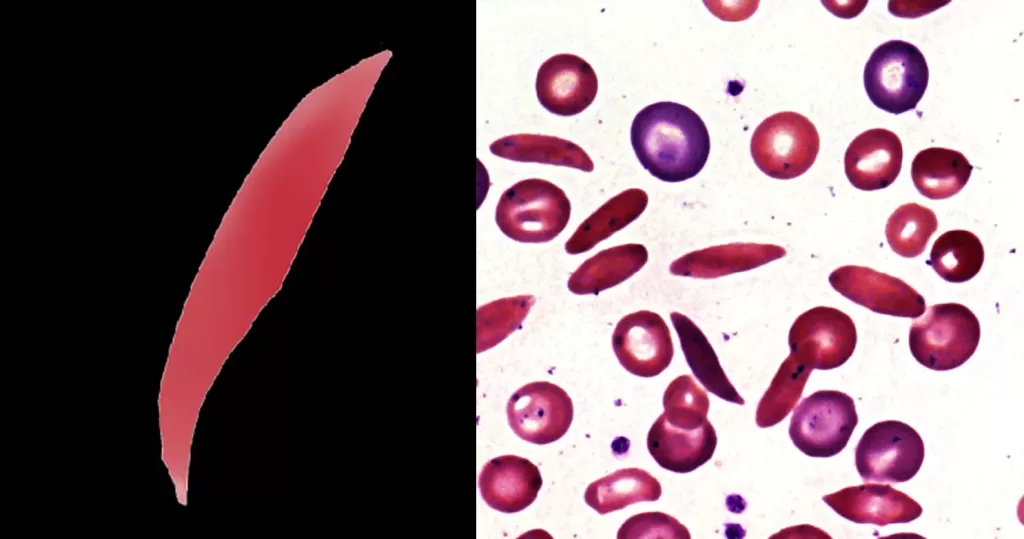
Indicates that the cells express the mutated gene for sickle hemoglobin (HbS), either in homozygous form (HbSS) or as a compound with another abnormal beta hemoglobin form. The number of these abnormal cells should not necessarily be considered an indicator of severity, but increased numbers of abnormal cells and polychromasia (or nucleated red cells) often occur during sickle crises.
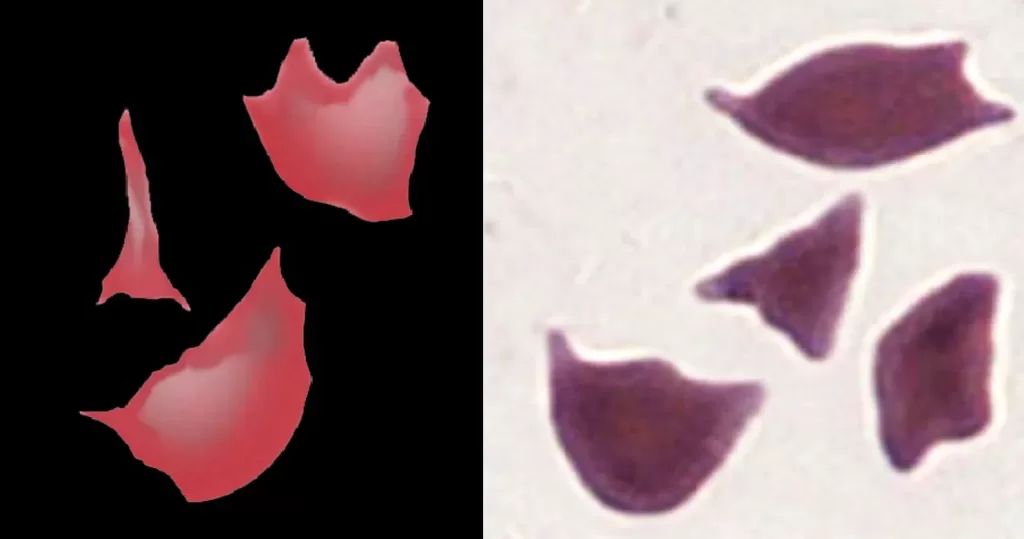
Fragmented cells are not found in normal blood. Sharp fragments may reflect “microangiopathic” damage – this form of fragmentation may therefore represent a medical emergency and should be reported immediately. More rounded fragments arise in significant dyserythropoiesis (such as severe myelodysplasia, membrane disorder or megaloblastic states), these are also important to diagnosis, but have a different origin.
These cells are formed when sickle hemoglobin (HbS) is present together with hemoglobin C (HbC) to form a compound heterozygote disorder (HbSC disease)
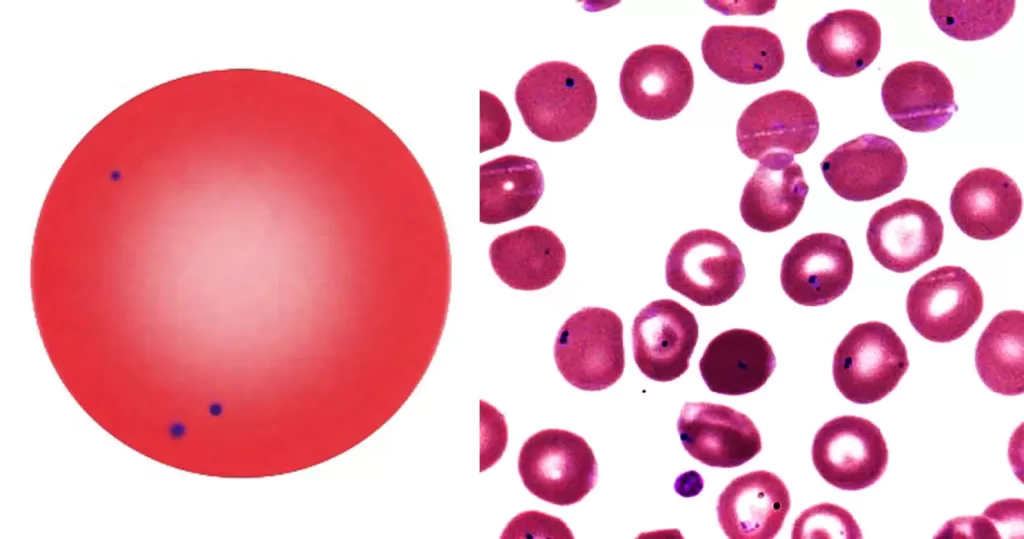
Small numbers of Pappenheimer Bodies may be seen in normal blood, particularly within polychromatic cells. When they are present in large number look for hyposplenic features, or for pathological states that have iron-loading or aberrant iron metabolism.
Myelodysplasia, iron deficiency, etc. S.E. Asian Ovalocytosis is a specific disorder that results from structural and functional defects of the band 3 protein causing ovalocytes with a stomatocytic appearance. May indicate previous malarial parasites.
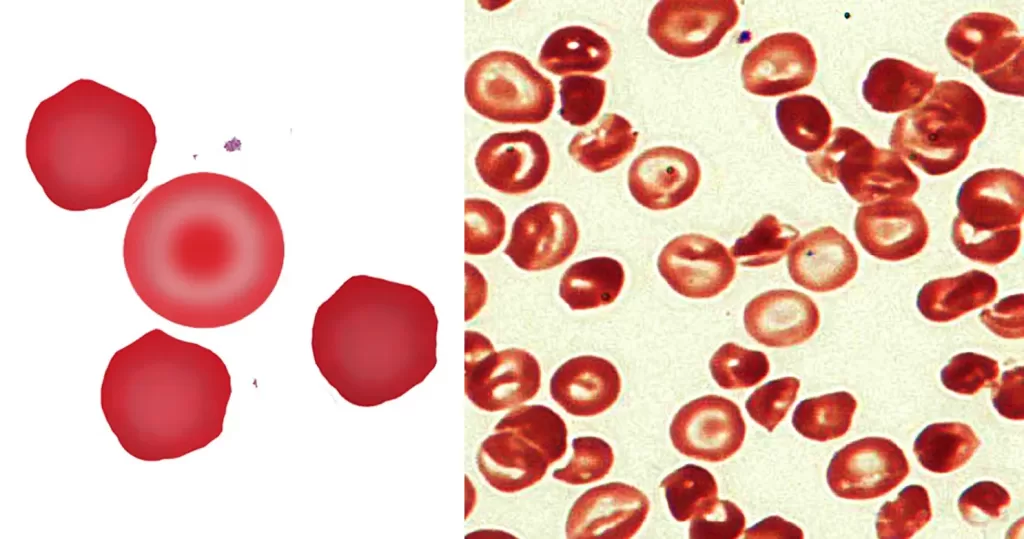
Morphological evidence of any accompanying disease should actively be sought. Most frequently these causes are B12 or folate deficiency, myelodysplasia, or liver disease.
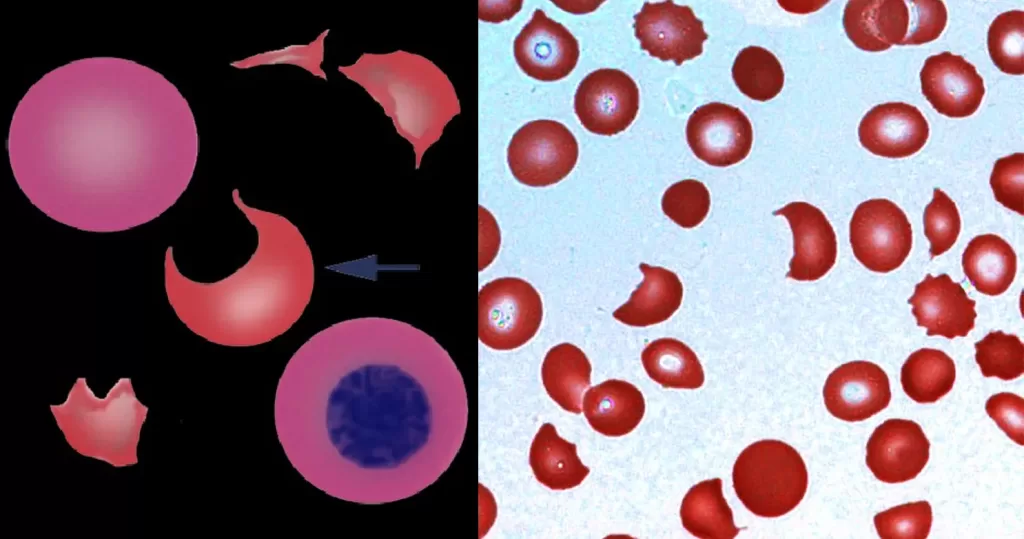
In some (although not all) cases, the pathological process may be life threatening particularly if they are associated with disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) or thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) knowledge of platelet count, clotting and additional morphological features such as fragments is essential.
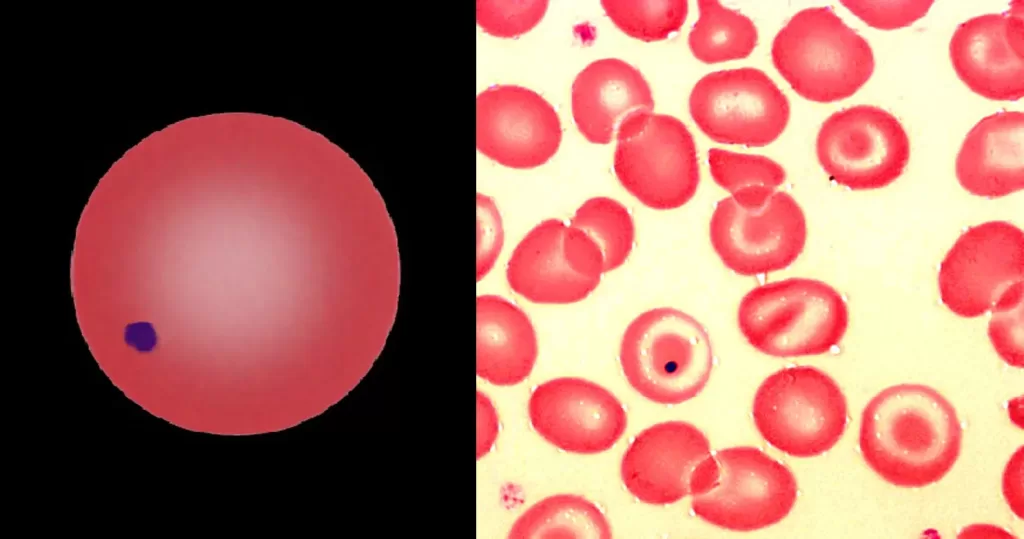
Implies damage to hemoglobin within the red cell often accompanied by cellular dehydration and membrane damage; acute oxidative damage to red cells should be considered.
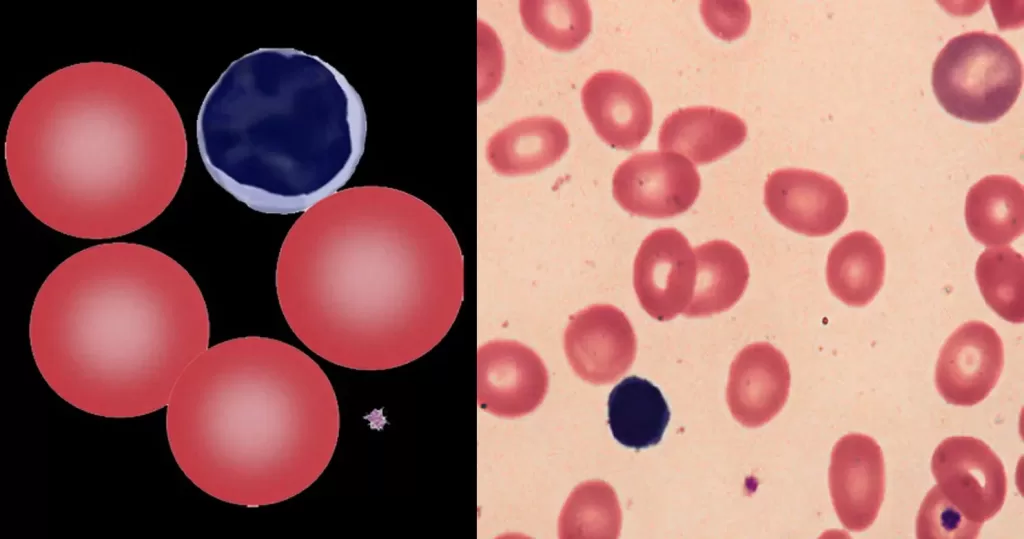
Howell-Jolly Bodies most commonly arise when spleen is absent or spleen function is impaired (hyposplenia). Occasional Howell Jolly bodies may arise in physiological conditions.
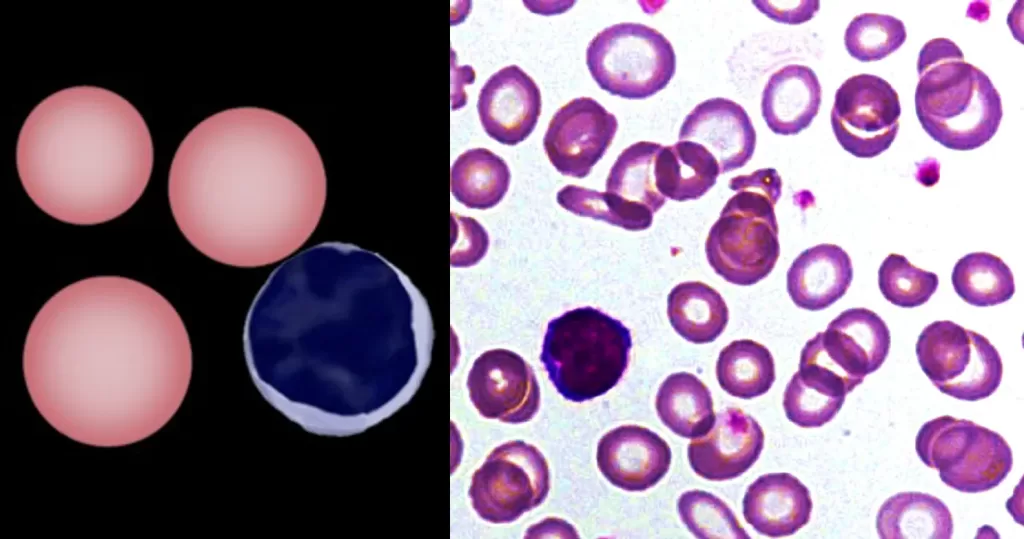
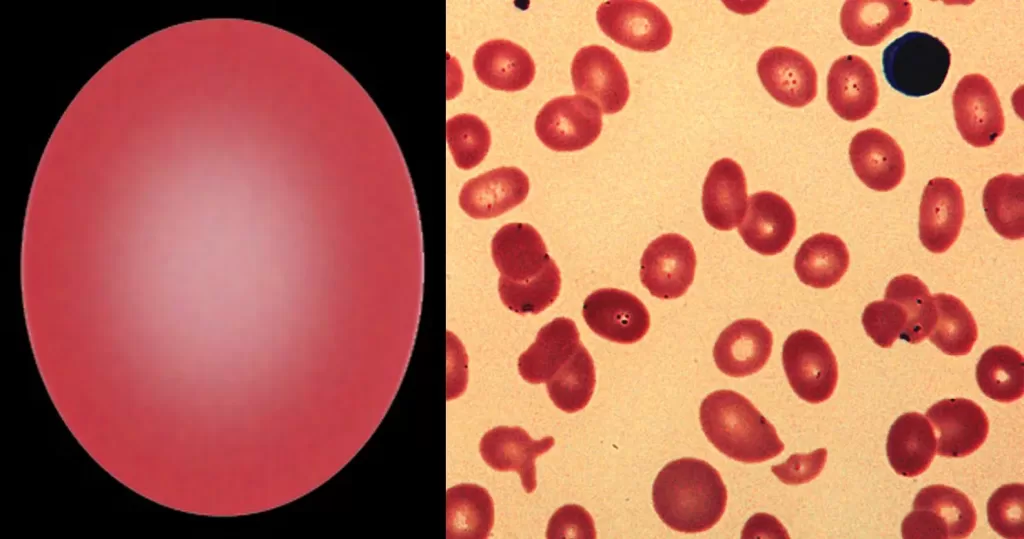
The presence of hypochromia indicates defective production of hemoglobin. Most cases result from iron deficiency or thalassemia – other typical features of these conditions should therefore be sought. Less frequently, hypochromia reflects defective iron utilization (e.g. chronic disease or sideroblastic anemia). The presence of hypochromia is not of itself an urgent problem unless there is severe anemia; however, it important to highlight the condition since clinicians may need to request further investigation to determine its cause.
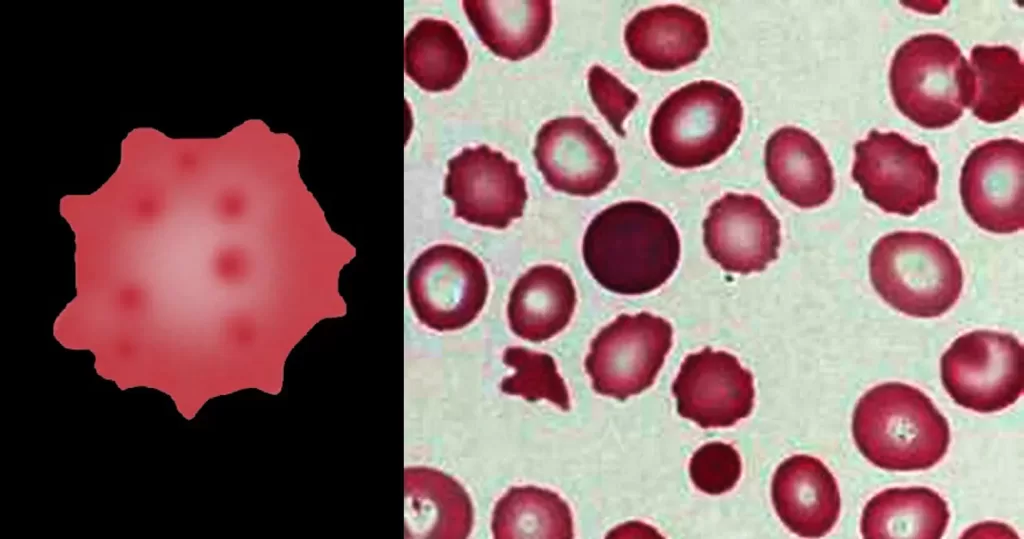
Always remember that echinocytes may be an artefact of blood storage or of cells on the edge of a live mount slide (artefactual echinocytosis), so look at the condition of other cells on the film and determine whether the echinocytosis is patchy in distribution. Where genuine there will usually be a significant systemic disease present. This most frequently will be renal failure.
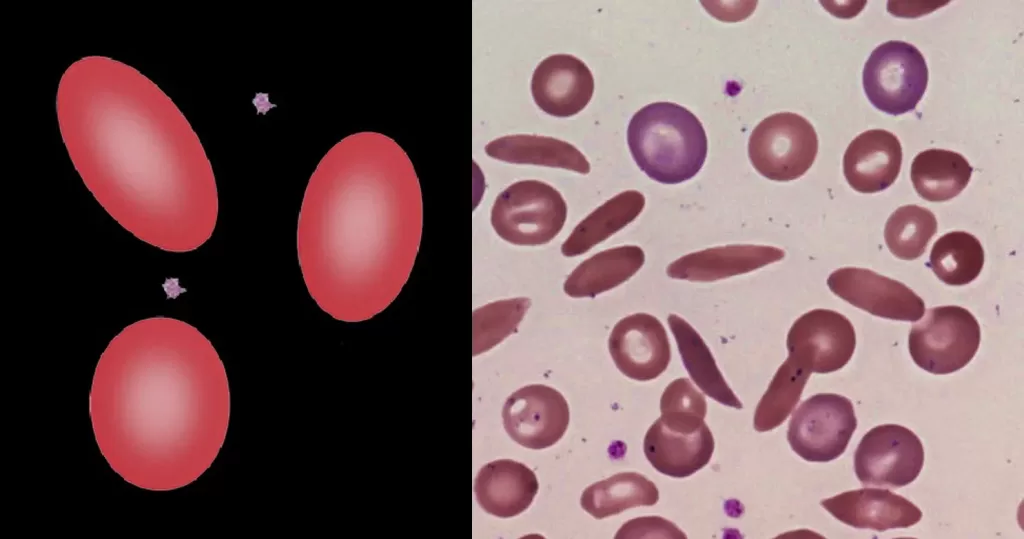
Iron deficiency or chronic disease. Multiple instances can indicate very severe hereditary pyropoikilocytosis.
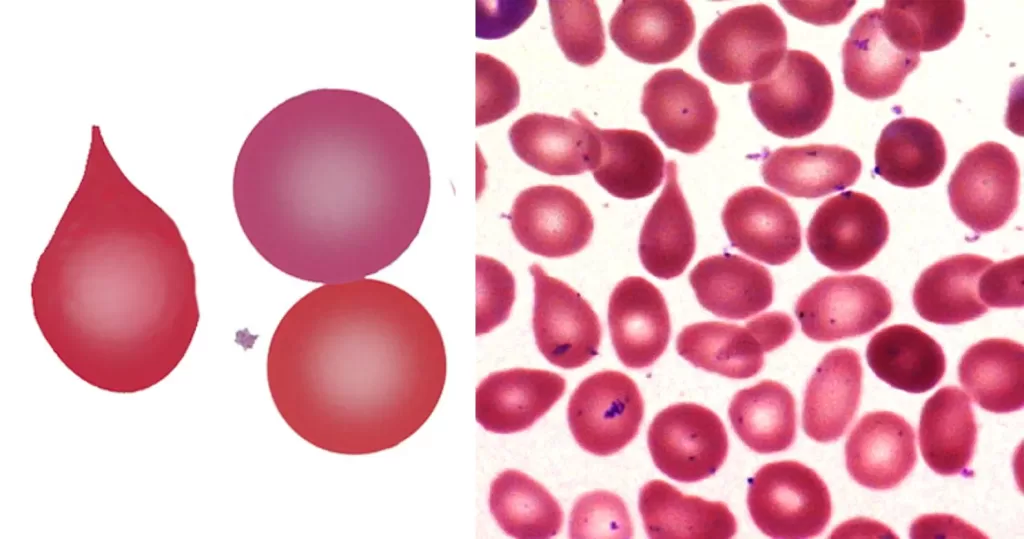
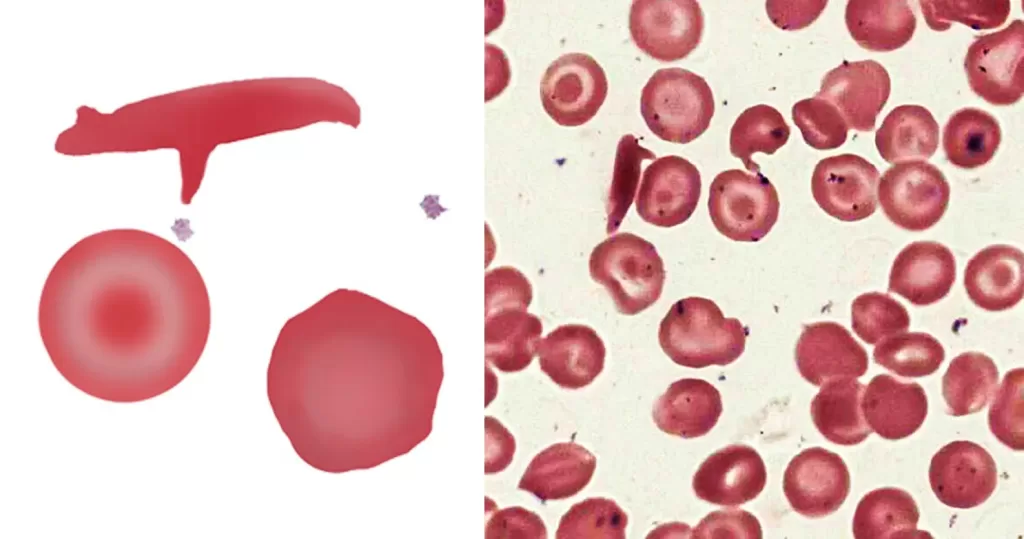
Strongly indicative of a “packed marrow”. May be the result of fibrosis (primary or secondary) or neoplasm (carcinoma or hematological neoplasm). May also arise where there is sustained or severe physiological increase in blood cell production (e.g. the expanded erythroid response to thalassemia). Less frequent tear drop forms may arise in other systemic disease. Ignore in fast-moving blood (vital force).
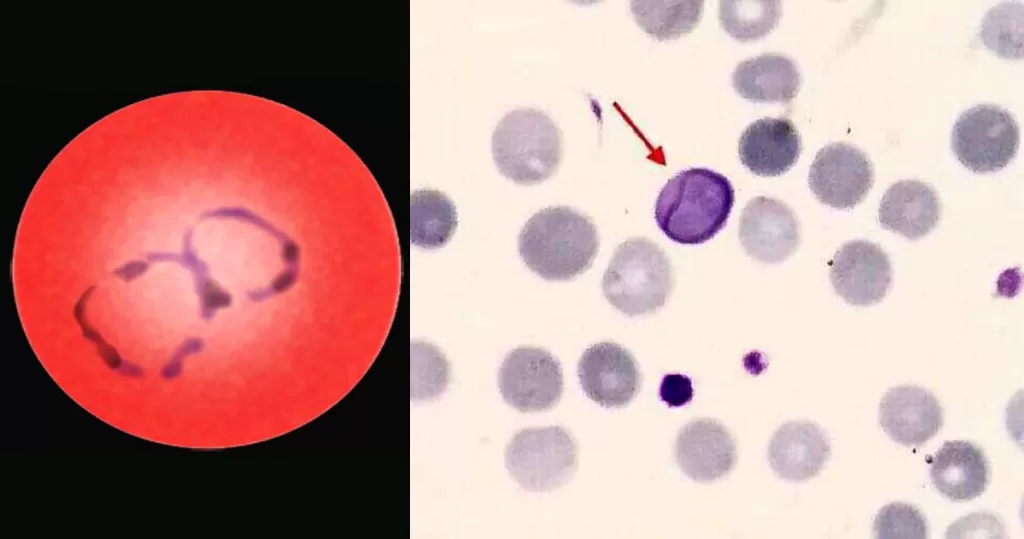
Cabot rings are ring-like or figure-of-eight loop-shaped inclusions composed of microtubule remnants from the mitotic spindle, or possibly nuclear remnants or abnormal histones. Can indicate B-12 anemia and related diseases, megaloblastic anemia, myelodysplastic syndrome, and lead poisoning.
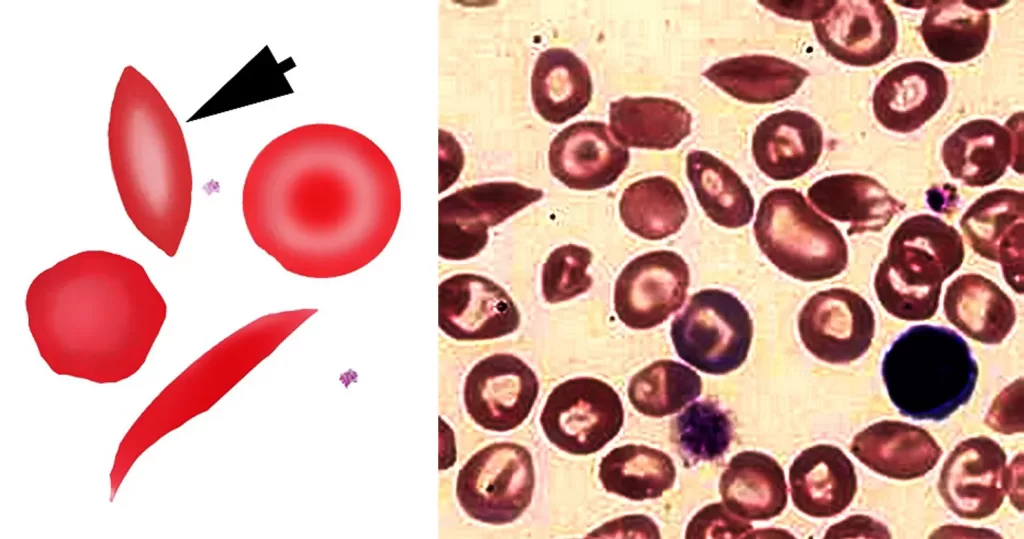
Although most closely associated with classical sickle disease (HbSS), boatshaped cells are also seen in compound heterozygotes between HbS and other abnormal haemoglobins.
Ignore boat cells in areas of blood movement, only consider if blood is static.
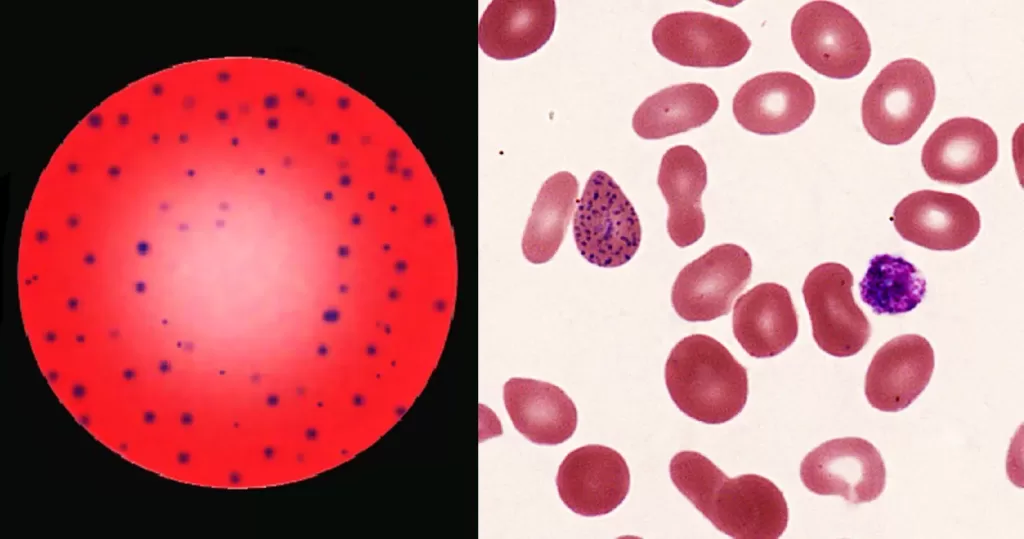
Most commonly arises when blood cell production is stressed or abnormal, may be associated with dysfunction of enzymes involved in RNA breakdown (either congenital deficiency or drug induced).
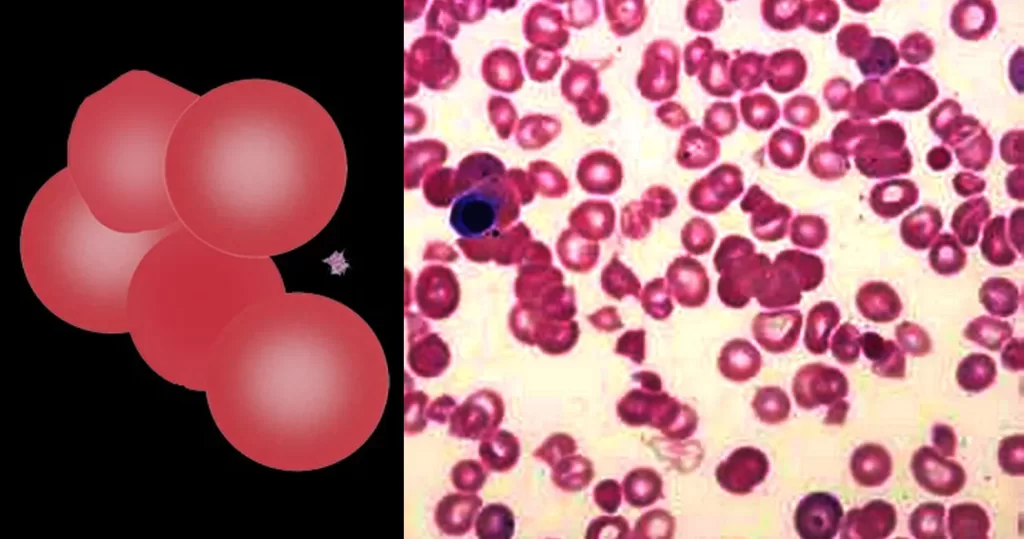
Agglutinates arise when antibodies attach to antigens on the membranes of adjacent red cells linking them together. The most common cause is “cold-reactive” IgM antibodies which do not cause overt symptoms. However, in some cases the effects may be clinically significant since antibodies may activate complement causing haemolysis, or the agglutinated cells can cause occlusion of small blood vessels in the cold (acrocyanosis). The clumped cells will sediment more rapidly leading to a raised erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). Finally, the antibodies that cause cold agglutination may indicate an underlying malignancy (particularly lymphoma), or by acute infection.
Platelets or thrombocytes react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by
clumping, thereby initiating a blood clot. Platelets have no cell nucleus. Platelets congregate around a wound creating a cap to stop blood flow out of the tissue (clotting). Platelets also contain cytokines and growth factors which can promote wound healing and regeneration of damaged tissues.
Platelets or thrombocytes react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by
clumping, thereby initiating a blood clot. Platelets have no cell nucleus;
they are fragments of cytoplasm derived from the megakaryocytes of the
bone marrow or lung, which then enter circulation. Platelets congregate
around a w ound creating a cap to stop blood flow out of the tissue
(clotting). Platelets also contain cytokines and growth factors which can
promote wound healing and regeneration of damaged tissues.
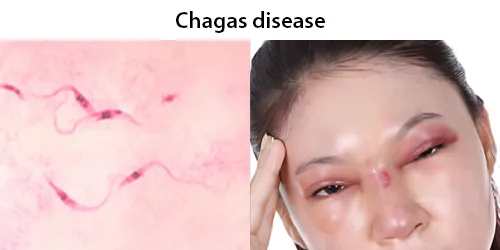
Dormancy Period: 2 months up to several years.
An estimated 6 to 7 million people worldwide are infected with T. cruzi Chagas disease. Chagas disease is caused by infection with the protozoan parasite T. cruzi, which is typically introduced into humans through the bite of triatomine bugs, also called “kissing bugs”. When the insect defecates at the bite site, motile T. cruzi forms called trypomastigotes enter the bloodstream and invade various host cells. Over many years, cycles of parasite replication and immune response can severely damage these tissues, particularly the heart and digestive tract.
After the parasite enters through an open wound or mucous membrane, the infectious trypomastigote is found in the bloodstream plasma. The amastigote stage of the parasites is found inside pseudocysts located in muscle or nerve cells. There is a predilection for the myocardium or myenteric plexus of the gastrointestinal tract, where it replicates by binary fission. There are three phases of the disease: acute, indeterminate and chronic.
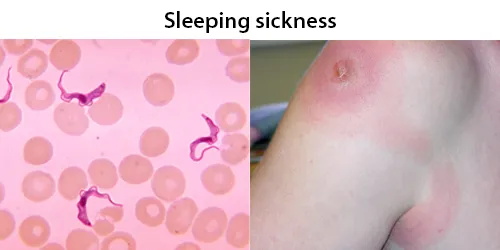
Dormancy Period: Unknown.
T. brucei is transmitted between mammal hosts by an insect vector belonging to different species of tsetse fly (Glossina). Transmission occurs by biting during the insect’s blood meal. Trypanosoma brucei is a species of parasitic kinetoplastid belonging to the genus Trypanosoma that is present in sub-Saharan Africa. Unlike other protozoan parasites that normally infect blood and tissue cells, it is exclusively extracellular and inhabits the blood plasma and body fluids. It causes deadly vector-borne diseases: African trypanosomiasis or sleeping sickness in humans, and animal trypanosomiasis or nagana in cattle and horses.
In later stages of a T. brucei infection of a mammalian host the parasite may migrate from the bloodstream to also infect the lymph and cerebrospinal fluids. It is under this tissue invasion that the parasites produce the sleeping sickness.
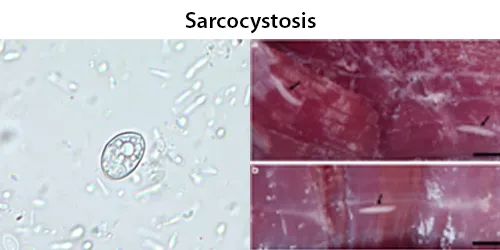
Dormancy Period: Up to 60 days. Many are asymptomatic.
If symptoms develop, they typically occur 20–40 days after ingestion of sporocysts and during the subsequent migration of sporozoites through the body vessels. Acute lesions (edema, hemorrhages, and necrosis) develop in the affected tissues. The parasite has a predilection for skeletal muscle (myositis), cardiac muscle (petechial hemorrhages of cardiac muscle and serosae), and lymph nodes (edema, necrosis, and hemorrhage).
Humans can experience nausea, vomiting, acute and severe enteritis, or chronic enteritis, but many infections appear to be mild or asymptomatic. Differences depend on the number, and perhaps the species, of sarcocysts ingested. Several cases of sarcocystosis have been detected in patients with various types of cancer. Related to cardiomyopathy, intramuscular sarcocystosis, intestinal sarcocystosis.
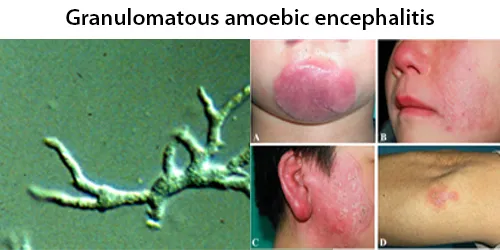
Dormancy Period: Days to weeks.
Balamuthia mandrillaris is a free-living amoeba that causes the rare but deadly neurological condition granulomatous amoebic encephalitis (GAE). B. mandrillaris can infect the body through open wounds or possibly by inhalation. It is distributed throughout the temperate regions of the world.
Upon introduction, the amoeba may form a skin lesion, or in some cases, may migrate to the brain, causing a condition known as granulomatous amoebic encephalitis (GAE), which is usually fatal. This granulomatous feature is mostly seen in immunocompetent patients; immunocompromised individuals exhibit a “perivascular cuffing”. Balamuthia-induced GAE can cause focal paralysis, seizures, and brainstem symptoms such as facial paralysis, difficulty swallowing, and double vision.
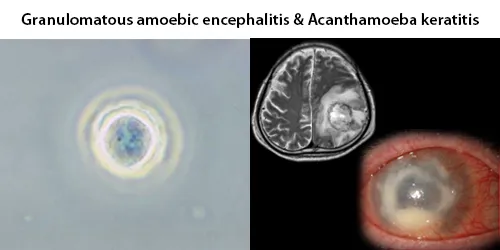
Dormancy Period: 1 week to months.
Acanthamoeba spp. are among the most prevalent protozoa found in the environment. They are distributed worldwide, and have been isolated from soil, air, sewage, seawater, chlorinated swimming pools, domestic tap water, bottled water, dental treatment units, hospitals, air-conditioning units, and contact lens cases. Additionally, they have been isolated from human skin, nasal cavities, throats, and intestines, as well as plants and other mammals.
They are opportunistic pathogens able to cause serious and sometimes fatal infections in humans and other animals. Diseases caused by Acanthamoeba include keratitis and granulomatous amoebic encephalitis (GAE). The latter is often but not always seen in immunosuppressed patients. GAE is caused by the amoebae entering the body through an open wound and then spreading to the brain. The combination of host immune responses and secreted amoebal proteases causes massive brain swelling resulting in death in about 95% of those infected, within one week to several months.
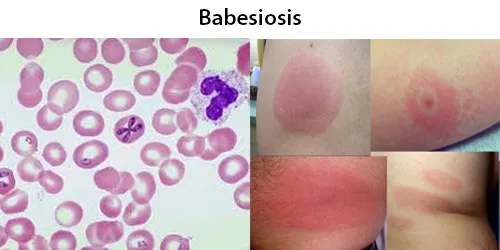
Dormancy Period: Up to 9 weeks, or the life of the patient if asymptomatic.
People can get infected with Babesia parasites by the bite of an infected tick, by getting a blood transfusion from an infected donor of blood products, or by congenital transmission (an infected mother to her baby). Ticks transmit the human strain of babesiosis, so it often presents with other tick-borne illnesses such as Lyme disease.
After trypanosomes, Babesia is thought to be the second-most common blood parasite of mammals. Half of all children and a quarter of previously healthy adults with Babesia infection are asymptomatic. People with symptoms usually become ill 1 to 4 weeks after the bite, or 1 to 9 weeks after transfusion of contaminated blood products.
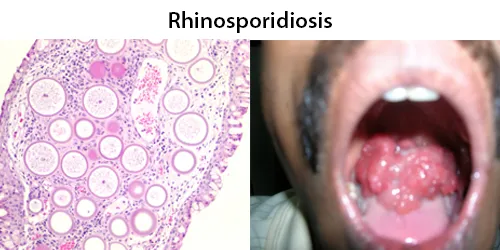
Dormancy Period: Can remain a dormant fungus or years.
This organism infects the mucosa of the nasal cavity, producing a mass-like lesion. This mass appears to be polypoidal in nature with a granular surface speckled with whitish spores. The rhinosporidial mass has been classically described as a strawberry-like mulberry mass. This mass may extend from the nasal cavity into the nasopharynx and present itself in the oral cavity. These lesions commonly cause bleeding from the nasal cavity. R. seeberi can also affect the lacrimal gland and also rarely the skin and genitalia.
Infection in humans with this organism has been reported from about 70 countries, with the majority of cases (95%) reported from India and Sri Lanka; per capita, Sri Lanka has the highest incidence in the world. The common factor found in these areas was the practice of bathing in common ponds.
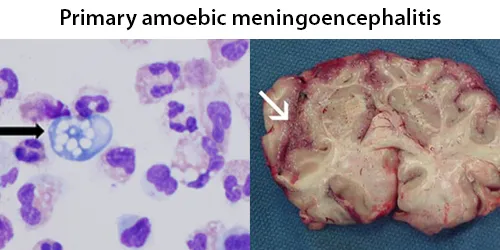
Dormancy Period: Up to 12 days, death up to two weeks after exposure. Early and accurate diagnosis is essential.
Naegleria fowleri, also known as the brain-eating amoeba. This free-living microorganism primarily feeds on bacteria but can become pathogenic in humans, causing an extremely rare, sudden, severe, and usually fatal brain infection known as naegleriasis or primary amoebic meningoencephalitis (PAM). A large proportion of reported cases of infection had a history of water exposure, 58% from swimming or diving, 16% from bathing, 10% from water sports such as jet skiing, water-skiing and wakeboarding and 9% from nasal irrigation. Swimmers should also avoid digging or stirring up sediment at the bottom of lakes, ponds and rivers as this is where amebae are most likely to live.
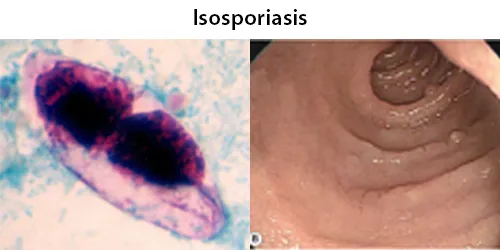
Dormancy Period: Days.
Isosporiasis, also known as cystoisosporiasis, is a human intestinal disease caused by the parasite. Infection often occurs in immuno-compromised individuals, notably AIDS patients. It is usually spread indirectly, normally through contaminated food or water. The infected host then produces an immature form of the parasite in their feces, and when the parasite matures, it is capable of infecting its next host, via food or water containing the parasite.
Infection causes acute, non-bloody diarrhea with crampy abdominal pain, which can last for weeks and result in malabsorption and weight loss. In immunodepressed patients, and in infants and children, the diarrhea can be severe.
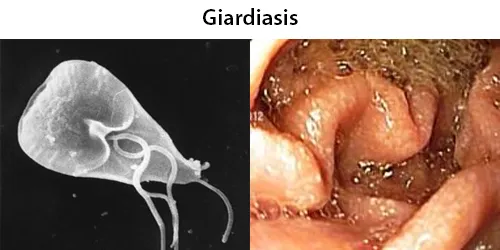
Dormancy Period: Up to three weeks, non-symptomatic for weeks.
Giardiasis is a parasitic disease caused by Giardia duodenalis (also known as G. lamblia and G. intestinalis). Infected individuals who experience symptoms (about 10% have no symptoms) may have diarrhea, abdominal pain, and weight loss. Less common symptoms include vomiting and blood in the stool. Symptoms usually begin one to three weeks after exposure and, without treatment, may last two to six weeks or longer.
Giardiasis is one of the most common parasitic human diseases. Infection rates are as high as 7% in the developed world and 30% in the developing world. Symptoms usually begin one to three weeks after exposure and, without treatment, may last two to six weeks or longer. Symptoms typically develop 9–15 days after exposure, but may occur as early as one day. Many people with Giardia infections have no or few symptoms. They may, however, still spread the disease.
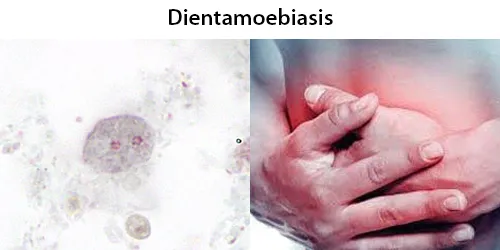
Incubation Period: Days.
Dientamoebiasis is a medical condition caused by infection with Dientamoeba fragilis, a single-cell parasite that infects the lower gastrointestinal tract of humans. It is an important cause of traveler’s diarrhea, chronic abdominal pain, chronic fatigue, and failure to thrive in children.
Many individuals are asymptomatic carriers of Dientamoebiasis fragilis. Pathogenic and non-pathogenic variants are proposed to exist. Generally considered not harmful if in balanced population.The most commonly reported symptoms in conjunction with infection with D. fragilis include abdominal pain (69%) and diarrhea (61%). Diarrhea may be intermittent and may not be present in all cases. It is often chronic, lasting over two weeks. The degree of symptoms may vary from asymptomatic to severe, and can include weight loss, vomiting, fever, and involvement of other digestive organs. D. fragilis is not considered to be invasive nor cause cell or tissue damage.

Incubation Period: 1 week
Cyclosporiasis primarily affects humans and other primates. When an oocyst of Cyclospora cayetanensis enters the small intestine, it invades the mucosa, where it incubates for about one week. After incubation, the infected person begins to experience severe watery diarrhea, bloating, fever, stomach cramps, and muscle aches.
Cyclosporiasis is a disease caused by infection with Cyclospora cayetanensis, a pathogenic apicomplexan protozoan transmitted by feces or feces-contaminated food and water. Outbreaks have been reported due to contaminated fruits and vegetables. It is not spread from person to person, but can be a hazard for travelers as a cause of diarrhea.
The parasite sporulation for Cyclosporiasisis is from 8–11 days, making the illness difficult to diagnose. It invades the mucosa, where it incubates for about one week. When examining feces, the unsporulated oocysts can easily be mistaken for fungal spores, and thus can be easily overlooked.
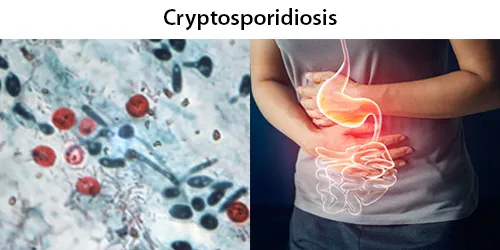
Dormancy Period: 2- 28 days.
Cryptosporidiosis, sometimes informally called crypto, is a parasitic disease caused by Cryptosporidium, a genus of protozoan parasites in the phylum Apicomplexa. It affects the distal small intestine and can affect the respiratory tract in both immunocompetent (i.e., individuals with a normal functioning immune system) and immunocompromised (e.g., persons with HIV/AIDS or autoimmune disorders) individuals, resulting in watery diarrhea with or without an unexplained cough. In immunosuppressed individuals, the symptoms are particularly severe and can be fatal. It is primarily spread through the fecal-oral route, often through contaminated water; recent evidence suggests that it can also be transmitted via fomites contaminated with respiratory secretions.
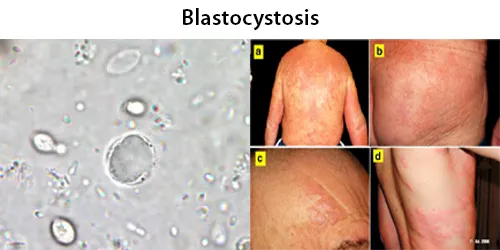
Dormancy Period: weeks to years.
Blastocystis is a protozoal, single-celled parasite that inhabits the gastrointestinal tracts of humans and other animals. Many different types of Blastocystis exist, and they can infect humans, farm animals, birds, rodents, amphibians, reptiles, fish, and even cockroaches. Blastocystosis has been found to be a possible risk factor for development of irritable bowel syndrome.
Common occurrences of Blastocystosis are both asymptomatic and symptomatic. Most cases of the infection appear to become diagnosed as irritable bowel syndrome. The timescale of infection with the parasite can range from weeks to years. Non-symptomatic humans and animals can act as reservoirs.
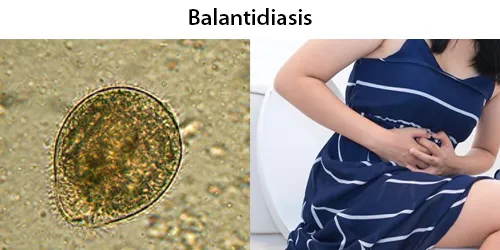
Dormancy Period: a few days to the lifetime of the patient.
Balantidiasis is a zoonotic disease and is acquired by humans via the feco-oral route from the normal host, the pig, where it is asymptomatic. Fecally contaminated food and water are the common sources of infection in humans.
Some people infected with Balantidiasis may have no symptoms or only mild diarrhea and abdominal discomfort but others may experience more severe symptoms reminiscent of an acute inflammation of the intestines. Balantidium mostly causes asymptomatic and self-limiting infections. Asymptomatic hosts serve as reservoirs of infection in the community.
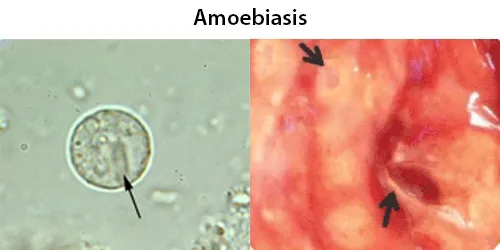
Dormancy Period: a few days to a few weeks, but usually it is about two to four weeks.
Most infected people, about 90%, are asymptomatic, but this disease has the potential to become serious. It is estimated that about 40,000 to 100,000 people worldwide die annually due to amoebiasis
Since amoebiasis is transmitted through contaminated food and water, it is often endemic in regions of the world with limited modern sanitation systems, including México, Central America, western South America, South and Southeast Asia, and western and southern Africa.
Amoebiasis / Entamoeba species exist in 2 forms: A dormant parasite (cyst),and an active parasite (trophozoite). They can cause brain problems. Symptoms usually develop within 2 to 4 weeks but can show up later.
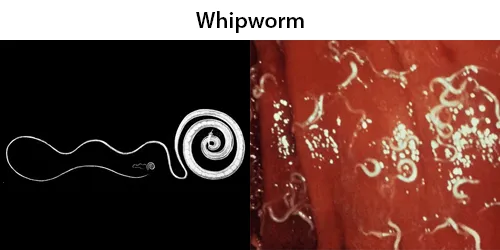
Dormancy Period: 3 months, up to 1 year or longer.
For about four weeks, the whipworms feed on blood vessels located within the cecum of the large intestine. Eventually, the whipworms leave the cecum and begin to lay thousands of eggs. These unembryonated eggs are then released from the host through feces. The process from egg ingestion to release takes around 12 weeks. The released eggs become embryonated in approximately nine to twenty-one days and are eventually ingested by another host. Eggs that are passed in the feces, can remain alive in soil for years.
The life cycle from the time of ingestion of eggs to the development of mature worms takes approximately three months. During this time, there may be limited signs of infection in stool samples, due to a lack of egg production and shedding. The female T. trichiura begin to lay eggs after three months of maturity. Worms commonly live for about one year, during which time females can lay up to 20,000 eggs per day.
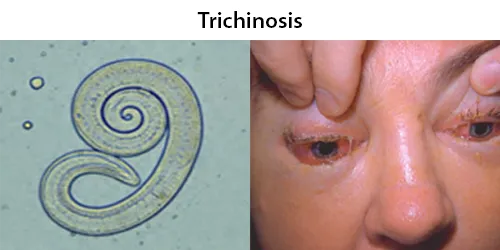
Dormancy Period: Up to 7 days.
About 11 million humans are infected with Trichinella. The great majority of trichinosis infections have either minor or no symptoms and no complications. Trichinosis. During the initial infection, invasion of the intestines can result in diarrhea, abdominal pain, and vomiting. Migration of larvae to muscle, which occurs about a week after being infected, can cause swelling of the face, inflammation of the whites of the eyes, fever, muscle pains, and a rash. Complications may include inflammation of heart muscle, central nervous system involvement, and inflammation of the lungs.
They may very rarely cause enough damage to produce serious neurological deficits (such as ataxia or respiratory paralysis) from worms entering the central nervous system, which is compromised by trichinosis in 10–24% of reported cases of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis, a very rare form of stroke (three or four cases per million annual incidence in adults).
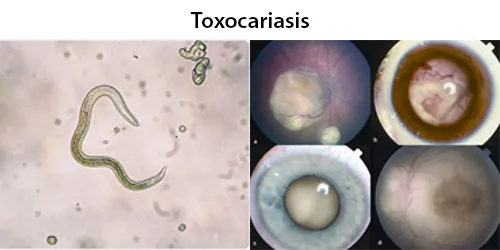
Dormancy Period: 2 weeks to several years.
Toxocariasis is an illness of humans caused by the dog roundworm (Toxocara canis) and, less frequently, the cat roundworm (Toxocara cati). These are the most common intestinal roundworms of dogs, coyotes, wolves and foxes and domestic cats. Humans are among the many “accidental” or paratenic hosts of these roundworms.
While this zoonotic infection is usually asymptomatic, it may cause severe disease. There are three distinct syndromes of toxocariasis:
Covert toxocariasis is a relatively mild illness very similar to Löffler’s syndrome. It is characterized by fever, eosinophilia, urticaria, enlarged lymph nodes, cough, bronchospasm, wheezing, abdominal pain, headaches, and/or hepatosplenomegaly.
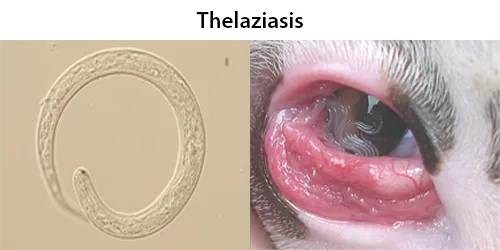
Dormancy Period: Days to 1 year.
Thelaziasis is the term for infestation with parasitic nematodes of the genus Thelazia. The adults of all Thelazia species discovered so far inhabit the eyes and associated tissues (such as eyelids, tear ducts, etc.) of various mammal and bird hosts, including humans. Thelazia nematodes are often referred to as “eyeworms”. In animal and human hosts, infestation by Thelazia may be asymptomatic, though it frequently causes watery eyes (epiphora), conjunctivitis, corneal opacity, or corneal ulcers (ulcerative keratitis). Infested humans have also reported “foreign body sensation” – the feeling that something is in the eye.
The larvae develop into adults in the eye or surrounding tissues of the host, where they may live for over one year.
Thelazia have been found in various tissues of the orbit (or socket) of the eye, including within the eyelids, in the tear glands, tear ducts, or the so-called “third eyelid” (nictitating membrane) or in the eyeball itself.
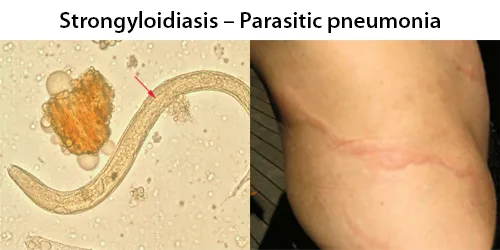
Dormancy Period: Lifetime of the patient.
The adult parasitic stage lives in tunnels in the mucosa of the small intestine. Many people infected are asymptomatic at first. Symptoms include dermatitis: swelling, itching, larva currens, and mild hemorrhage at the site where the skin has been penetrated. Spontaneous scratch-like lesions may be seen on the face or elsewhere. If the parasite reaches the lungs, the chest may feel as if it is burning, and wheezing and coughing may result, along with pneumonia-like symptoms (Löffler’s syndrome). The intestines could eventually be invaded, leading to burning pain, tissue damage, sepsis, and ulcers. Stools may have yellow mucus with a recognizable smell. Chronic diarrhea can be a symptom. In severe cases, edema may result in obstruction of the intestinal tract, as well as loss of peristaltic contractions.
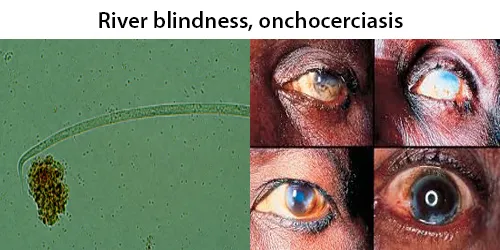
Dormancy Period: 12 months to 15 years.
The average adult worm lifespan is 15 years, and mature females can produce between 500 and 1,500 microfilariae per day. The normal microfilarial lifespan is 1.0 to 1.5 years; however, their presence in the bloodstream causes little to no immune response until death or degradation of the microfilariae or adult worms. It is spread from person to person via female biting blackflies of the genus Simulium, and humans are the only known definitive host.
O. volvulus causes onchocerciasis, which causes severe itching. Long-term infection can cause keratitis, an inflammation of the cornea in the eye, and ultimately leads to blindness. Symptoms are caused by the microfilariae and the immune response to infection, rather than the adults themselves.
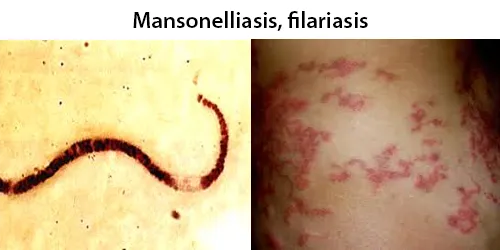
Dormancy Period: Days to weeks
The infection of these roundworms typically causes no overt symptoms but may sometimes cause a mild dermatitis of the thorax and shoulders. M. streptocerca infections fortunately do not cause any nodules, skin disease, or ocular infections like that of Onchocerca volvulus. However they may become visible just under the skin surface, and perhaps decrease skin health and immunity.
During a blood meal, an infected midge (genus Culicoides) or blackfly (genus Simulium) introduces third-stage filarial larvae onto the skin of the human host, where they penetrate into the bite wound. They develop into adults that reside in body cavities, most commonly the peritoneal cavity or pleural cavity, but also occasionally in the pericardium (M. perstans), subcutaneous tissue (M. ozzardi) or dermis (M. steptocerca).
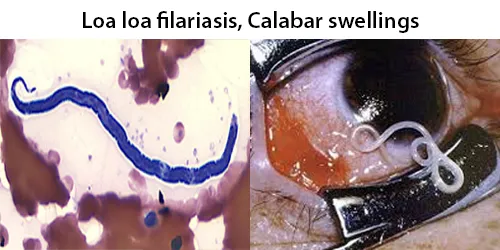
Dormancy Period: Up to 1 year.
Loa loa filariasis, (Loiasis) is a skin and eye disease caused by the nematode worm Loa loa. Humans contract this disease through the bite of a deer fly (Chrysops spp.) or mango fly. These carriers are blood-sucking and day-biting, and they are found in rainforest-like environments in western and central Africa.
A filariasis such as loiasis most often consists of asymptomatic microfilaremia. Some patients can develop lymphatic dysfunction causing lymphedema. Episodic angioedema (Calabar swellings) in the arms and legs, caused by immune reactions, are common. Loa loa is also called the “African eye worm”. The passage over the eyeball can be sensed, but it usually takes less than 15 minutes. Eyeworms affect men and women equally, but advanced age is a risk factor. Eosinophilia is often prominent in filarial infections. Dead worms may cause chronic abscesses, which may lead to the formation of granulomatous reactions and fibrosis.
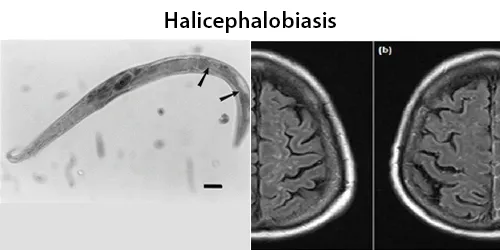
Dormancy Period: Possibly days to weeks.
Halicephalobus gingivalis is a free-living saprophagous nematode species. It is a facultative parasite of horses, invading the nasal cavity, and sometimes numerous other areas, where it produces granulomatous masses. On rare occasion, it can infect humans as well, causes a universally lethal meningoencephalitis. Infection of the brain is common, followed by the kidneys, oral and nasal cavities, lymph nodes, lungs, spinal cord, and adrenal gland, and also reports of infection of heart, liver, stomach and bone.
The site of entry for the parasite is thought to be through breaks in the skin or through mucous membranes. This nematode is now distributed worldwide, in all climates. It dwells actively in soil, around plants and other organically rich environments including manure and compost.
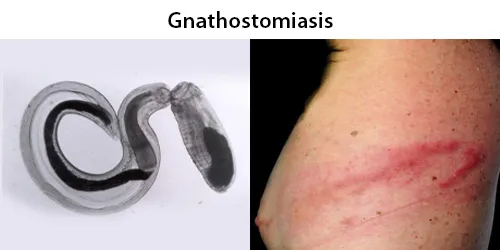
Dormancy Period: Up to 4 weeks.
Gnathostomiasis is transmitted by the ingestion of third-stage larvae from raw or insufficiently cooked second intermediate or paratenic hosts such as freshwater fish, snakes, poultry, or frogs. The incubation period for gnathostomiasis is 3–4 weeks when the larvae begin to migrate through the subcutaneous tissue of the body.
A few days after ingestion epigastric pain, fever, vomiting, and loss of appetite resulting from migration of larvae through intestinal wall to the abdominal cavity will appear in the patient. Migration of parasites in the subcutaneous tissues causing intermittent, migratory, painful, pruritic swellings is known as cutaneous larva migrans. Patches of edema appear after initial symptoms clear and are usually found on the abdomen.
Migration to other tissues causes visceral larva migrans and can result in cough, hematuria, ocular involvement, meningitis, encephalitis and eosinophilia. Eosinophilic myeloencephalitis may also result from invasion of the central nervous system by the larvae.
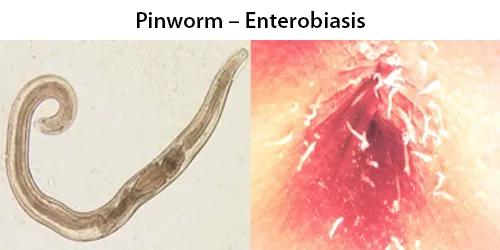
Dormancy Period: Up to 8 weeks, often asymtomatic.
The disease is spread between people by pinworm eggs. The eggs initially occur around the anus. The period of time from swallowing eggs to the appearance of new eggs around the anus is 4 to 8 weeks. The main symptoms are itching in and around the anus and perineum. One-third of individuals with pinworm infection are totally asymptomatic. The eggs are hardy and can remain infectious, outside the body, in a moist environment for up to three weeks.
They may move onto the vulva and into the vagina, from there moving to the external orifice of the uterus, and onwards to the uterine cavity, fallopian tubes, ovaries, and peritoneal cavity. This can cause inflammation of the vulva and vagina. This causes vaginal discharge and itchiness of the vulva. Pinworms can also enter the urethra, and presumably, they carry intestinal bacteria with them.
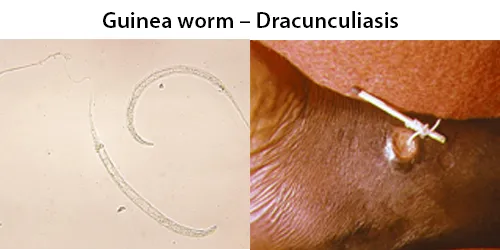
Dormancy Period: One year or longer. The first signs of dracunculiasis occur around a year after infection, as the full-grown female worm prepares to leave the infected person’s body.
About a year after the initial infection, the female migrates to the skin, forms an ulcer, and emerges. When the wound touches fresh water, the female spews a milky-white substance containing hundreds of thousands of larvae into the water. Over the next several days as the female emerges from the wound, she can continue to discharge larvae into surrounding water. The larvae are eaten by copepods (small aquatic crustaceans), and after two to three weeks of development, they are infectious to humans again. Infected people commonly harbor multiple worms – on average 1.8 worms per person, but as many as 40 – which will emerge from separate blisters at the same time. 90% of worms emerge from the legs or feet. However, worms can emerge from anywhere on the body.
Humans typically get infected when they unintentionally ingest copepods while drinking water or exposure while swimming.
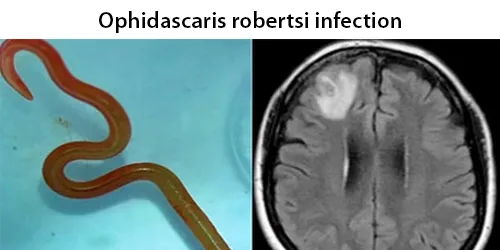
Dormancy Period: Possibly days to years.
Ophidascaris robertsi is a nematode (also known as roundworm) usually parasitic in the carpet python (Morelia spilota). It is found in Australia and Papua New Guinea,and possibly Indonesia. Pythons serve as the typical hosts for Ophidascaris robertsi. Humans and mammals that live near carpet python habitat and forage for native vegetation to cook can be exposed by consuming the roundworm’s eggs.These eggs, which are commonly shed in snake droppings due to the snakes’ diet of infected animals, likely contaminates the grass and soil eaten by small mammals. Other vectors, such as domestic and wild animals, are yet to be investigated.
Doctors theorize that the various symptoms (diarrhea and abdominal pain, along with night sweats and dry cough, lung infection) result from the migration of the parasitic eggs and larva from the bowel, through various other organs, before arriving in the brain.
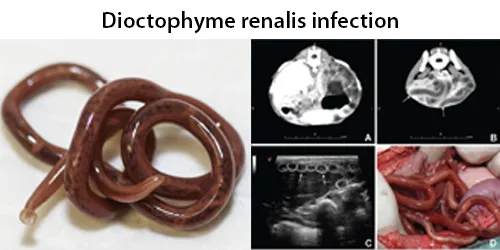
Dormancy Period: Up to 50 days.
After maturing for approximately 50 days, the juveniles then migrate to the kidneys (typically the right kidney). Upon maturation, D. renale can survive for five years. D. renale is distributed worldwide, but is less common in Africa and Oceania. It affects fish-eating mammals, particularly mink, wolves, coyotes, foxes, dogs, raccoons, and weasels. Human infestation is rare, but results in kidney destruction.
The only means of obtaining a definitive diagnosis is through the identification of D. renale eggs in a patient’s urine. However, obtaining patient history (i.e., if the patient has consumed under-cooked or raw freshwater fish) is an important first step that can be coupled with radiological exams to search for enlarged or calcified kidneys. Urinalysis will likely show hematuria, blood tests may reveal eosinophilia.
D. renale is the largest nematode to parasitize humans. Adult male worms are 20–40 cm long and 5–6 mm wide; females can grow to 103 cm in length with a width of 10–12 mm.
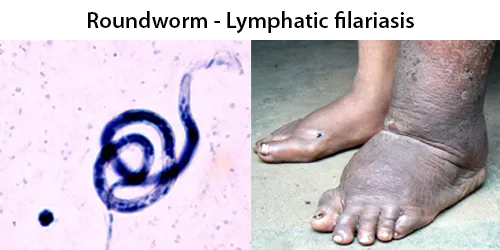
Dormancy Period: 1 month to 2 years.
The incubation period for infection ranges from 1 month to 2 years and typically microfilariae appear before overt symptoms.The accumulation of many infective mosquito bites – several hundreds to thousands – is required to establish infection. Lymphedema can develop within six months and development of elephantiasis has been reported within a year of infection. Men tend to develop worse symptoms than women. The Brugia mosquito injects larvae into human blood stream. Adult worms can survive in the lymphatic system for 5–15 years. The accumulation of many mosquito bites is required to establish infection.
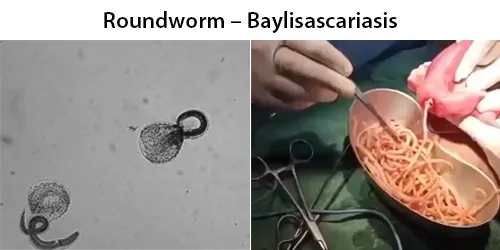
Dormancy Period: Several years asymptomatic.
Most people are asymptomatic unless heavily infected. Human infection with Baylisascaris procyonis has been relatively rare. However, disease caused by this parasite can be extremely dangerous, causing death or severe symptoms. The parasite has been known to infect more than 90 kinds of wild and domestic animals. Reported disease has primarily afflicted children and almost all cases were a result of the ingestion of contaminated soil or feces, via the oral fecal route. the infection results in the penetration of the gut wall by the larvae and subsequent invasion of tissue, resulting in severe disease.
This parasite’s eggs are able to live for years, extremely resistant to many disinfectants, and cause serious infections in humans with poor treatment options. Community water supplies are easily susceptible to contamination due to the lack of filtration and treatment methods to get rid of the eggs.
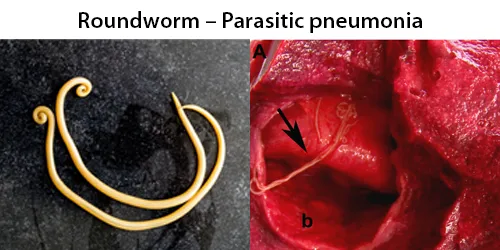
Dormancy Period: Up to 3 years.
Often, people show no overt symptoms but may suffer from intestinal problems. When symptoms do occur, the person is usually infected with a large number of worms. Ascaris lumbricoides is one of the most difficult pathogens to kill (second only to prions), and the eggs commonly survive 1–3 years before hatching.
The A. lumbricoides roundworm lives in the intestine where it lays eggs. Infection occurs when the eggs, too small to be seen by the unaided eye, are eaten. The eggs may get onto vegetables when improperly washed. Ascaris lumbricoides infect and estimated 819 million people worldwide. A lumbricoides is the largest intestinal roundworm and is the most common helminth infection of humans worldwide. The worms lack teeth. However, they can rarely cause bowel perforations by inducing volvulus and closed-loop obstruction. Infestation can be deadly if not treated. Occasionally, a worm can travel through the biliary tree and even into the gallbladder, causing acute cholangitis or acute cholecystitis.
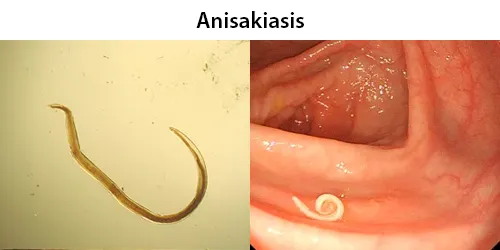
Dormancy Period: If no immediate allergic reaction, more severe digestive reactions may be experienced within a few days.
Anisakiasis is a human parasitic infection of the gastrointestinal tract caused by the consumption of raw or undercooked seafood containing larvae of the nematode Anisakis simplex. Reactions, mostly seen as fish allergies, tend to occur soon after consumption.
Within a few hours of ingestion, the parasitic worm tries to burrow though the intestinal wall, but since it cannot penetrate it, it gets stuck and dies. The presence of the parasite triggers an immune response; immune cells surround the worms, forming a ball-like structure that can block the digestive system, causing severe abdominal pain, malnutrition, and vomiting. Occasionally, the larvae are regurgitated. If the larvae pass into the bowel or large intestine, a severe eosinophilic granulomatous response may also occur one to two weeks following infection, causing symptoms mimicking Crohn’s disease.
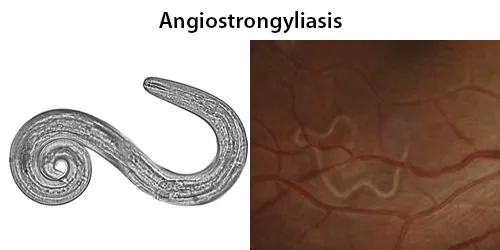
Dormancy Period: The incubation period in humans is usually from 1 week to 47 days after infection. Most cases are asymptomatic.
In humans, A. cantonensis is the most common cause of eosinophilic meningitis or meningoencephalitis. Frequently the infection will resolve without treatment or serious consequences, but in cases with a heavy load of parasites the infection can be so severe it can cause permanent damage to the central nervous system or death.
Humans and rats acquire the infection when they ingest contaminated snails or paratenic (transport) hosts including prawns, crabs, and frogs, or raw vegetables containing material from these intermediate and paratenic hosts. After passing through the gastrointestinal tract, the worms enter circulation. The larvae then migrate to the meninges and develop for about a month before migrating to the pulmonary arteries, where they fully develop into adults. The larvae cannot reproduce in humans.
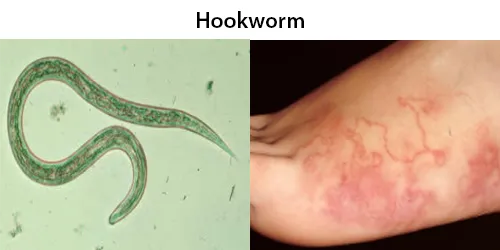
Dormancy Period: May remain undetected for many years, however anemia may be an indicator of long term infection..
Hookworms account for a high proportion of debilitating disease in the tropics and 50–60,000 deaths per year These worms produce an iron deficiency anemia by sucking blood from the host’s intestinal walls.
The infection is usually contracted by people walking barefoot over contaminated soil. In penetrating the skin, the larvae may cause an allergic reaction. It is due to the itchy patch at the site of entry that the early infection gets its nickname “ground itch”. Once larvae have broken through the skin, they enter the bloodstream and are carried to the lungs (however, unlike ascarids, hookworms do not usually cause pneumonia).

Dormancy Period: Up to several years, depending on the vector.
Ticks are external parasites, living by feeding on the blood of mammals, birds, and sometimes reptiles and amphibians. Ticks have up to seven nymphal stages (instars), each one requiring blood ingestion, and as such, Ticks undergo a multihost life cycle. Because of their hematophagous (blood-ingesting) diets, ticks act as vectors of many serious diseases that affect humans and other animals.
Ticks are extremely resilient animals. They can survive in a near vacuum for as long as half an hour. Their slow metabolism during their dormant periods enables them to go prolonged durations between meals. Even after 18 weeks of starvation, they can endure repeated two-day bouts of dehydration followed by rehydration, but their survivability against dehydration drops rapidly after 36 weeks of starvation.

Dormancy Period: Up to six weeks.
Scabies, also sometimes known as the seven-year itch, is a contagious human skin infestation by the tiny (0.2–0.45 mm) mite Sarcoptes scabiei, In a first-ever infection, the infected person usually develops symptoms within two to six weeks. During a second infection, symptoms may begin within 24 hours. The mites burrow into the skin to live and deposit eggs.The symptoms of scabies are due to an allergic reaction to the mites. Scabies is most often spread during a relatively long period of direct skin contact with an infected person (at least 10 minutes) such as that which may occur during sexual activity or living together. Spread of the disease may occur even if the person has not developed symptoms yet.
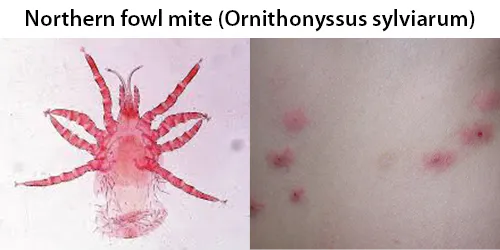
Dormancy Period: Up to many years depending on the related vector.
Diagnosis can be challenging as the small size of avian mites make them “barely visible to the unaided eye”. Dermanyssus gallinae can also infest various body parts, including the ear canal and scalp. commonly found in the bedroom or where the patient sleeps, as they prefer to stay close to their host for optimal feeding. D. gallinae generally visit their host for up to 1–2 hours, leave after completing their blood meal, and typically feed every 2–4 days. They are able to move extremely quickly, and can take less than 1 second to bite; enough time to inject their saliva and to induce rash and itching.They locate potential hosts through temperature changes, vibrations, chemical signals and CO2.
They primarily infect egg laying chickens, canaries, sparrows, starlings, pigeons, and poultry and also cats, dogs, hamsters, gerbils. This blood-feeding parasite is broadly distributed, and has been reported on 72 host species of North American birds in 26 families.

Dormancy Period: Up to several years with vectored diseases.
Mosquito-borne diseases or illnesses are caused by bacteria, viruses, or parasites transmitted by mosquitoes. Nearly 700 million people contract mosquito-borne illnesses each year, resulting in more than a million deaths.
Diseases transmitted by mosquitoes include malaria, dengue, West Nile virus, chikungunya, yellow fever, filariasis, tularemia, dirofilariasis, Japanese encephalitis, Saint Louis encephalitis, Western equine encephalitis, Eastern equine encephalitis, Venezuelan equine encephalitis, Ross River fever, Barmah Forest fever, La Crosse encephalitis, and Zika fever, as well as newly detected Keystone virus and Rift Valley fever.
When a mosquito bites a human, it injects saliva and anti-coagulants. With the initial bite to an individual, there is no reaction, but with subsequent bites, the body’s immune system develops antibodies. The bites become inflamed and itchy within 24 hours. Avoid all mosquito bites, but especially those from larger black-and-white mosquitos.
Dormancy Period: Rickettsial pox is generally mild and resolves within 2–3 weeks if untreated. There are no known deaths resulting from the disease. Other vectors have been lab tested but not proven outside the lab.
It can transmit human disease, is associated with causing rodent mite dermatitis in humans and is noted for carrying Rickettsia akari, which causes rickettsialpox. Rodent mites are capable of surviving for long periods without feeding and traveling long distances when seeking hosts. Cases have been reported in homes, libraries, hospitals and care homes. A similar condition, known as gamasoidosis, is caused by avian mites.
No human disease has been definitively found to be naturally vectored by these mites. Lab demonstrations have proved that they are at least capable of vectoring murine typhus, rickettsial pox, tularemia, plague, coxsackievirus, and Q fever, although it has not been known to do so outside the lab. The mite was reported as capable of vectoring human typhus, but these reports are not generally accepted.

Dormancy Period: Adult lice will die within 2 days without a blood meal. Rare vectors in Africa with up to 20 days incubation.
Head lice feed only on human blood and are only able to survive on human head hair. They only spread by human to human contact. When adults, they are about 2 to 3 mm long. When not attached to a human, they are unable to live beyond three days. In Ethiopia, head lice appear to be able to spread louse-born epidemic typhus and Bartonella quintana. Elsewhere head lice do not appear to carry these infections.
During its lifespan of 4 weeks a female louse lays 50-150 eggs. Eggs hatch within 6–9 days, each nymphal stage last for 4–5 days and accordingly the period from egg to adults lasts for 18–24 days. Adult lice live for an additional 3–4 weeks. Although any part of the scalp may be colonized, lice favor the nape of the neck and the area behind the ears, where the eggs are usually laid. Head lice are repelled by light and move towards shadows or dark-colored objects in their vicinity.
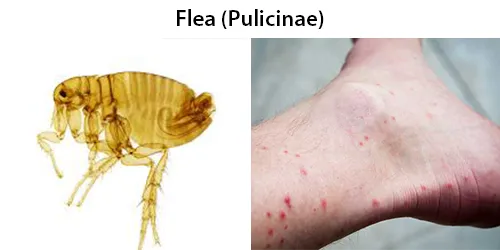
Dormancy Period: Several months without food. Numerous dangerous vectors can emerge up to years later.
Fleas feed on a wide variety of warm-blooded vertebrates including dogs, cats, rabbits, squirrels, ferrets, rats, mice, birds, and sometimes humans. Female fleas can lay 5000 or more eggs over their life, an adult flea only lives for 2 or 3 months. Without a host to provide a blood meal. A flea’s life can be as short as a few days, or can live for up to a year and a half, can live for several months without eating, so long as they do not emerge from their puparia.
Fleas are vectors for viral, bacterial and rickettsial diseases of humans and other animals, as well as of protozoan and helminth parasites. Bacterial diseases carried by fleas include murine or endemic typhus and bubonic plague. Fleas can transmit Rickettsia typhi, Rickettsia felis, Bartonella henselae, and the myxomatosis virus. They can carry Hymenolepiasis tapeworms and Trypanosome protozoans.
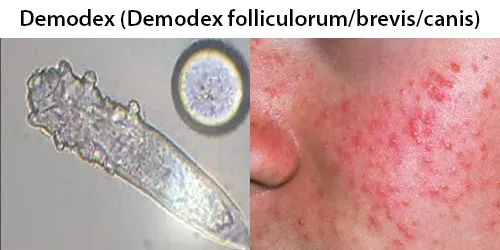
Dormancy Period: The total lifespan of a Demodex mite is several weeks, with skin diseases evolving over days or months.
Demodex canis lives on the domestic dog, can become mange, and are easily transferred from them. Demodicosis is most often seen in folliculitis (inflammation of the hair follicles of the skin). It may result in small pustules (pimples) at the base of a hair shaft on inflamed, congested skin.
Demodicosis may also cause itching, swelling, and erythema of the eyelid margins. Scales at the base of the eyelashes may develop. Typically, patients complain of eyestrain. Older people are much more likely to carry face mites; about a third of children and young adults, half of adults, and two-thirds of elderly people carry them. The lower rate in children may be because children produce less sebum, or simply have had less time to acquire the mite. The six-legged larvae hatch after 3–4 days, and the larvae develop into adults in about 7 days. The total lifespan of a Demodex mite is several weeks.
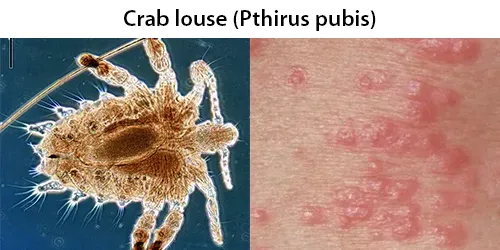
Dormancy Period: Adult louse live for up to 30 days. No vectored diseases are known.
Feeding exclusively on blood, the crab louse usually is found in the person’s pubic hair. Although the louse cannot jump, it can also live in other areas of the body that are covered with coarse hair, such as the peri-anal area, the entire body (in men), and the eyelashes (in children).
The total life cycle from egg to adult is 16–25 days. Adults live for up to 30 days. Crab lice feed exclusively on blood, and take a blood meal 4–5 times daily. Outside the host they can survive for 24–48 hours. Crab lice are transmitted from person to person most commonly via sexual contact, although fomites (bedding, clothing) may play a minor role in their transmission. Crab lice are not known to transmit disease; however, secondary bacterial infection can occur from scratching of the skin. Symptoms of crab louse infestation in the pubic area include itching, redness and inflammation.
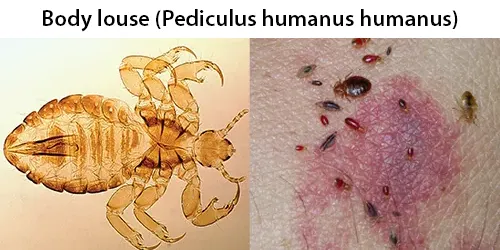
Dormancy Period: From vectored pathogens up to 20 days.
Body lice may lay eggs on the host hairs and clothing, but clothing is where the majority of eggs are usually secured. The most important pathogens which are transmitted by them are Rickettsia prowazekii (causes epidemic typhus), Borrelia recurrentis (causes relapsing fever), and Bartonella quintana (causes trench fever). Adult lice can live for about thirty days, but if they are separated from their host they will die within two days.

Dormancy Period: Bug can be dormant up to 12 months. No vectored diseases are known.
Although they move away from the host after feeding, they remain within the confines of their host’s roost, nest or dwelling. They may be considered to be micro-predatory bloodsuckers. Adult bedbugs have been reported to live three to twelve months if in an untreated household situation. The effects of cimicid feeding on the host include causing an immune response that results in discomfort, the transmission of pathogens, secondary infections at the wound site, physiological changes such as iron deficiency, and reduced fitness. Although viruses and other pathogens can be acquired by cimicids, they rarely transmit them to their hosts, unless the host is immune compromised.

Dormancy Period: If progressed to Scrub Typhus, 21 days
Leptotrombidium deliense is considered a dangerous pest in East Asia and the South Pacific because it often carries Orientia tsutsugamushi, the tiny bacterium that causes scrub typhus, which is known alternatively as the Japanese river disease, scrub disease, or tsutsugamushi. The mites are infected by the Rickettsia passed down from parent to offspring before eggs are laid in a process called transovarial transmission. Symptoms of scrub typhus in humans include fever, headache, muscle pain, cough, and gastrointestinal symptoms.
The chiggers’ digestive enzymes in the saliva cause “the intensely itchy welts”. Humans are possible hosts. The length of the mite’s cycle normally lasts two to 12 months. After about six days, the prelarvae grow into their larval stage. the mite may still be attached for up to 3 days. The itching can be alleviated through use of over-the-counter topical corticosteroids and antihistamines. According to Mayo Clinic, the chiggers “fall off after a few days, leaving behind red, itchy welts”, which normally heal on their own within one to two weeks. Hot showers or baths also help reduce itching.
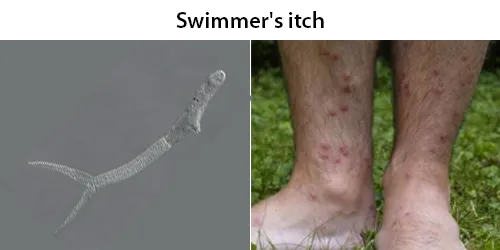
Dormancy Period: Up to 20 years.
Schistosoma (Schistosomatidae) are responsible for human schistosomosis affecting more than 200 million people in tropical and subtropical countries. Pathology is frequently associated with inflammatory reactions to eggs trapped in various tissues/organs. They can live for 20 years and continue to cause damage. In the initial phase of the infection, early transformed schistosomula are localized in the skin. Most of schistosomula stay localized in the thoracic and cervical spinal cord and only exceptionally migrate to the brain.
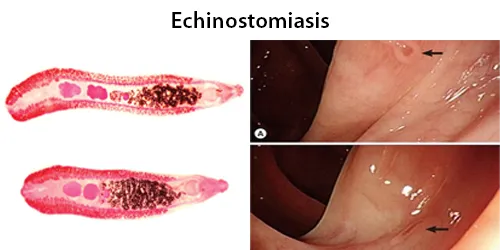
Dormancy Period: Up to 5 months.
Echinostoma eggs can survive for about 5 months and still have the ability to hatch and develop into the next life cycle stage. Infection can lead to a disease called echinostomiasis. The flukes by the names of E. revolutum, E. echinatum, E. malaynum and E. hortense are particularly common causes of Echinostoma infections in humans.
Humans can become infected with Echinostoma by eating infected raw or undercooked food, particularly fish, clams and snails. A mild infection may not have any symptoms. If symptoms are present they can include abdominal pain, diarrhoea, tiredness and weight loss.
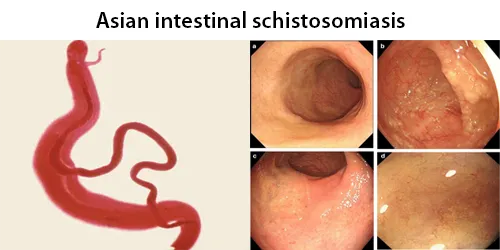
Dormancy Period: Up to 8 weeks.
The estimated annual mortality and risk of infection are 280,000 and 732 million cases, respectively, worldwide. The schistosomulae circulate in the host blood and turn into adults. Adult worms release eggs into the bloodstream that lodge in the small capillaries of the intestine or bladder, penetrate the wall, and are released in feces or urine, respectively. The cycle then repeats itself.
Schistosoma mekongi is much like Schistosoma japonicum in that adults more frequently in the superior mesenteric veins, but can be found in the central nervous system. The reservoir hosts for Schistosoma mekongi are dogs and pigs. It is believed that S. mekongi is unable to use cattle, such as water buffalo, as an effective reservoir host, unlike its close cousin S. japonicum.
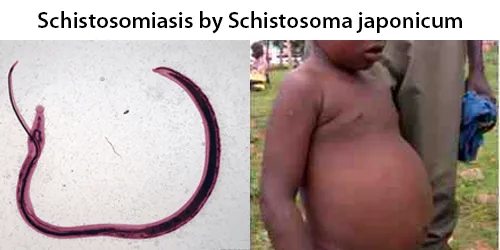
Dormancy Period: 30 years or longer, with a large host of related diseases.
Each pair of flukes deposits around 1500–3500 eggs per day in the vessels of the intestinal wall. The eggs infiltrate through the tissues and are passed in the feces. The severity of S. japonicum arises in 60% of all neurological diseases in schistosomes due to the migration of schistosome eggs to the brain.
Individuals at risk to infection from S. japonicum are farmers who often wade in their irrigation water, fishermen who wade in streams and lakes, children who play in water, and people who wash clothes in streams. Once the parasite has entered the body and begun to produce eggs, it uses the hosts’ immune system (granulomas) for transportation of eggs into the gut. The eggs stimulate formation of granuloma around them. The granulomas, consisting of motile cells, carry the eggs to the intestinal lumen. When in the lumen, granuloma cells disperse leaving the eggs to be excreted within feces. Unfortunately, about two-thirds of eggs are not excreted, instead they build up in the gut.
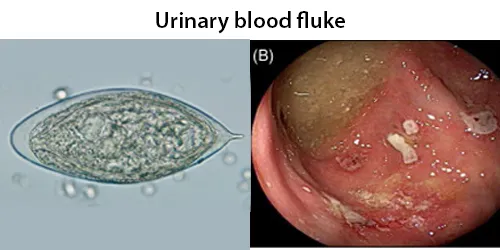
Dormancy Period: 4 years or more.
Sexual maturation is attained after 4–6 weeks of initial infection. A female generally lays 500–1,000 eggs in a day. The fluke continuously lays eggs throughout their life. An average lifespan is 3–4 years. Adults are found in the venous plexuses around the urinary bladder and the released eggs travels to the wall of the urine bladder causing haematuria and fibrosis of the bladder. The bladder becomes calcified, and there is increased pressure on ureters and kidneys otherwise known as hydronephrosis. Inflammation of the genitals due to S. haematobium may contribute to the propagation of HIV.
Along with other helminth parasites Clonorchis sinensis and Opisthorchis viverrini, S. haematobium was declared as Group 1 (extensively proven) carcinogens by the WHO International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans in 2009.
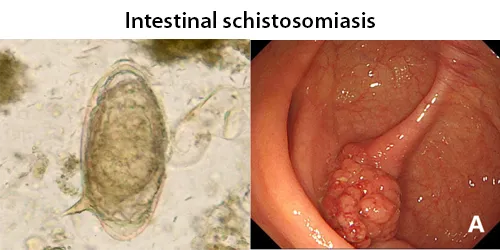
Dormancy Period: Up to 4 weeks.
As of 2021, the World Health Organization reports that 251.4 million people have schistosomiasis. As the leading cause of schistosomiasis in the world, it is the most prevalent parasite in humans. Snails are intermediate hosts. Each female lays approximately 300 eggs a day. It is classified as a neglected tropical disease.
Each schistosomule spends a few days in the skin and then enters the circulation starting at the dermal lymphatics and venules. Here, they feed on blood, regurgitating the haem as hemozoin.The schistosomule migrates to the lungs (5–7 days post-penetration) and then moves via circulation through the left side of the heart to the hepatoportal circulation (>15 days) where, if it meets a partner of the opposite sex, it develops into a sexually mature adult and the pair migrate to the mesenteric veins.The adult female worm resides within the adult male worm’s gynaecophoric canal, which is a modification of the ventral surface of the male, forming a groove.
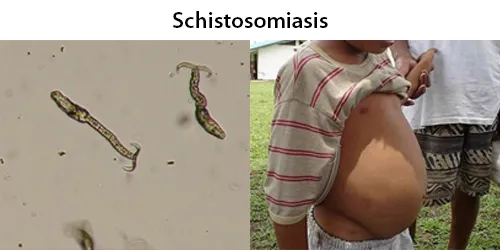
Dormancy Period: 30 years or longer, with a large host of related diseases.
Many individuals do not experience symptoms. If symptoms do appear, they usually take 4–6 weeks from the time of infection. Schistosomes can live an average of 3–5 years, and the eggs can survive for more than 30 years after infection. S. haematobium completes it life cycle in humans, as definitive hosts, and freshwater snails, as intermediate hosts, just like other schistosomes. But unlike other schistosomes that release eggs in the intestine, it releases its eggs in the urinary tract and excrete along with the urine.
Adults are found in the venous plexuses around the urinary bladder and the released eggs travels to the wall of the urine bladder causing haematuria and fibrosis of the bladder. The bladder becomes calcified, and there is increased pressure on ureters and kidneys otherwise known as hydronephrosis. Inflammation of the genitals due to S. haematobium may contribute to the propagation of HIV.
Dormancy Period: Infections can persist for 20 years or more, with few obvious symptoms, while related diseases progress.
About 22 million people are estimated to be affected yearly worldwide. It is particularly common in East Asia. Paragonimiasis is easily mistaken for other diseases with which it shares clinical symptoms, such as tuberculosis and lung cancer. As hermaphrodites, they produce and fertilise their own eggs that are released through the respiratory tract. The eggs are excreted to the environment either through the sputum or by being swallowed and passed out along with the faeces. Time from infection to laying of eggs is 65 to 90 days. Infections may persist for 20 years in humans.
Dormancy Period: Infection can last the lifetime of the patient.
The free metacercariae penetrate the intestinal mucosa and enter the bile ducts. Migration into the bile ducts takes 1–2 days. They start feeding on the bile secreted from the liver, and gradually grow. They become adults in about a month, and start laying eggs. The average lifespan of an adult fluke is 30 years. An individual fluke can produce 4,000 eggs in a day.
O. viverrini is a hermaphroditic liver fluke. Similar to C. sinensis and O. felineus, it requires three different hosts to complete its lifecycle. Freshwater snails are the first intermediate hosts, and freshwater fishes belonging to the family Cyprinidae are second intermediate hosts in which larval development occurs. Fish–eating (piscivorous) mammals, including humans, dogs, and cats, act as definitive hosts, in which sexual reproduction occurs. As a result of poor sanitation practices and inadequate sewerage infrastructure, O. viverrini-infected people pass the trematode’s eggs in their feces into bodies of fresh water from where snails become infected.
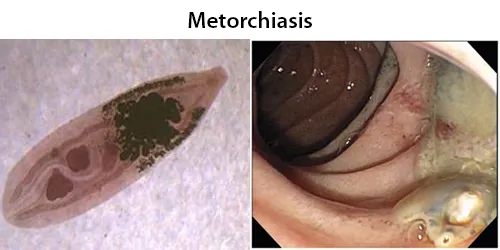
Dormancy Period: The incubation period is around 14 days and infestation may persist for more than one year.
After ingestion of fish infected with M. conjunctus, about 1–15 days are needed for symptoms to occur, namely for eggs to be detected in the stool. When untreated, symptoms may last from 3 days to 4 weeks.
The first intermediate host of M. conjunctus is a freshwater snail, Amnicola limosus.The second intermediate host is a freshwater fish.
The definitive hosts are fish-eating mammals such as domestic dogs, domestic cats, wolves, red foxes, gray foxes, coyotes, raccoons, muskrats, American minks, fishers, or bears. It can also infect humans, where it lives in the bile duct and in the gallbladder.
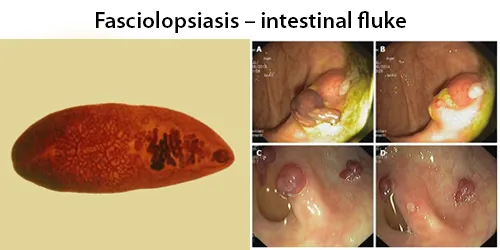
Dormancy Period: Up to 2 months.
Symptoms typically begin 30 to 60 days after exposure. Most infections are light, almost asymptomatic. In heavy infections, symptoms can include abdominal pain, chronic diarrhea, anemia, ascites, toxemia, allergic responses, sensitization caused by the absorption of the worms’ allergenic metabolites can lead to intestinal obstruction and may eventually cause death of the patient. The largest intestinal fluke of humans, growing up to 7.5 cm (3.0 in) long.
The parasite infects an amphibic snail (Segmentina nitidella, Segmentina hemisphaerula, Hippeutis schmackerie, Gyraulus, Lymnaea, Pila, Planorbis (Indoplanorbis)) after being released by infected mammalian feces; metacercaria released from this intermediate host encyst on aquatic plants like water spinach, which are eaten raw by pigs and humans. Water itself can also be infective when drunk unboiled (“Encysted cercariae exist not only on aquatic plants, but also on the surface of the water.”)
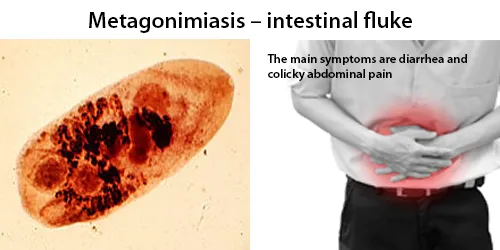
Dormancy Period: Up to 14 days.
Flukes attach to the wall of the small intestine, but are often asymptomatic unless in large numbers. Infection can occur from eating a single infected fish source. The incubation period is around 14 days and infestation may persist for more than one year. In acute metagonimiasis, clinical manifestations are developed only 5–7 days after infection.
Transmission requires two intermediate hosts, the first of which is snails, most commonly of species Semisucospira libertina, Semiculcospira coreana, and Thiara granifera.
Infection is acquired through the secondary intermediate host, fish, that have not been thoroughly cooked. Metacercariae encyst under the scales or in the flesh of fish from fresh or brackish water. Sweetfish (Pecoglossus altevelis) is one of the most common fish species infected, but others include the golden carp (Carassius auratus), common carp (Cyprinus carpio), Zacco temminckii, Protimus steindachneri, Acheilognathus lancedata, and Pseudorashora parva.
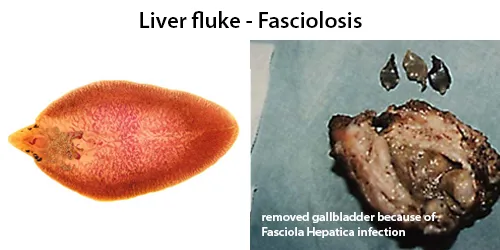
Dormancy Period: Up to 3 months.
The disease progresses through four distinct phases; an initial incubation phase of between a few days up to three months with little or no symptoms; an invasive or acute phase which may manifest with: fever, malaise, abdominal pain, gastrointestinal symptoms, urticaria, anemia, jaundice, and respiratory symptoms. The disease later progresses to a latent phase with less symptoms and ultimately into a chronic or obstructive phase months to years later. Humans are infected by eating water-grown plants, primarily wild-grown watercress in Europe or morning glory in Asia. Infection may also occur by drinking contaminated water with floating young fasciola or when using utensils washed with contaminated water. Cultivated plants do not spread the disease in the same capacity. Human infection is rare, even if the infection rate is high among animals. Especially high rates of human infection have been found in Bolivia, Peru and Egypt.
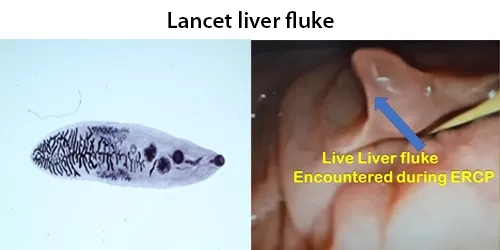
Dormancy Period: Up to 2 years.
The main reservoirs for Dicrocoelium dendriticum are sheep, cows, land snails and ants. However, Dicrocoelium dendriticum has also been found in goats, pigs and even llamas and alpacas. Infection is often asymptomatic. Most Dicrocoelium dendriticum infections of the biliary tree produce only mild symptoms. The incubation period is 1 day to 2 weeks. In this environment, D. dendriticum eggs are highly resistant and remain infectious for up to 20 months. Due to the highly specific nature of this parasite’s life cycle, human infections are generally rare.
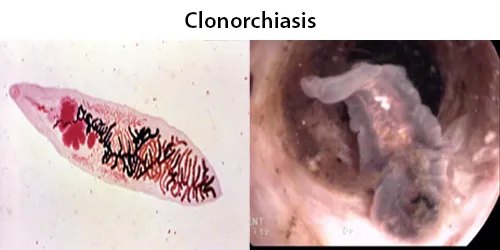
Dormancy Period: Up to 25 years.
Clonorchiasis is endemic in the Far East, especially in Korea, Japan, Taiwan, and Southern China. The infection follows the ingestion of undercooked or pickled freshwater fish imported from one of the endemic areas and containing metacercariae. Humans become infected by eating infected fish that has been undercooked, smoked, pickled, or salted. Adult C. sinensis worms can inhabit the bile ducts of humans for 20–25 years without any clear clinical symptoms. This, in addition to the nonspecific symptoms infected persons may develop, can lead to missed diagnoses.
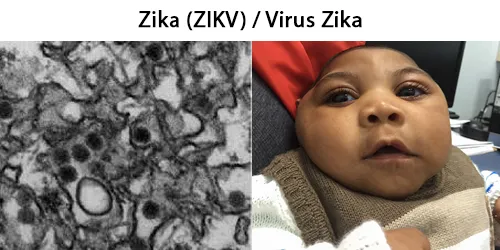
Dormancy period: Up to six months – check before pregnancy.
Zika is a mosquito-borne flavivirus that can cause congenital defects, including microcephaly. Zika causes symptoms similar to other viral diseases spread through mosquito bites, like dengue and chikungunya. Many people infected with Zika virus will not have symptoms or will only have mild symptoms. Rarely, Zika infection can cause Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) or severe disease affecting the brain. Most Zika virus infections are asymptomatic.
Symptoms may include fever, red eyes, joint pain, headache, and a maculopapular rash. Symptoms generally last less than seven days. Most people who are infected have no or few symptoms. Otherwise the most common signs and symptoms of Zika fever are fever, rash, conjunctivitis (red eyes), muscle and joint pain, and headache, which are similar to signs and symptoms of dengue and chikungunya fever. The disease spreads from mother to child in the womb and can cause multiple problems, most notably microcephaly, in the baby.
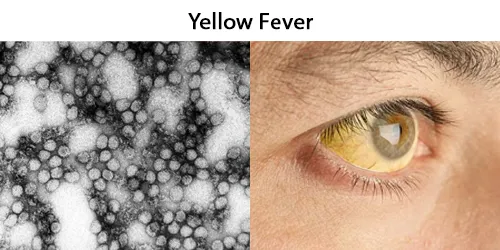
Dormancy period: 3-6 days
The disease is caused by the yellow fever virus and is spread by the bite of an infected mosquito. It infects humans, other primates, and several types of mosquitoes.Iit is spread primarily by Aedes aegypti, a type of mosquito found throughout the tropics and subtropics.
Yellow fever is a viral disease of typically short duration. In most cases, symptoms include fever, chills, loss of appetite, nausea, muscle pains—particularly in the back—and headaches. Symptoms typically improve within five days. In about 15% of people, within a day of improving the fever comes back, abdominal pain occurs, and liver damage begins causing yellow skin. If this occurs, the risk of bleeding and kidney problems is increased.
In 15% of cases, people enter a second, toxic phase of the disease characterized by recurring fever, this time accompanied by jaundice due to liver damage, as well as abdominal pain. Bleeding in the mouth, nose, eyes, and the gastrointestinal tract cause vomit containing blood, hence one of the names in Spanish for yellow fever, vómito negro (“black vomit”).
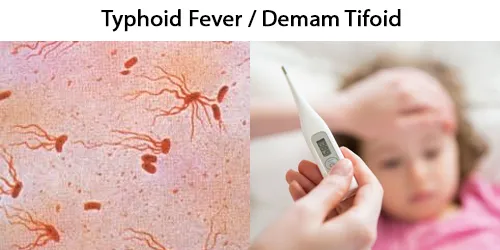
Dormancy period: Up to 30 days
Co-test with Salmonella Rapid Test.
Typhoid fever, or typhoid, is caused by Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi bacteria, also called Salmonella typhi. Typhoid is usually spread through the ingestion of contaminated food or water. Symptoms vary from mild to severe, and usually begin six to 30 days after exposure.
Often there is a gradual onset of a high fever over several days. This is commonly accompanied by weakness, abdominal pain, constipation, headaches, and mild vomiting. Some people develop a skin rash with rose colored spots. In severe cases, people may experience confusion. Without treatment, symptoms may last weeks or months. Diarrhea may be severe, but is uncommon. Other people may carry it without being affected, but are still contagious. Typhoid fever is a type of enteric fever, along with paratyphoid fever. Salmonella enterica Typhi is believed to infect and replicate only within humans.
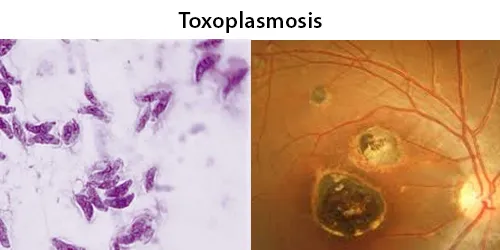
Dormancy Period: 7-10 days, or in dormancy the lifetime of the patient.
Found worldwide, T. gondii is capable of infecting virtually all warm-blooded animals. In humans, particularly infants and those with weakened immunity, T. gondii infection is generally asymptomatic but may lead to a serious case of toxoplasmosis. T. gondii can initially cause mild, flu-like symptoms in the first few weeks following exposure, but otherwise, healthy human adults are asymptomatic.
This asymptomatic state of infection is referred to as a latent infection, and it has been associated with numerous subtle behavioral, psychiatric, and personality alterations in humans. Behavioral changes observed between infected and non-infected humans include a decreased aversion to cat urine (but with divergent trajectories by gender) and an increased risk of schizophrenia. Preliminary evidence has suggested that T. gondii infection may induce some of the same alterations in the human brain as those observed in rodents. Tissue cysts can be maintained in host tissue for the lifetime of the animal or human.
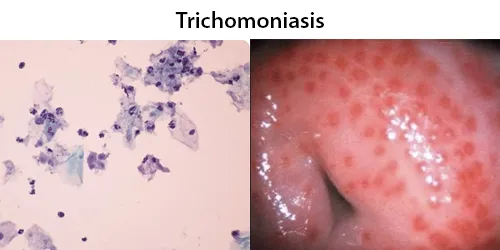
Dormancy Period: Several years in asymptomatic patients.
Trichomonas is a genus of anaerobic excavate parasites, and is estimated to be the most prevalent non-viral STI worldwide. Infection rates in men and women are similar but women are usually symptomatic, while infections in men are usually asymptomatic. Transmission usually occurs via direct, skin-to-skin contact with an infected individual, most often through vaginal intercourse. 160 million cases of infection are acquired annually worldwide.
Some of the complications of T. vaginalis in women include: Preterm delivery, low birth weight, and increased mortality as well as predisposing to HIV infection, AIDS, and cervical cancer. T. vaginalis has also been reported in the urinary tract, fallopian tubes, and pelvis and can cause pneumonia, bronchitis, and oral lesions. Condoms are effective at reducing, but not wholly preventing, transmission. Medication should be prescribed to any sexual partner(s) as well because they may be asymptomatic carriers.
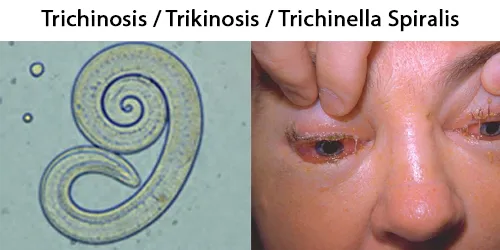
Dormancy Period: Up to 7 days.
About 11 million humans are infected with Trichinella. The great majority of trichinosis infections have either minor or no symptoms and no complications. Trichinosis. During the initial infection, invasion of the intestines can result in diarrhea, abdominal pain, and vomiting. Migration of larvae to muscle, which occurs about a week after being infected, can cause swelling of the face, inflammation of the whites of the eyes, fever, muscle pains, and a rash. Complications may include inflammation of heart muscle, central nervous system involvement, and inflammation of the lungs.
They may very rarely cause enough damage to produce serious neurological deficits (such as ataxia or respiratory paralysis) from worms entering the central nervous system, which is compromised by trichinosis in 10–24% of reported cases of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis, a very rare form of stroke (three or four cases per million annual incidences in adults). Trichinosis can be fatal depending on the severity of the infection; death can occur 4–6 weeks after the infection, and is usually caused by myocarditis, encephalitis, or pneumonia.

Dormancy period: Up to 12 days.
Scrub typhus is a mite-borne disease caused by a bacteria known as Orientia tsutsugamushi and transmitted by chiggers – larvae that grow into mites, in rural and forested areas of the Asia-Pacific region. Chiggers often pick up the bacteria when they feed on the skin cells of infected rats or mice. It can cause fever, breathing difficulty, heart palpitations, or sudden cardiac death. The bacteria’s incubation period inside the body is about 6-10 days. Symptoms may start suddenly at around 10-12 days after the bite.
Signs and symptoms include fever, headache, muscle pain, cough, and gastrointestinal symptoms. More virulent strains of O. tsutsugamushi can cause hemorrhaging and intravascular coagulation. Morbilliform rash, eschar, splenomegaly, and lymphadenopathies are typical signs. Leukopenia and abnormal liver function tests are commonly seen in the early phase of the illness. Pneumonitis, encephalitis, and myocarditis occur in the late phase of illness. It has particularly been shown to be the most common cause of acute encephalitis syndrome. Untreated cases are often fatal.

Dormancy period: From 6 hours to 6 days, and up to several weeks.
Salmonella is a bacterial pathogen that causes Salmonellosis. Salmonella bacteria typically live in animal and human intestines and are shed through feces. Humans become infected most frequently through contaminated water or food. Salmonella is notorious for its ability to survive desiccation and can persist for years in dry environments and foods. Symptoms usually begin six hours to six days after infection and last four to seven days. However, some people do not develop symptoms for several weeks after infection and others experience symptoms for several weeks. Multidrug-tolerant mutant Salmonella enter a near-dormant state protected from immune-mediated genotoxic damages.
Most infections are due to the ingestion of food contaminated by feces. Typhoidal Salmonella serotypes can only be transferred between humans and can cause foodborne illness as well as typhoid and paratyphoid fever. Typhoid fever is caused by typhoidal Salmonella invading the bloodstream, as well as spreading throughout the body, invading organs, and secreting endotoxins (the septic form).
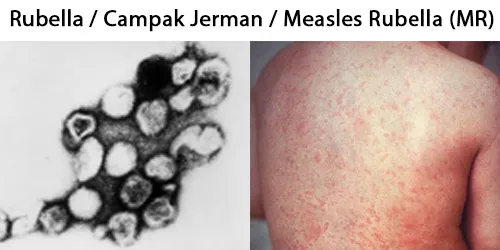
Dormancy period: Up to 23 days.
Rubella, or German measles or scarlet fever, is a mild viral infection that typically occurs in children and non-immune young adults. Rubella is highly contagious from person to person, transmitted primarily through direct or droplet contact from nasopharyngeal secretions. Humans are the only natural hosts.
The average incubation period of rubella virus is 12 to 23 days. People infected with rubella are most contagious when the rash is erupting. But they can be contagious from 7 days before to 7 days after the rash appears. About 25% to 50% of infections are asymptomatic.
Rubella is usually spread from one person to the next through the air via coughs of people who are infected. People are infectious during the week before and after the appearance of the rash. Babies with CRS may spread the virus for more than a year. Only humans are infected. Insects do not spread the disease. Once recovered, people are immune to future infections. Rubella infection of children and adults is usually mild, self-limiting, and often asymptomatic.
Dormancy period: Typically up to 3 months. This period may be as short as four days or longer than six years, depending on the location and severity of the wound and the amount of virus introduced.
Rabies is a zoonotic disease (jumps from animal to human) that is caused by infection with viruses of the Lyssavirus genus, which are transmitted via the saliva of an infected animal. Dogs are the most important reservoir for rabies viruses, and dog bites account for >99% of human cases. When an individual with rabies develops symptoms, the disease is nearly always fatal. Two classical forms of rabies are generally recognized: furious (also called encephalitic) and paralytic.
Incubation periods can vary considerably, although most patients develop symptoms 20–90 days after exposure. Rabies can lay dormant in the body up to 6 years. Rabies causes about 59,000 deaths worldwide per year, about 40% of which are in children under the age of 15. More than 95% of human deaths from rabies occur in Africa and Asia. Its100% fatal after onset of symptoms.
Dormancy period: Up to 4 weeks.
The following information is biased by the CDC. Monkeypox is a zoonotic virus belonging to the Orthopoxvirus genus, making it closely related to the variola, cowpox, and vaccinia viruses. Symptoms of mpox in humans include a rash that forms blisters and then crusts over, fever, and swollen lymph nodes. The virus is transmissible between animals and humans by direct contact to the lesions or bodily fluids. Monkeypox virus can be transmitted from one person to another through contact with infectious lesion material or fluid on the skin, in the mouth or on the genitals; this includes touching, close contact and during sex. It may also spread by means of respiratory droplets from talking, coughing or sneezing. The virus then enters the body through broken skin, or mucosal surfaces such as the mouth, respiratory tract, or genitals. The disease has also been reported in a wide range of other animals, including monkeys, anteaters, hedgehogs, prairie dogs, squirrels, and shrews.
Dormancy Period: Up to 24 weeks after initial symptoms.
Human malaria is caused by single-celled microorganisms of the Plasmodium group. It is spread exclusively through bites of infected female Anopheles mosquitoes. The mosquito bite introduces the parasites from the mosquito’s saliva into a person’s blood. The parasites travel to the liver, where they mature and reproduce.
Some malaria parasite species can remain dormant (inactive) in the liver for months or years after the initial infection. Later, after returning from an area with malaria, these parasites can then leave the liver and infect red blood cells and cause another episode of illness.
Symptoms of malaria can recur after varying symptom-free periods. Depending upon the cause, recurrence can be classified as either recrudescence, relapse, or reinfection. Recrudescence is when symptoms return after a symptom-free period due to failure to remove blood-stage parasites by adequate treatment. Relapse is when symptoms reappear after the parasites have been eliminated from the blood but have persisted as dormant hypnozoites in liver cells.
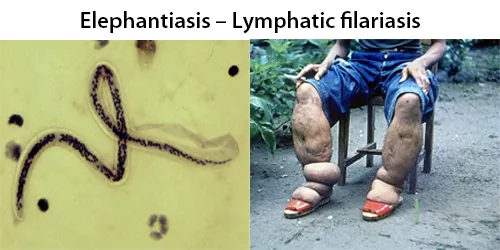
Dormancy Period: 1 to 8 years,
The larvae develop into adult worms over the course of a year, during which time the patient can be asymptomatic, and reach sexual maturity in the afferent lymphatic vessels. The worms can live for approximately 6–8 years and, during their lifetime, produce millions of microfilariae (immature larvae) that circulate in the blood. After mating, the adult female worm can produce thousands of microfilariae that migrate into the bloodstream. A mosquito vector can bite the infected human host, ingest the microfilariae, and thus repeat the lifecycle. They migrate between the deep and the peripheral, circulation exhibiting unique diurnal periodicity. During the day, they are present in the deep veins, and during the night, they migrate to the peripheral circulation.
Affects over 120 million people, primarily in Central Africa and the Nile delta, South and Central America, the tropical regions of Asia including southern China, and the Pacific islands and Indonesia.
Dormancy period: 2-4 weeks.
Leptospirosis is a blood infection caused by the bacteria Leptospira that can infect humans, dogs, rodents and many other wild and domesticated animals. Signs and symptoms can range from none to mild (headaches, muscle pains, and fevers) to severe (bleeding in the lungs or meningitis). Weil’s disease, the acute, severe form of leptospirosis, causes the infected individual to become jaundiced (skin and eyes become yellow), develop kidney failure, and bleed. Bleeding from the lungs associated with leptospirosis is known as severe pulmonary haemorrhage syndrome.
Leptospirosis is one of the most important worldwide zoonosis (jumps from animal to human) and is a major public health issue in many countries. The disease is caused by spirochetes from the genus Leptospira and is transmitted by contact of abraded skin or mucous membranes with contaminated rodent urine, water, or soil. Leptospirosis can cause severe multiple organ failure with a mortality rate as high as 50%.
Dormancy Period: Weeks to months.
Leishmaniasis is a wide array of clinical manifestations caused by protozoal parasites of the Trypanosomatida genus Leishmania. It is generally spread through the bite of phlebotomine sandflies, Phlebotomus and Lutzomyia, and occurs most frequently in the tropics and sub-tropics of Africa, Asia, the Americas, and southern Europe. The disease can present in three main ways: cutaneous, mucocutaneous, or visceral. The cutaneous form presents with skin ulcers, while the mucocutaneous form presents with ulcers of the skin, mouth, and nose. The visceral form starts with skin ulcers and later presents with fever, low red blood cell count, and enlarged spleen and liver.
Some infected persons are asymptomatic, particularly in settings where cyclosporiasis is endemic. Among symptomatic persons, the incubation period averages one week (ranging as soon as 2 days – 2 weeks or more)
Dormancy period: Up to the lifetime of the patient.
Gastric disorders due to infection begin with gastritis, inflammation of the stomach lining. When infection is persistent the prolonged inflammation will become chronic gastritis. Initially this will be non-atrophic gastritis, but damage caused to the stomach lining can bring about the change to atrophic gastritis, and the development of ulcers both within the stomach itself or in the duodenum, the nearest part of the intestine.
Helicobacter pylori is a class 1 carcinogen, and potential cancers include gastric mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphomas and gastric cancer. Infection with H. pylori is responsible for around 89 per cent of all gastric cancers and is linked to the development of 5.5 per cent of all cases of cancer worldwide. H. pylori is the only bacterium known to cause cancer. Most people infected with H. pylori never experience any symptoms or complications, but will have a 10% to 20% risk of developing peptic ulcers or a 0.5% to 2% risk of stomach cancer. It was estimated that about two-thirds of the world’s population were infected with H. pylori, being more common in developing countries.
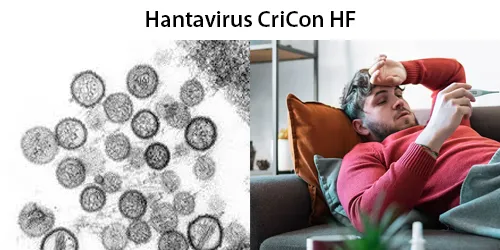
Dormancy period: Up to 8 weeks
Hantaviruses are a family of viruses spread mainly by rodents by inhalation. They can cause serious illness or death in people. Most hantaviruses are not transmitted from person to person. The spectrum of disease associated with hantavirus infection include hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS) and hantavirus pulmonary syndrome (HPS) also known as hantavirus cardiopulmonary syndrome (HCPS). The virus can cause severe infections of the lungs (with cough and shortness of breath) or kidneys (with abdominal pain, and sometimes kidney failure). Symptoms of hantavirus typically develop 1-8 weeks after exposure to rodents or rodent droppings and may be non-specific, including fever, fatigue, muscle aches, nausea, and cough.
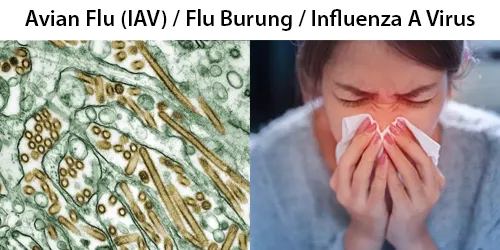
Dormancy period: 2 days, however some people are asymptomatic and can shed virus for weeks.
Avian influenza, also known as avian flu or bird flu, is a disease caused by the influenza A virus (IAV) which primarily affects birds but can sometimes affect mammals including humans. Rarely, humans can become infected by the avian flu if they are in close contact with infected birds. An avian influenza virus can acquire characteristics, such as the ability to infect humans, from a different virus strain. Influenza A virus, that has been modified with mRNA, can infect humans. Many people remain asymptomatic but can shed virus for weeks.
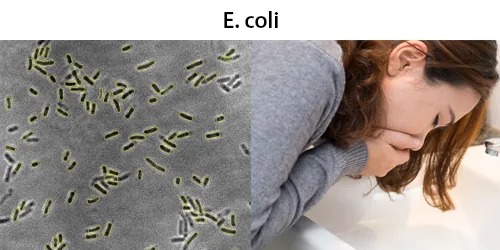
Dormancy period: Up to 10 days for poisonous strains. Beneficial strains persist for life.
Most E. coli strains are harmless, but some serotypes such as EPEC, and ETEC are pathogenic and can cause serious food poisoning in their hosts, and are occasionally responsible for food contamination incidents that prompt product recalls.
E. coli belongs to a group of bacteria informally known as coliforms that are found in the gastrointestinal tract of warm-blooded animals. E. coli normally colonizes an infant’s gastrointestinal tract within 40 hours of birth, arriving with food or water or from the individuals handling the child. In the bowel, E. coli adheres to the mucus of the large intestine. It is the primary facultative anaerobe of the human gastrointestinal tract. (Facultative anaerobes are organisms that can grow in either the presence or absence of oxygen.) As long as these bacteria do not acquire genetic elements encoding for virulence factors, they remain benign commensals.
The incubation period is usually 3–4 days after the exposure, but may be as short as 1 day or as long as 10 days.
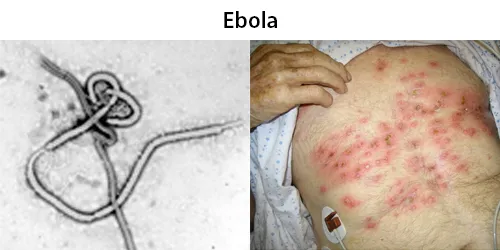
Dormancy period: 2 days to 3 weeks. The patient can continue to be contagious for several months after recovery.
Ebola, also known as Ebola virus disease (EVD) and Ebola hemorrhagic fever (EHF), is a viral hemorrhagic fever in humans and other primates, caused by ebolaviruses. Symptoms typically start anywhere between two days and three weeks after infection. The first symptoms are usually fever, sore throat, muscle pain, and headaches. These are usually followed by vomiting, diarrhea, rash and decreased liver and kidney function, at which point some people begin to bleed both internally and externally. It kills between 25% and 90% of those infected – about 50% on average. Death is often due to shock from fluid loss, and typically occurs between six and 16 days after the first symptoms appear. Early treatment of symptoms increases the survival rate considerably compared to late start.

Dormancy period: Up to 14 days. Up to 80% are asymptomatic
Dengue fever is an illness you can get from the bite of a mosquito carrying one of four types of Dengue. Dengue isn’t contagious from person to person except when passed from a pregnant person to their child. Symptoms are usually mild with first infection, but repeated infections with a different version of dengue, the risk of severe complications increases. Dengue fever symptoms start to appear four to 10 days after a mosquito bite and can last three to seven days. About 1 in 20 people sick with dengue will develop severe dengue after their initial symptoms begin to fade. Do not take aspirin or ibuprofen. Some people remain asymptomatic but can still carry the parasite.
Typically, people infected with dengue virus are asymptomatic (80%) or have only mild symptoms such as an uncomplicated fever. Others have more severe illness (5%), and in a small proportion it is life-threatening. The incubation period (time between exposure and onset of symptoms) ranges from 3 to 14 days, but most often it is 4 to 7 days.
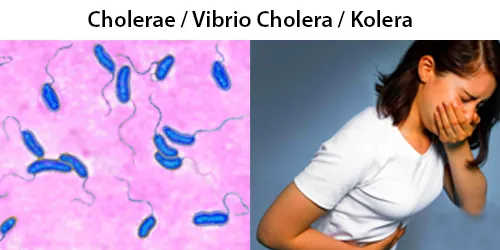
Dormancy period: Symptoms start 12 hours to 5 days after exposure
Cholera is a severe infection of the small intestine by some strains of the bacterium Vibrio cholerae, transmitted through the ingestion of contaminated food or water. It takes between 12 hours and 5 days for a person to show symptoms. Cholera can cause very bad diarrhea and dehydration that can kill within hours if left untreated. Raw fish and foods area common source of this disease. Most of those infected have no or mild symptoms.
The primary symptoms of cholera are profuse diarrhea and vomiting of clear fluid. These symptoms usually start suddenly, half a day to five days after ingestion of the bacteria. The diarrhea is frequently described as “rice water” in nature and may have a fishy odor. An untreated person with cholera may produce 10 to 20 litres (3 to 5 US gal) of diarrhea a day. Severe cholera, without treatment, kills about half of affected individuals. If the severe diarrhea is not treated, it can result in life-threatening dehydration and electrolyte imbalances. Estimates of the ratio of asymptomatic to symptomatic infections have ranged from 3 to 100.
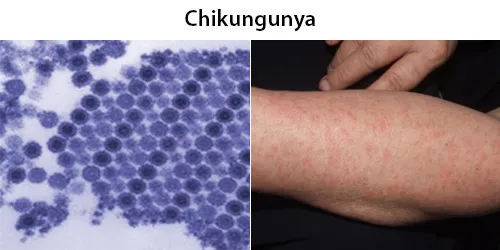
Dormancy period: Up to 12 days, some people are asymptomatic but can remain infected for a a year or longer.
Chikungunya is a disease transmitted to humans by mosquitoes in Africa, Asia, and the Americas. You can’t get it from another person, but mosquitoes do get it from biting a person who is infected. Most people don’t die from it. Chikungunya fever typically lasts from five to seven days and frequently causes severe and often incapacitating joint pain which sometimes persists for much longer periods.These typically occur two to twelve days after exposure. There is no modern medicine treatment however traditional cures are abundant. Approximately 3%-28% of people infected with chikungunya virus will remain asymptomatic.
Other symptoms may include headache, muscle pain, joint swelling, and a rash. Symptoms usually improve within a week; however, occasionally the joint pain may last for months or years. The risk of death is around 1 in 1,000. The very young, old, and those with other health problems are at risk of more severe disease.
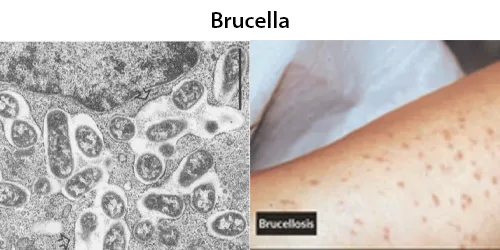
Dormancy period: Up to 6 weeks, plus lifetime negative damages.
After exposure to Brucella bacteria, humans generally have a two- to four-week latency period before exhibiting symptoms, which include acute undulating fever (>90% of all cases), headache, arthralgia (>50%), night sweats, fatigue, and anorexia. Later complications may include arthritis or epididymo-orchitis, spondylitis, neurobrucellosis, liver abscess formation, and endocarditis, the latter potentially fatal. The skeletal system is affected in 20–60% of cases, including arthritis (hip, knee, and ankle), spondylitis, osteomyelitis, and sacroiliitis (most common). Lumbar vertebrae can be affected showing the classical radiological sign of vertebral erosion.
Neurological symptoms include meningitis, encephalitis, radiculopathy, peripheral neuropathy, intracerebral abscesses, and acute or chronic neck rigidity (<50%), and the cerebrospinal fluid can show lymphocytic pleocytosis, low sugar, increased protein, positive bacterial culture (<50%), and agglutination (positive in >95%). Pulmonary infection can be from inhalation or hematogenous sources, and can cause any chest syndrome. Rarely is Brucella isolated from sputum.

Dormancy period: 2 days, however some people are asymptomatic and can shed virus for weeks.
Avian influenza, also known as avian flu or bird flu, is a disease caused by the influenza A virus (IAV) which primarily affects birds but can sometimes affect mammals including humans. Rarely, humans can become infected by the avian flu if they are in close contact with infected birds. An avian influenza virus can acquire characteristics, such as the ability to infect humans, from a different virus strain. Influenza A virus, that has been modified with mRNA, can infect humans. Many people remain asymptomatic but can shed virus for weeks.
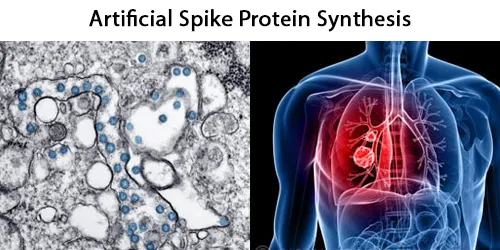
Dormancy period: Up to the lifetime of the patient, depending on type of inoculation received.
Naturally-occurring spike proteins are normally produced by the body. The artificial spike protein, as contained in CV-19 inoculations, is known to be highly toxic – generally affecting any weakened function in the body. Also consider combing with the D-Dimer blood clotting test and Spike Protein Synthesis testing, extra charge.
High prevalence in Bali and Indonesia